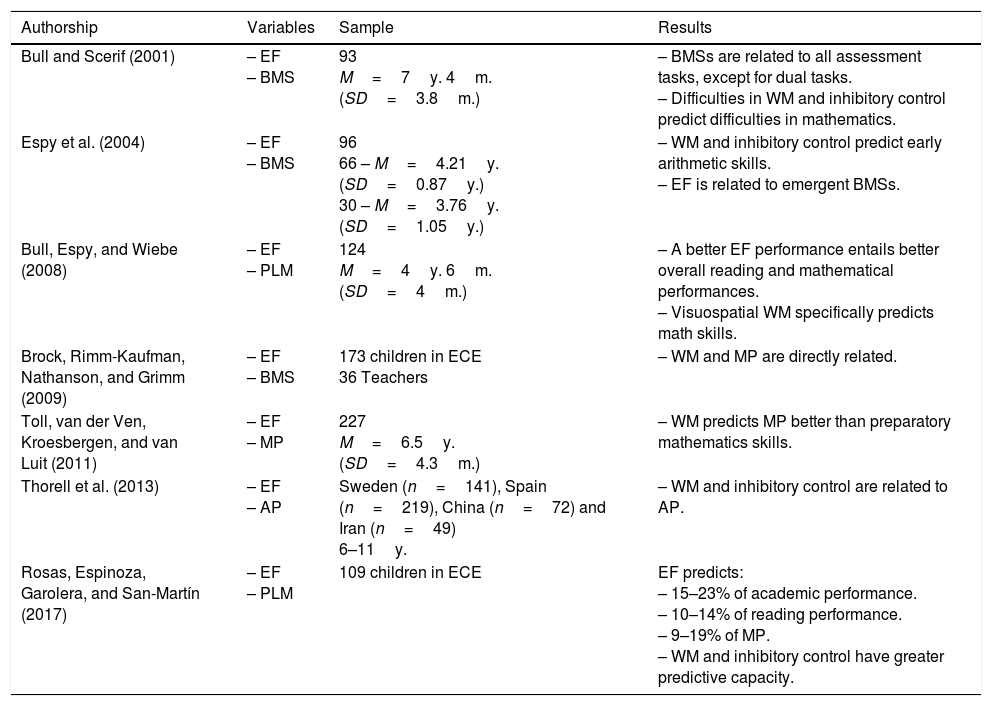
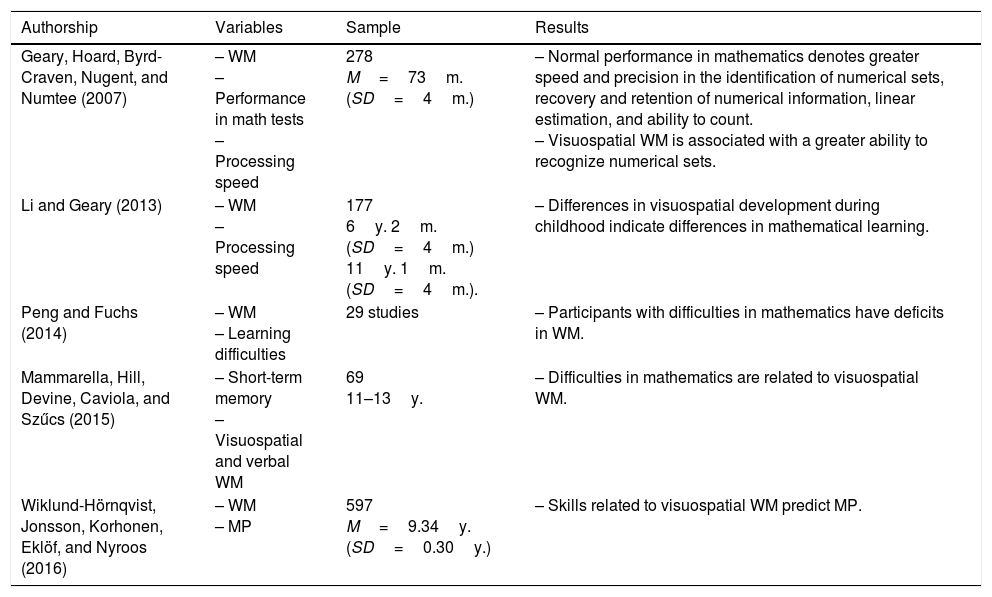
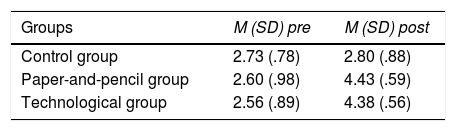
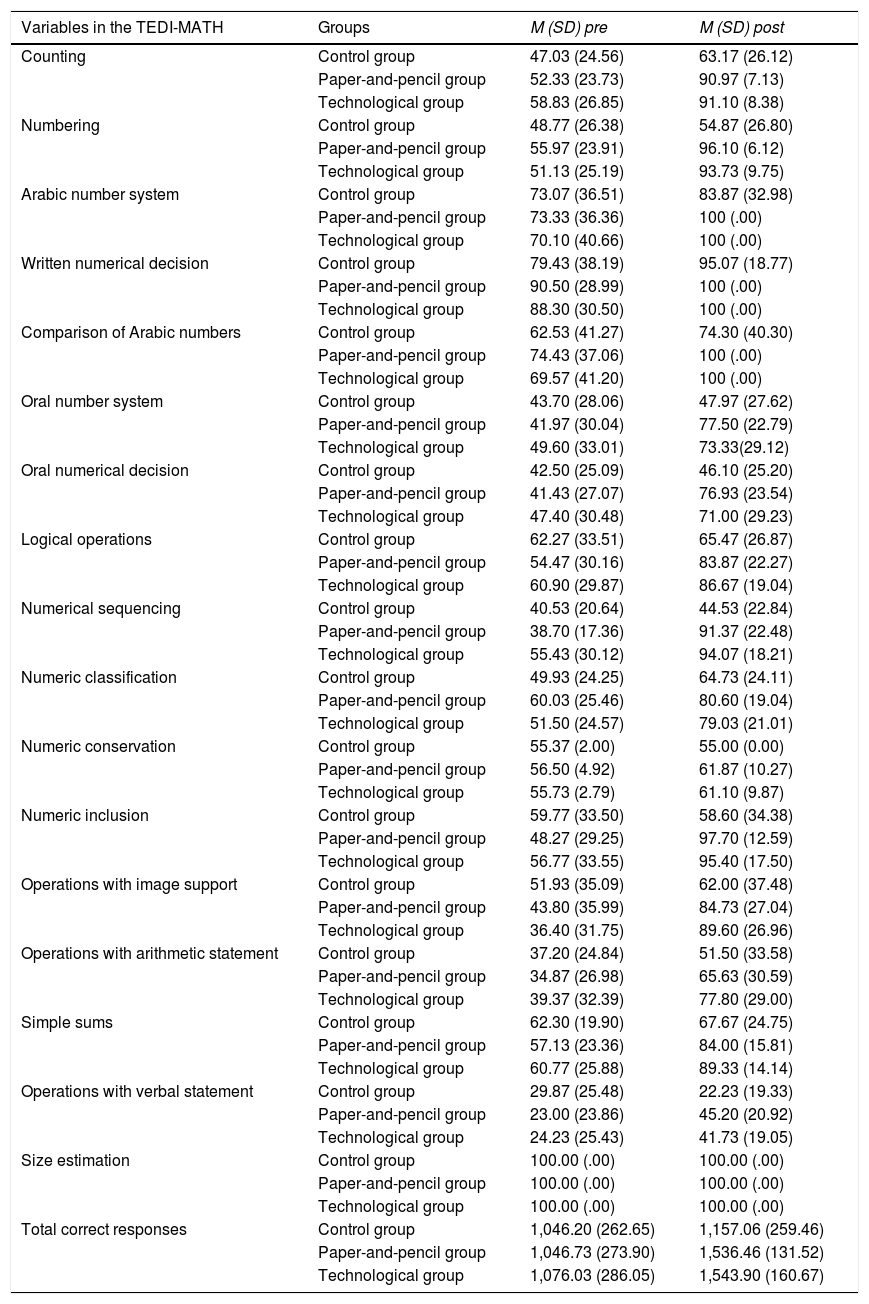
The present work proposes as the main objective the design and implementation of a virtual educational intervention programme, based on interactive learning through gesture play, to improve working memory and basic mathematical skills. In addition, the results were compared with those of the application of the programme in paper and pencil format. A factorial design of repeated measurements was used with an inter-group factor (control, paper and pencil and technology) and an intra-group factor (pretest–postest). As dependent variables, the visuospatial memory width provided by the Corsi Test was used, as well as the individual results according to the scale, and the total number of successes in the Test for the Diagnosis of Basic Mathematical Competences (TEDI-MATH). Ninety children between the ages of 5 and 6 participated and were distributed in three groups of 30 subjects: one group to which the programme was applied in virtual format, another to which the programme was applied in paper and pencil format and a control group without treatment. The results showed improvements in both working memory and basic mathematical skills in the two groups that received the intervention versus the control group. Therefore, it seems that it is the structure and content of the tasks and not so much the resources used that are responsible for the changes observed.
