To perform a literature review aimed to analyze if acupoint stimulation increases lactation quantity.
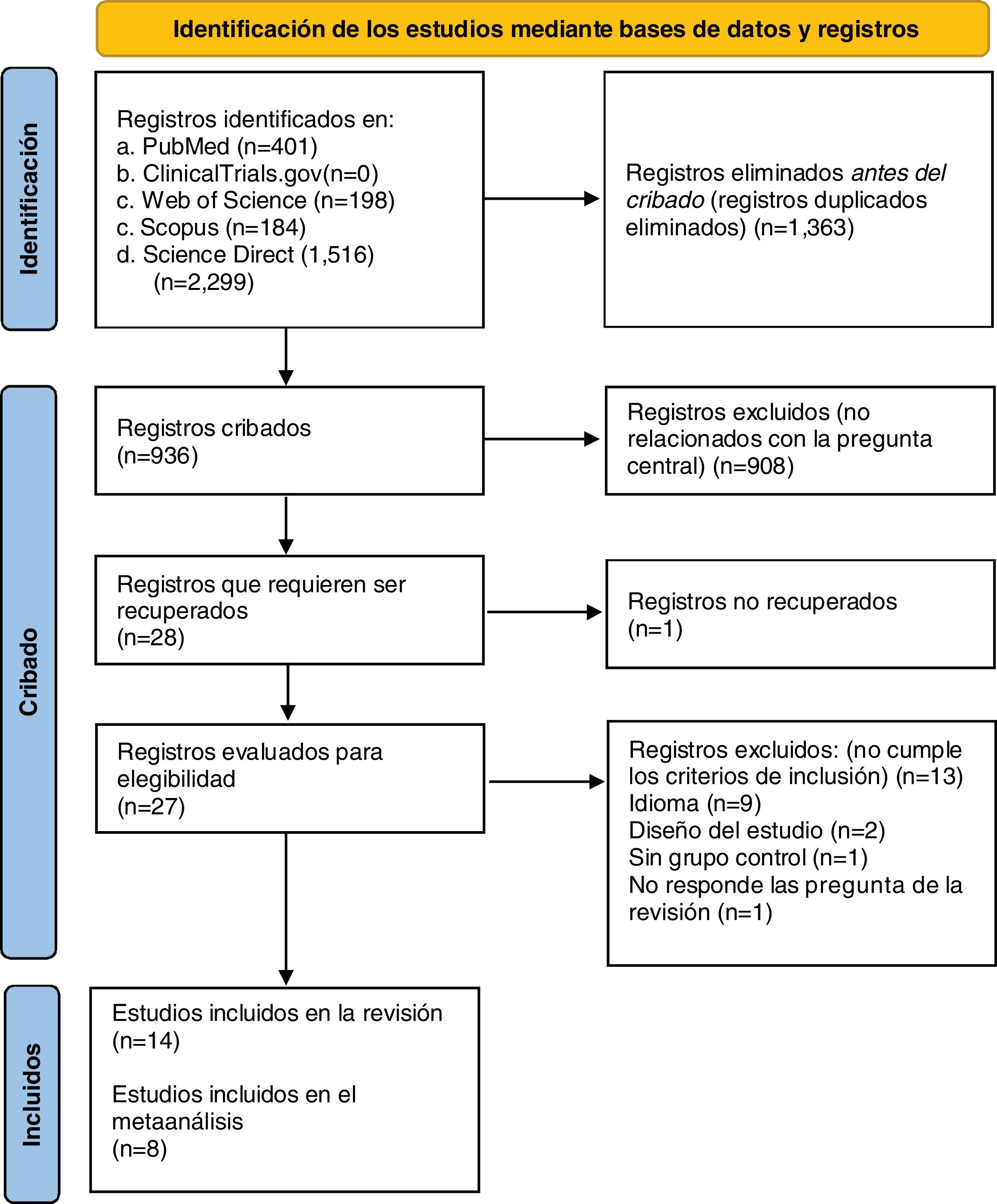
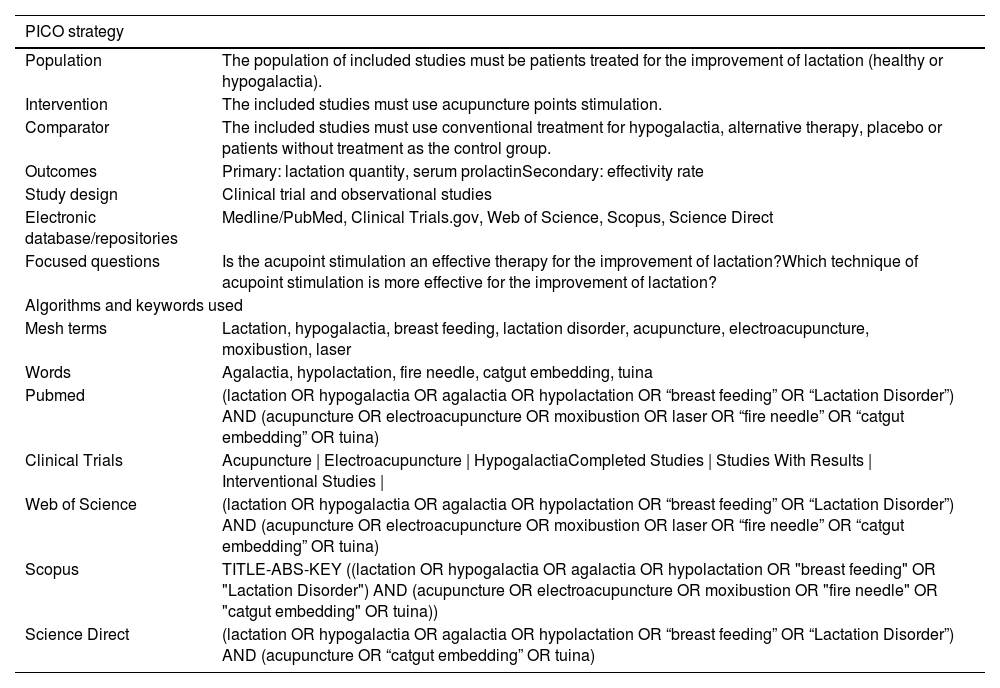
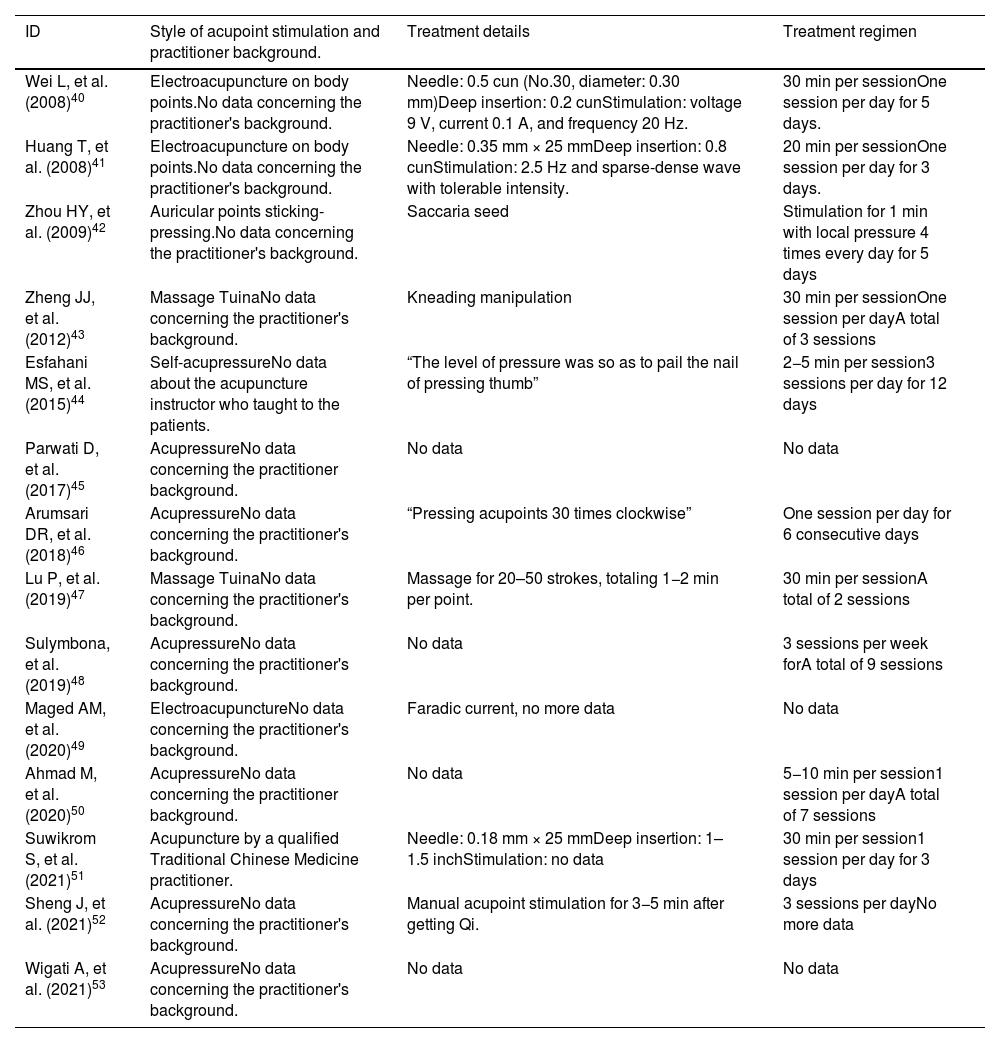
MethodStudies were collected from five electronic databases following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines for systematic reviews. Eligibility criteria were full-text articles in English or Spanish with clinical trial design and observational studies, with no restriction on time of publication, in which the effect of acupoint