This study aims to evaluate the diagnostic value of early static and delayed imaging in conjunction with standard 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT scans to detect prostate malignant lesions in prostate cancer patients.
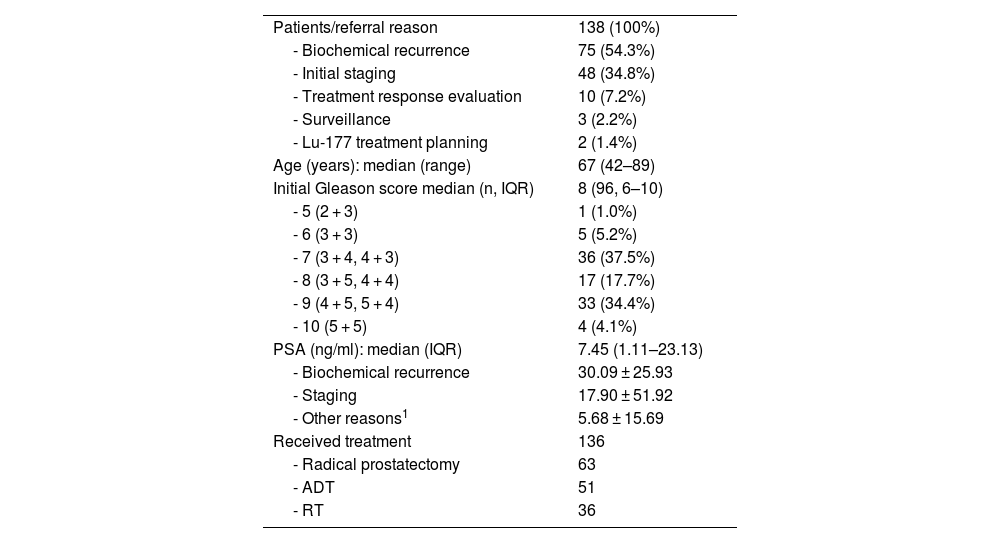
MethodsOne hundred and thirty-eight prostate cancer patients underwent routine [68 Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT imaging, 4-minute static acquisition post-injection, and delayed imaging 3 h post-injection. The imaging results were analysed for lesion count, type, localisation, and maximum standardised uptake values.
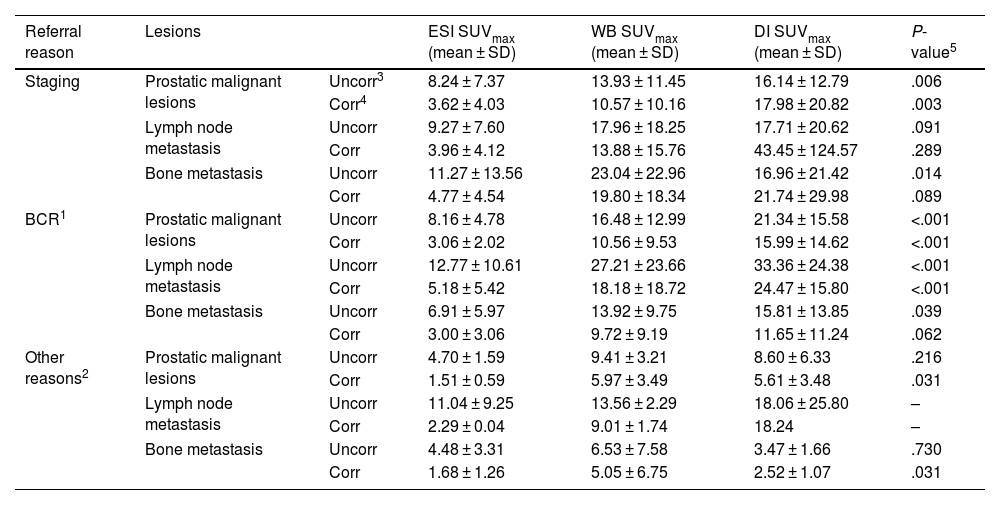
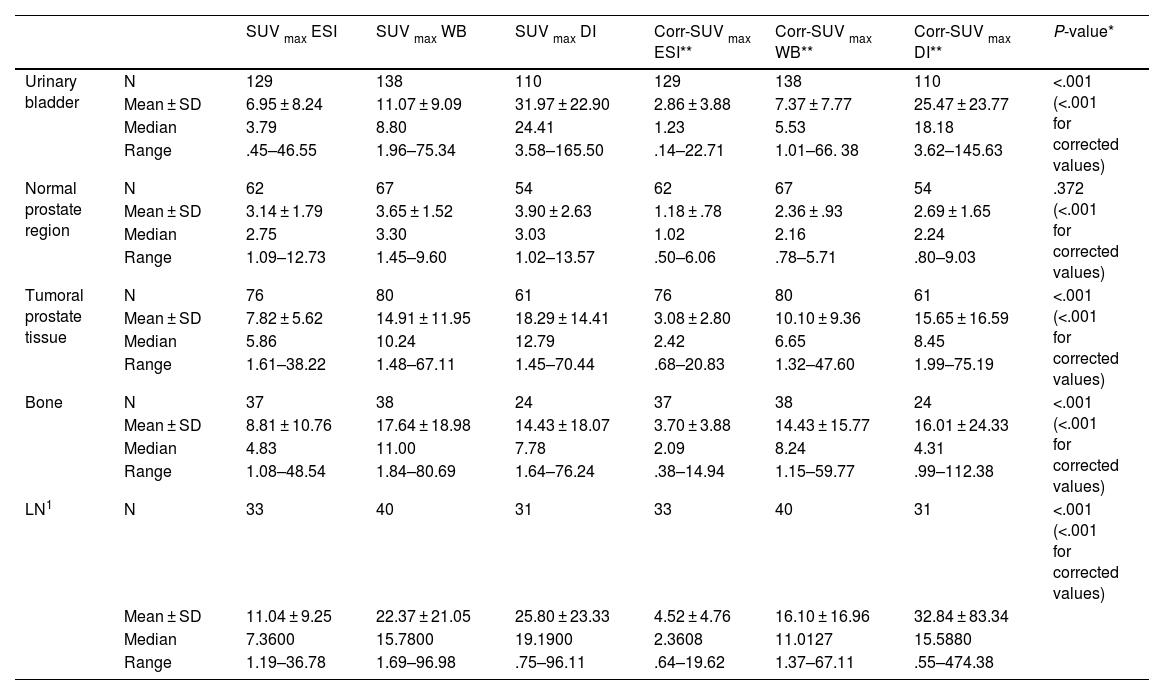
Results57.97% exhibited positive findings for pathologic prostatic lesions in the standard PET scans (SUVmax: 10.24). In contrast, early PET imaging detected lesions in 58.01% of patients (SUVmax of 5.86), while delayed scans revealed lesions suggestive of malignancy in 55.45% of patients (SUVmax of 12.79). The analysis demonstrated a statistically significant difference in SUVmax values across the time points (P < .001). Pathologic lymph nodes on images 60 min p.i. were revealed by an SUV max 60 min p.i.: 15.78; this number for the first 4 min and after 3 h were 7.36, 19.19, respectively. Metastatic bone lesions on WB were found in 38 patients, more than the ESI (n = 37) and DI (n = 24). In comparison, urinary bladder activity assessment was detectable with the WB imaging SUVmax 60 min 11.07. Even though the SUV max for ESI and DI were 6.95 and 31.97, respectively. In the statistical analysis, pathologic radiotracer uptake in tumour lesions was statistically higher in ESI and WB than in urinary bladder activity.
ConclusionsThe findings indicate that neither early [68 Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT nor delayed imaging significantly enhanced the overall detection rate of malignant lesions in prostate cancer patients. However, the early 4-minute post-injection acquisition of PET images proved beneficial for distinguishing local bladder invasion more effectively.