El presente trabajo plantea como objetivo principal el diseño y la puesta en práctica de un programa de intervención educativa virtual, basado en el aprendizaje interactivo a través del juego de gestos, para la mejora de la memoria de trabajo y las habilidades matemáticas básicas. Además, se comparan los resultados con los de la aplicación del programa en formato papel y lápiz. Se utiliza un diseño factorial de medidas repetidas con un factor inter-grupo (control, papel y lápiz y tecnológico) y un factor intra-grupo (pretest-postest). Como variables dependientes se utilizan la amplitud de memoria visoespacial proporcionada por el Test de Corsi, así como los resultados individuales según baremo, y el total de aciertos en el Test para el Diagnóstico de las Competencias Básicas en Matemáticas (TEDI-MATH). Han participado 90niños y niñas de entre 5 y 6años que se distribuyen en tres grupos de 30 sujetos: un grupo al que se aplica el programa en formato virtual, otro al que se aplica el programa en formato papel y lápiz y un grupo control sin tratamiento. Los resultados han mostrado mejoras tanto en memoria de trabajo como en habilidades matemáticas básicas en los dos grupos que han recibido la intervención frente al grupo control. Por lo tanto, parece que son la estructura y el contenido de las tareas, y no tanto el formato, los responsables de los cambios observados.