The aim of our study was to determine whether volumetric parameters measured from the primary lesion and metastatic lymph node (LN) using [18F]FDG PET/CT imaging affect prognosis and survival in nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC) patients.
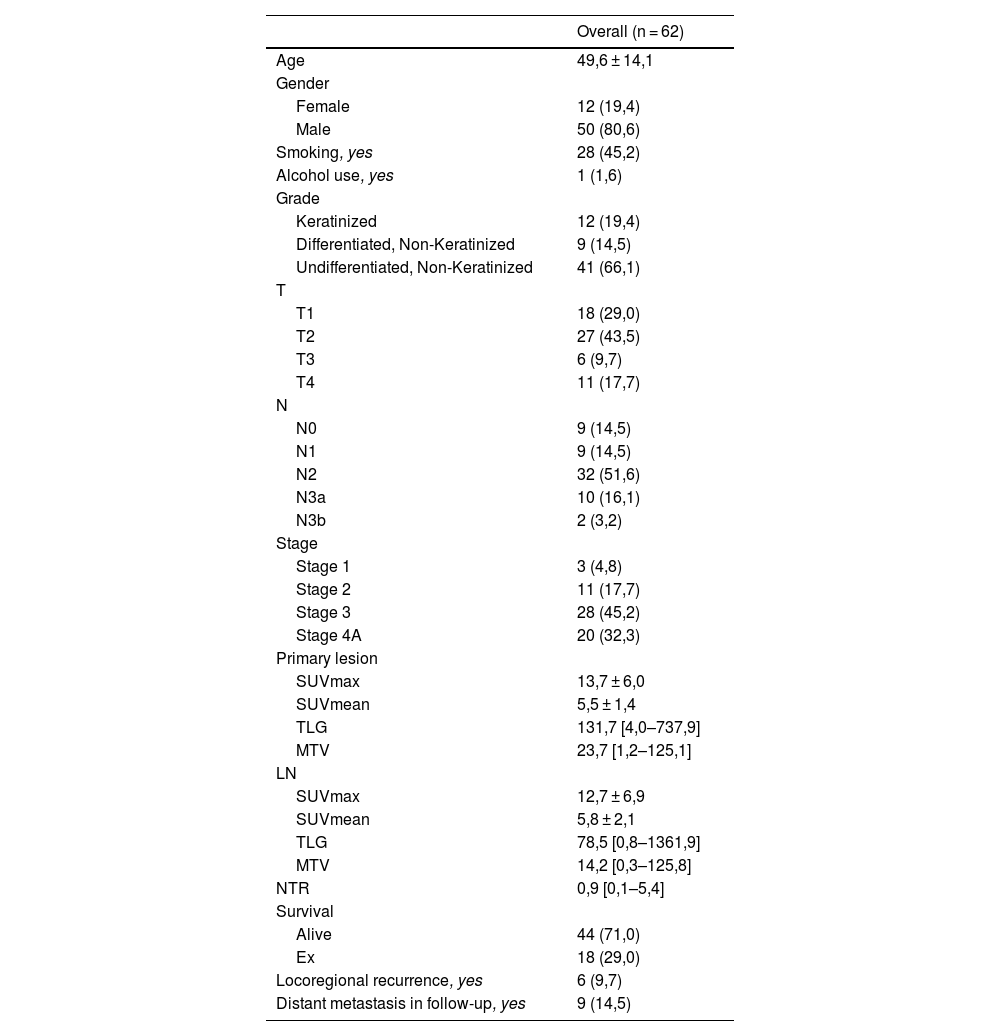
Material and methodsOur study included 62 patients diagnosed with NPC who underwent [18F]FDG PET/CT imaging for pre-treatment staging. SUVmax, SUVmean, MTV and TLG values were measured from the primary tumor and LN. Lymph node/primary tumor SUV ratio (NTR) was calculated. The relationships between volumetric parameters and overall survival (OS), locoregional recurrence-free survival (LRRFS), distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were evaluated.