stimulation on improving the quantity of lactation by conventional acupuncture, electroacupuncture, laser, fire needling, manual stimulation, tuina or catgut had been evaluated. Two authors independently extracted data for the characteristics and main outcomes of the studies selected for inclusion. The risk of bias (RoB 2 and Robins-I) and the quality assessments (GRADE) were performed. For the quantitative synthesis, the standardized mean difference was calculated for each individual study selected and then the data were combined using a random-effects meta-analysis.
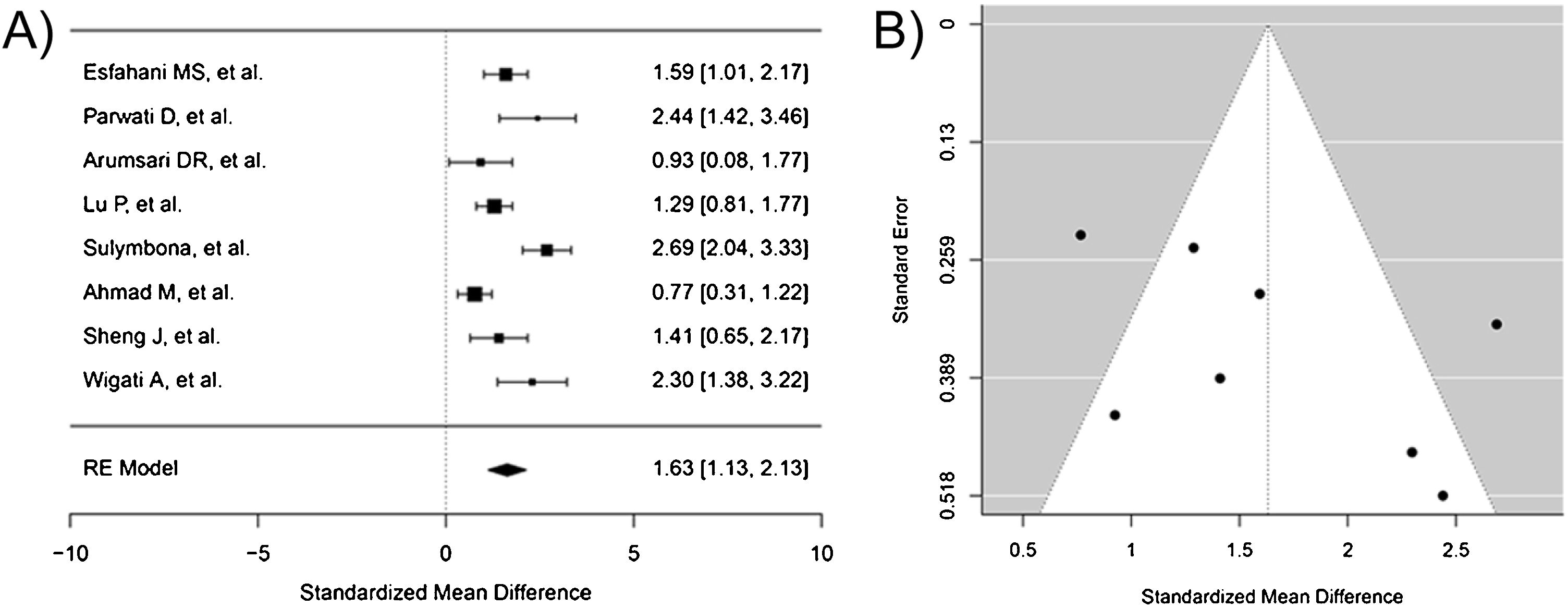
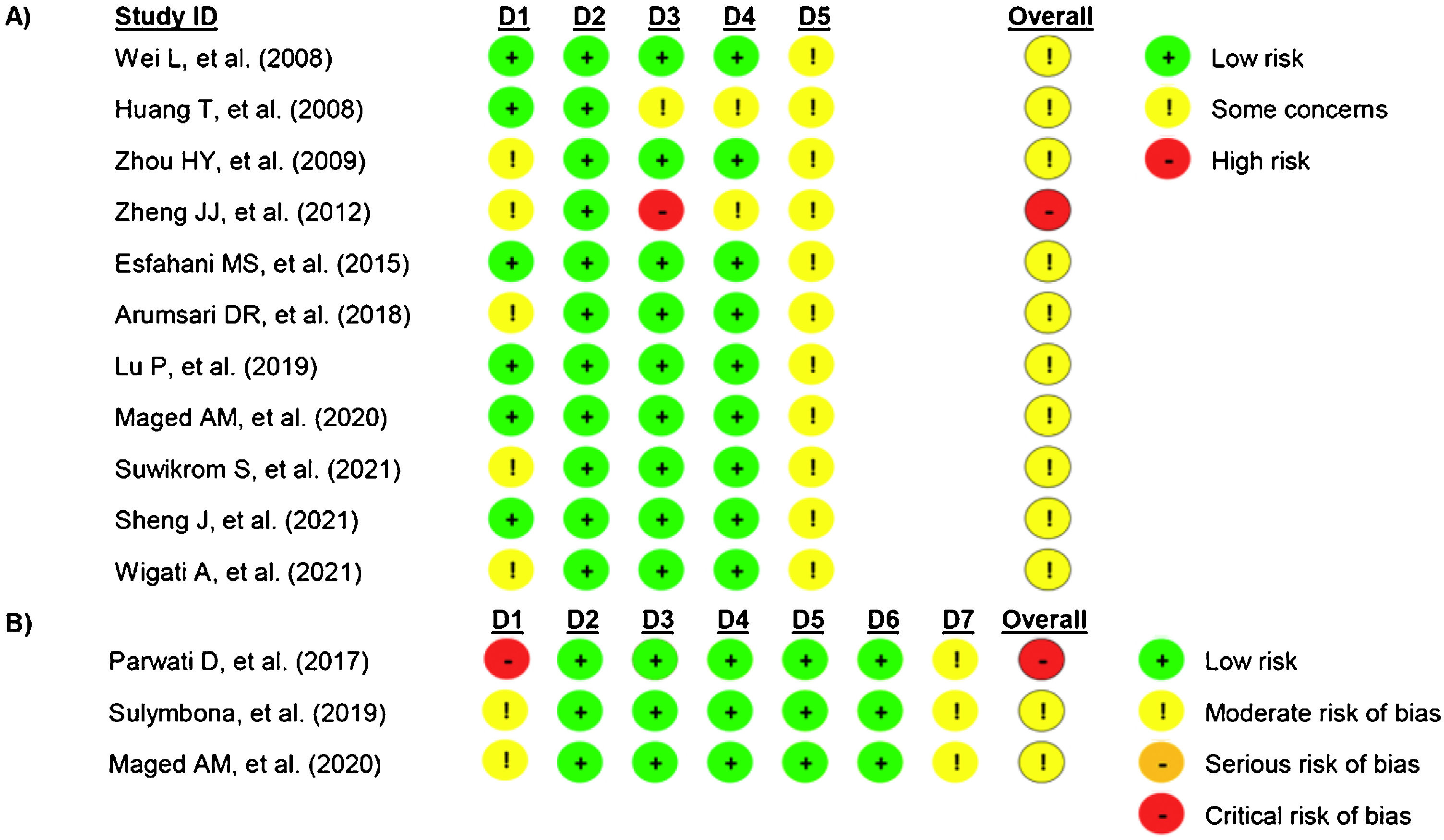
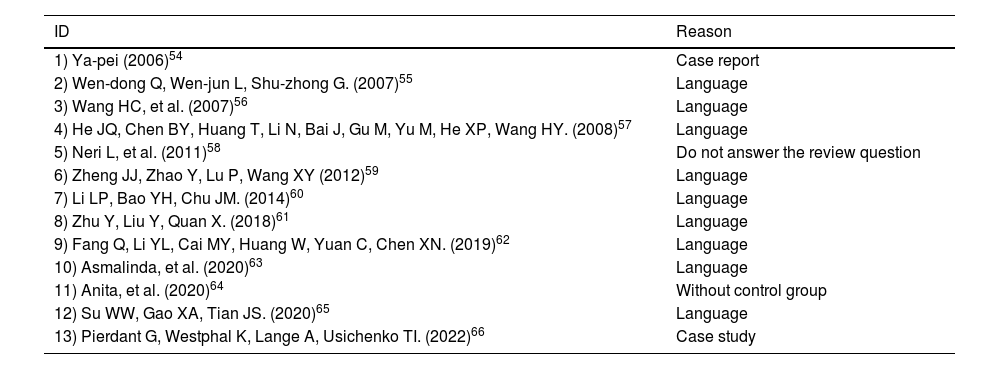
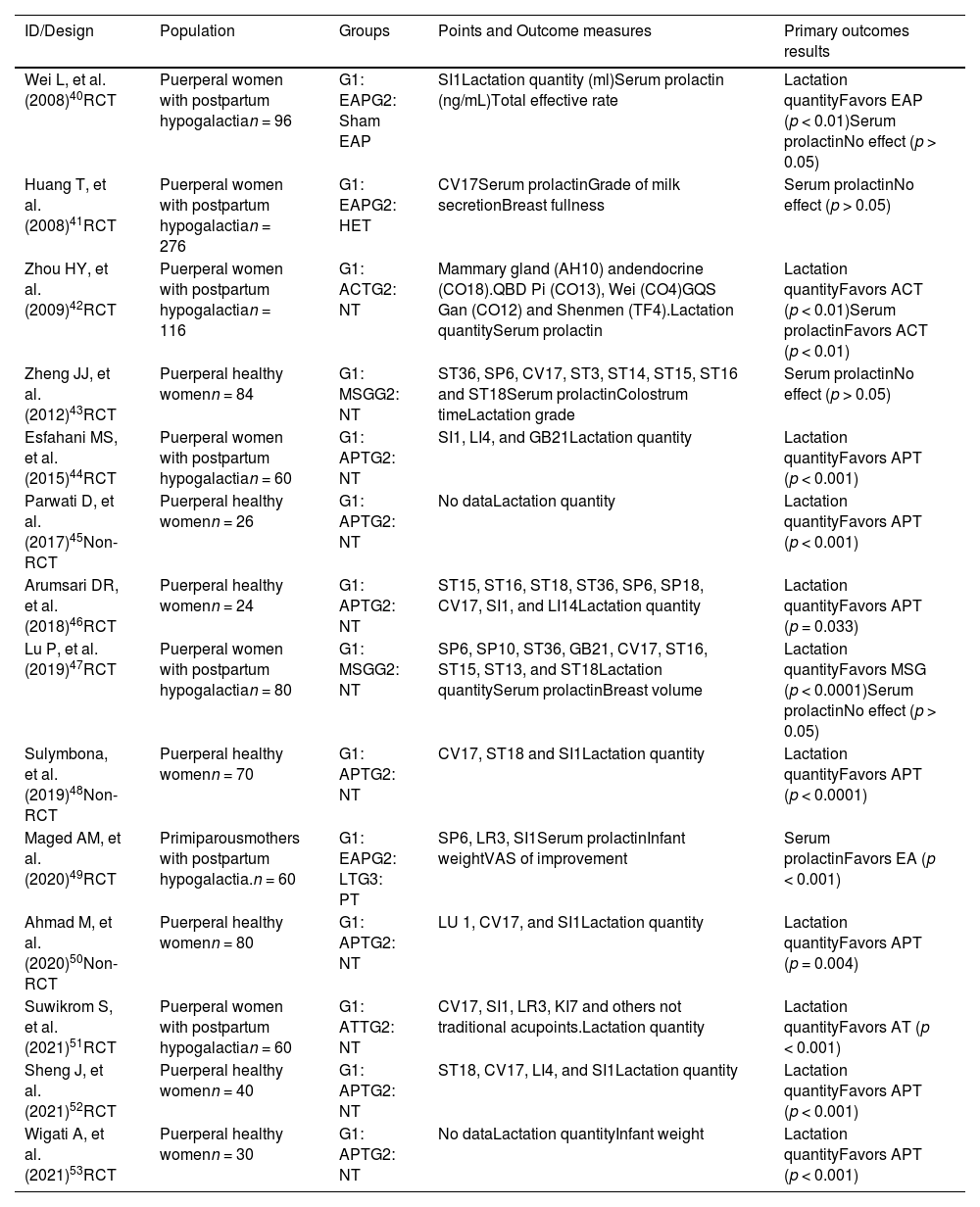
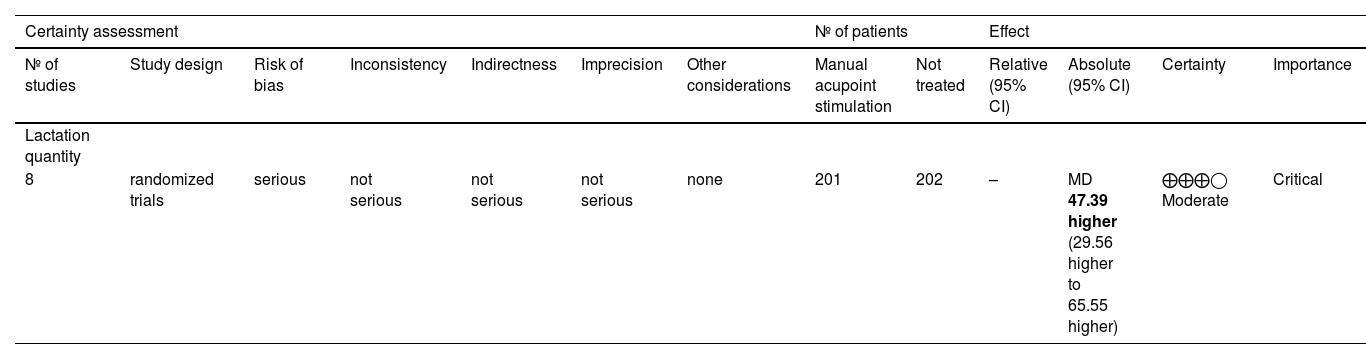
ResultsA total of 14 studies were included in the present review. Most of the included studies exhibited some concerns in the risk of bias assessment. The quality of the studies was moderate. The meta-analysis showed that manual acupoint stimulation improves the lactation quantity (SMD 95% CI = 1.63 [1.13–2.13]; p < 0.0001).