La precisión de los estudios con [68 Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 puede mejorarse mediante estrategias de imagen multifásica. Este estudio pretende evaluar el valor diagnóstico de las imágenes estáticas precoces y tardías en combinación con los estudios estándares de 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/TC para la detección de lesiones pélvicas en pacientes con cáncer de próstata.
MétodosA 138 pacientes con cáncer de próstata se les realizó estudio estándar con [68 Ga]Ga-PSMA 11 PET/TC, así como una adquisición estática precoz de 4 minutos post-inyección e imágenes tardías a las 3 horas post-inyección. Los hallazgos de las imágenes se analizaron en cuanto al número de lesiones, tipo, localización y captación (SUVmax).
ResultadosEl 57.97% mostraron hallazgos patológicos en región prostática en los estudios PET estándar (SUVmax: 10.24). En contraste, las imágenes PET precoces detectaron lesiones en el 58.01% de los pacientes (SUVmax: 5.86), mientras que las imágenes tardías revelaron lesiones sugestivas de malignidad en el 55.45% de los pacientes (SUVmax: 12.79). El análisis demostró diferencias estadísticamente significativas en los valores de SUVmax entre los distintos tiempos de adquisición (P < .001). Los ganglios patológicos en las imágenes a los 60 minutos post-inyección mostraron un SUVmax de 15.78; este valor fue de 7.36 en las imágenes precoces y de 19.19 en las tardías. Se encontraron lesiones óseas metastásicas en las imágenes de cuerpo completo (WB) en 38 pacientes, más que en las imágenes estáticas precoces (ESI, n = 37) y en las imágenes tardías (DI, n = 24). En comparación, la actividad en la vejiga urinaria fue detectable en imágenes WB a los 60 minutos con un SUVmax de 11.07, mientras que los SUVmax para ESI y DI fueron 6.95 y 31.97, respectivamente. El análisis estadístico mostró que la captación del radiotrazador en las lesiones patológicas fue significativamente mayor en ESI y WB que la actividad de la vejiga urinaria.
ConclusionesNuestros resultados indican que ni las imágenes precoces de [68 Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT ni las tardías mejoraron significativamente la tasa general de detección de lesiones pélvicas en pacientes con cáncer de próstata. Sin embargo, las imágenes precoces a los 4 minutos post-inyección demostró ser beneficiosa para distinguir más efectivamente la invasión local de la vejiga urinaria.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)