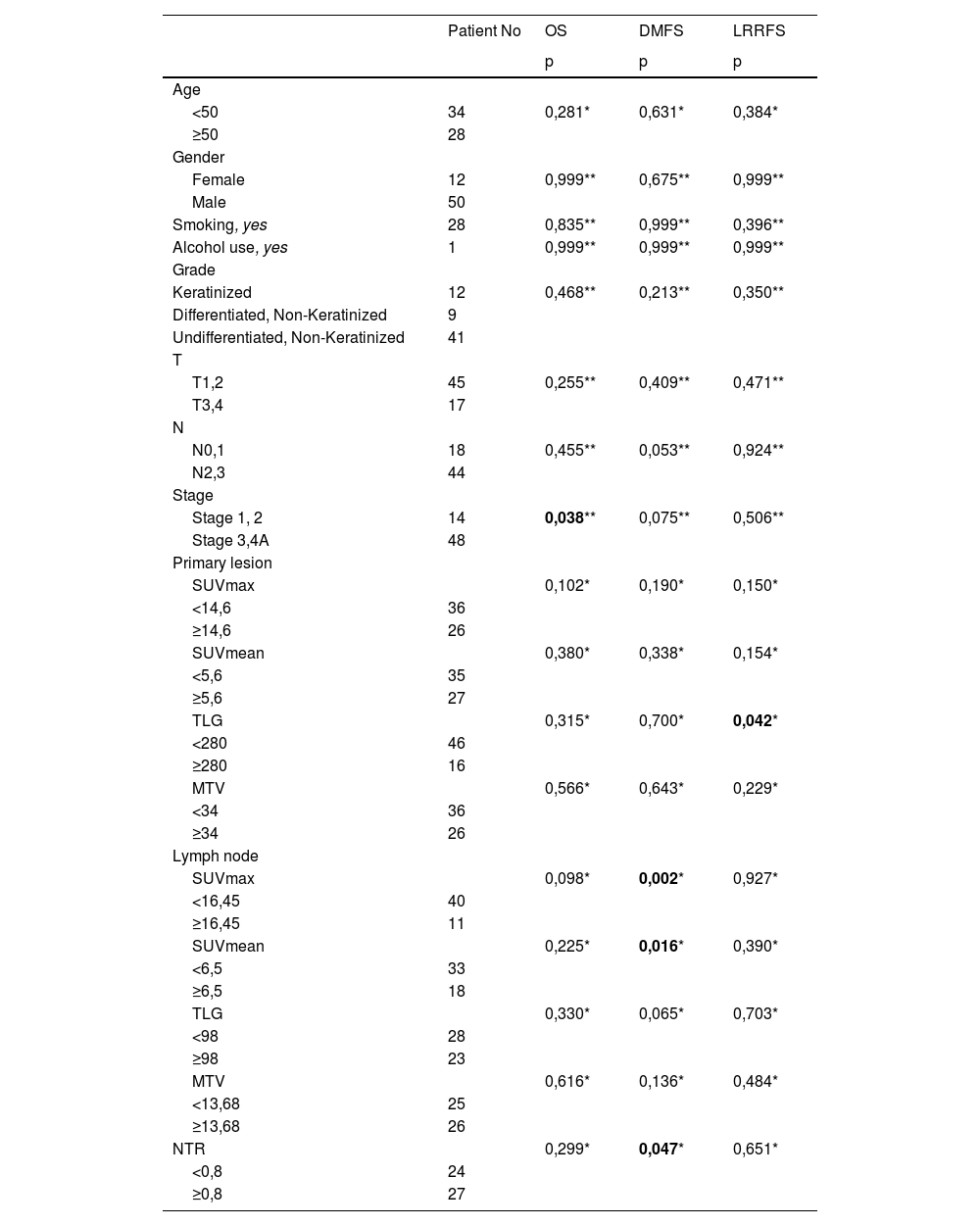
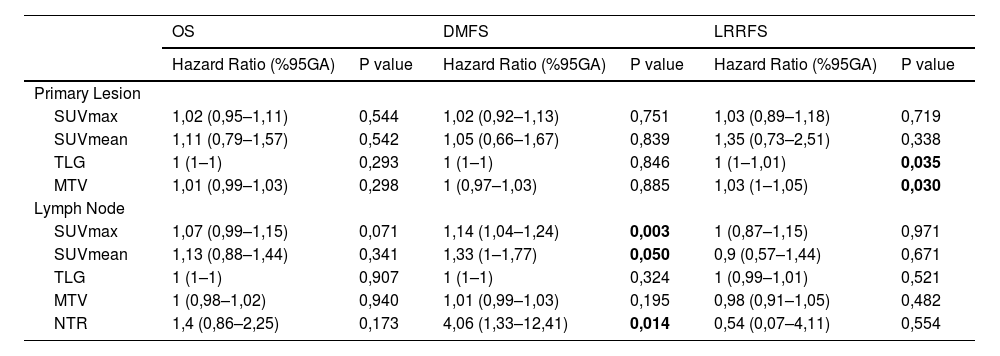
ResultsLN SUVmax and LN SUVmean values were significantly higher in patients with distant metastases (p = 0.002 and p = 0.016, respectively). NTR values were significantly higher in patients with distant metastases (p = 0.047). The ideal LN SUVmax and SUVmean cut-off values for predicting distant metastasis in patients with LN metastasis were 16.45 and 6.5, respectively. There was a statistically significant difference between the DMFSs of the two groups when the NTR cut-off value was 0.8 (p = 0.047). Multivariate analysis showed that LN SUVmax, LN SUVmean and NTR were associated with DMFS (P = 0.003, 0.05 and 0.014, respectively), while primary tumor TLG and MTV values were associated with LRRFS (P = 0.035 and 0.03, respectively).
ConclusionIn conclusion, we believe that LN SUVmax, SUVmean and NTR may be prognostic indicators for distant metastasis, and MTV and TLG for locoregional recurrence.
El objetivo de nuestro estudio fue determinar si los parámetros volumétricos medidos a partir de la lesión primaria y el ganglio linfático metastásico (GL) utilizando imágenes de PET/CT con [18F]FDG afectan el pronóstico y la supervivencia en pacientes con cáncer nasofaríngeo (NPC).