ConclusionThe literature suggests that manual stimulation of acupuncture points improves the amount of milk produced during lactation.
Realizar una revisión de la literatura para analizar si la estimulación de puntos de acupuntura aumenta la cantidad de leche producida durante la lactancia.
MétodoSe recopilaron estudios de cinco bases de datos electrónicas siguiendo las recomendaciones internacionales para la elaboración de revisiones sistemáticas y metaanálisis. Los criterios de elegibilidad fueron artículos de texto completo en inglés o español con diseño de ensayos clínicos y estudios observacionales, sin restricción en el tiempo de publicación, en los cuales se hubiera evaluado el efecto de la estimulación de puntos de acupuntura en la mejora de la cantidad de lactancia mediante acupuntura convencional, electroacupuntura, láser, agujas de fuego, estimulación manual, Tui Na o catgut. Dos autores extrajeron de forma independiente los datos de las características y los resultados principales de los estudios seleccionados para su inclusión. Se realizaron las evaluaciones de riesgo de sesgo y de calidad (GRADE). Para la síntesis cuantitativa, se calculó la diferencia de medias estandarizada para cada estudio individual seleccionado y luego se combinaron los datos mediante un metaanálisis de efectos aleatorios.
ResultadosEn la presente revisión, se incluyeron un total de 14 estudios, la mayoría de estos mostraron riesgo de sesgo y una calidad moderada. El metaanálisis mostró que la estimulación manual del punto de acupuntura aumenta la cantidad de leche materna (DME 95% IC = 1,63 [1,13−2,13]; p < 0,0001).
ConclusiónLa literatura sugiere que la estimulación manual de puntos de acupuntura mejora la cantidad de leche producida durante de lactancia.