Material y métodosNuestro estudio incluyó a 62 pacientes diagnosticados con NPC que se sometieron a imágenes de PET/CT con [18F]FDG para la estadificación previa al tratamiento. Los valores de SUVmax, SUVmean, MTV y TLG se midieron en el tumor primario y en los ganglios linfáticos. Se calculó la relación SUV entre los ganglios linfáticos y el tumor primario (NTR). Se evaluaron las relaciones entre los parámetros volumétricos y la supervivencia global (SG), la supervivencia libre de recurrencia locorregional (SLRLR), la supervivencia libre de metástasis a distancia (SLMD) y la supervivencia libre de progresión (SLP).
ResultadosLos valores de GL SUVmax y GL SUVmean fueron significativamente más altos en pacientes con metástasis a distancia (p = 0.002 y p = 0.016, respectivamente). Los valores de NTR fueron significativamente más altos en pacientes con metástasis a distancia (p = 0.047). Los valores de corte ideales de GL SUVmax y SUVmean para predecir metástasis a distancia en pacientes con metástasis de GL fueron 16.45 y 6.5, respectivamente. Hubo una diferencia estadísticamente significativa entre el SLMD de los dos grupos cuando el valor de corte de NTR fue 0.8 (p = 0.047). El análisis multivariante mostró que GL SUVmax, GL SUVmean y NTR estaban asociados con SLMD (P = 0.003, 0.05 y 0.014, respectivamente), mientras que los valores de TLG y MTV del tumor primario estaban asociados con SLRLR (P = 0.035 y 0.03, respectivamente).
ConclusionesEn conclusión, creemos que GL SUVmax, SUVmean y NTR pueden ser indicadores pronósticos para la metástasis a distancia, y MTV y TLG para la recurrencia locorregional.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)