In this study we aimed to investigate prediction of response with [68Ga]Ga-PSMA PET-derived parameters and the effectiveness of RECIP criteria and PSA response in predicting survival after [177Lu]Lu-PSMA therapy.
MethodsPatients who received at least 2 cycles of [177Lu]Lu-PSMA therapy were retrospectively included in the study. All lesions in the PET images were segmented and PSMA PET-based parameters were extracted. The treatment response was evaluated according to RECIP and PSA criteria. ROC analyses were performed to assess their discriminatory power in predicting response. Correlation of overall survival with RECIP and PSA-based response was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier survival analysis.
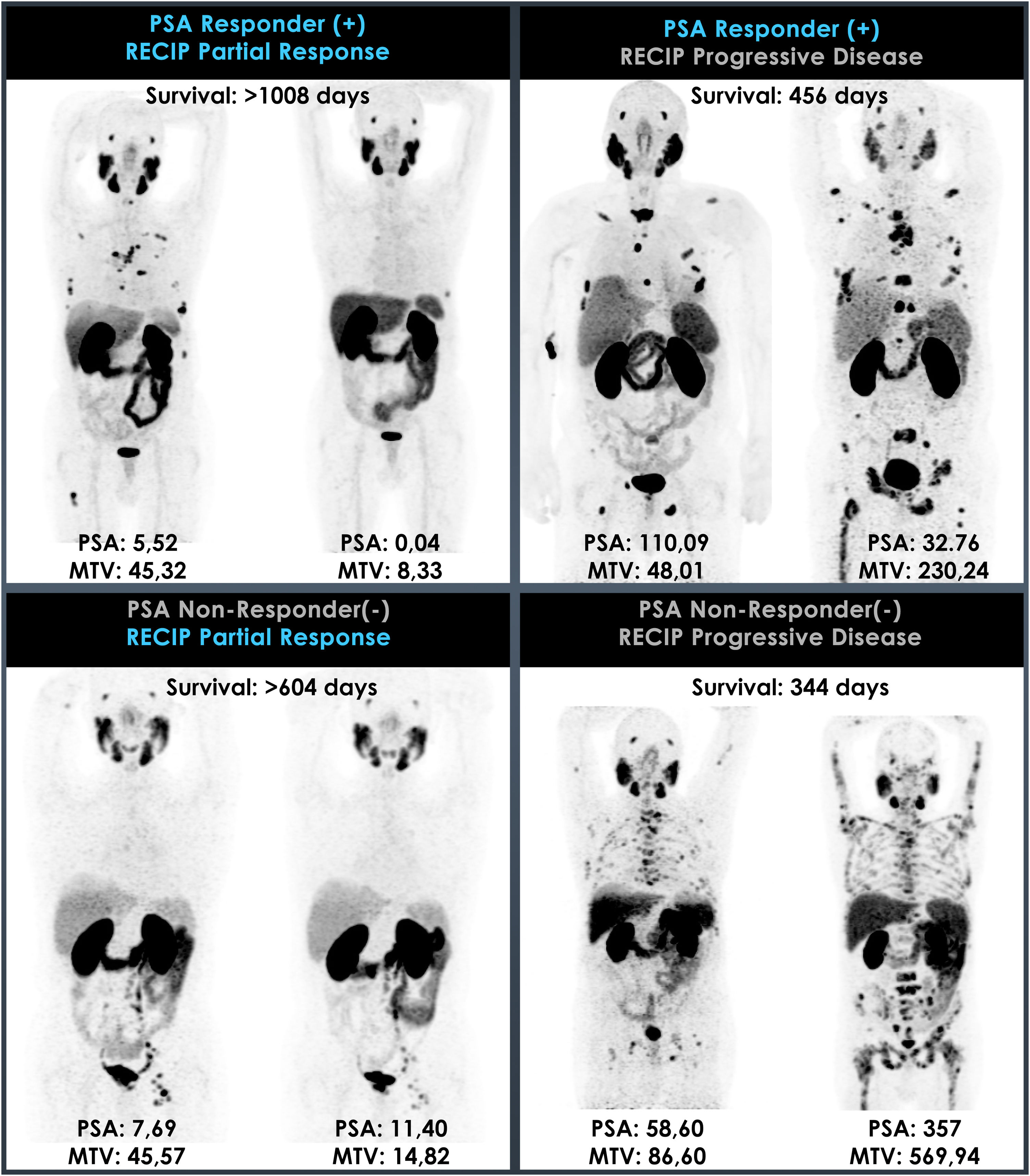
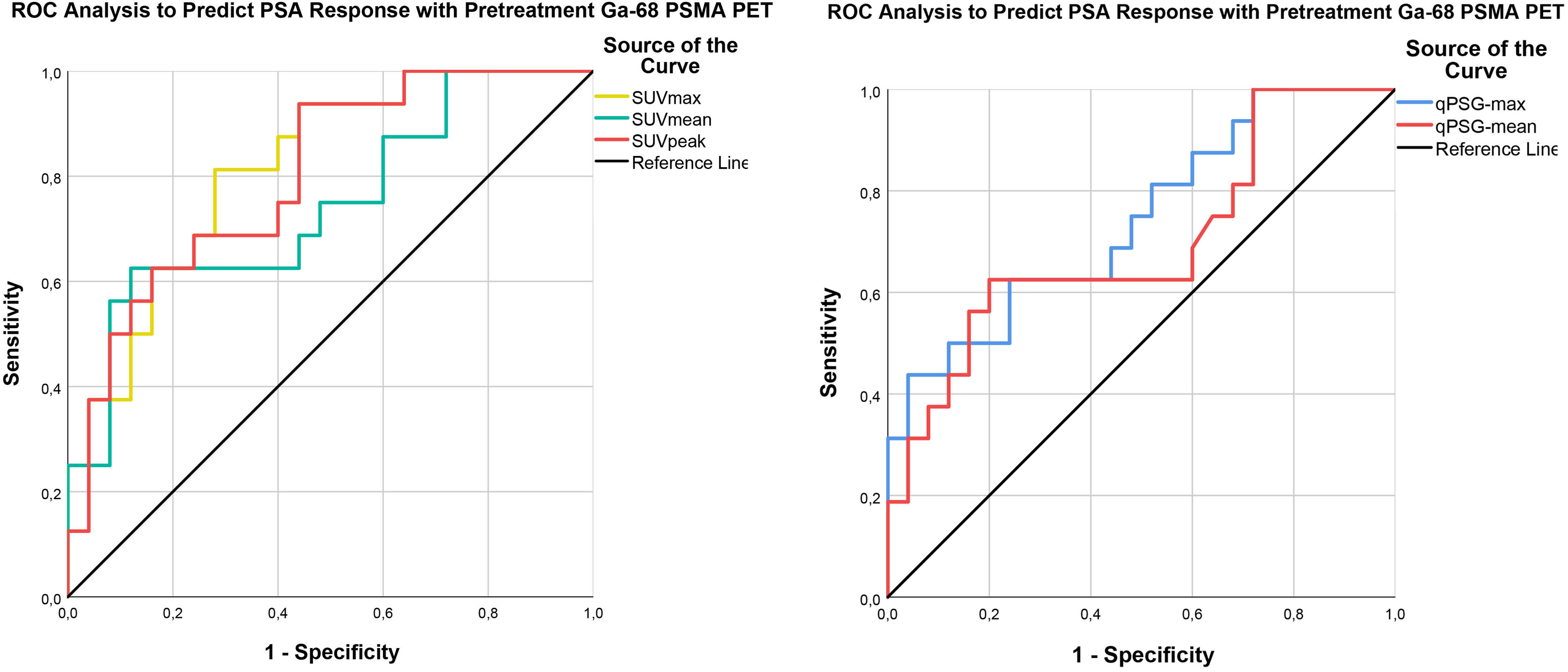
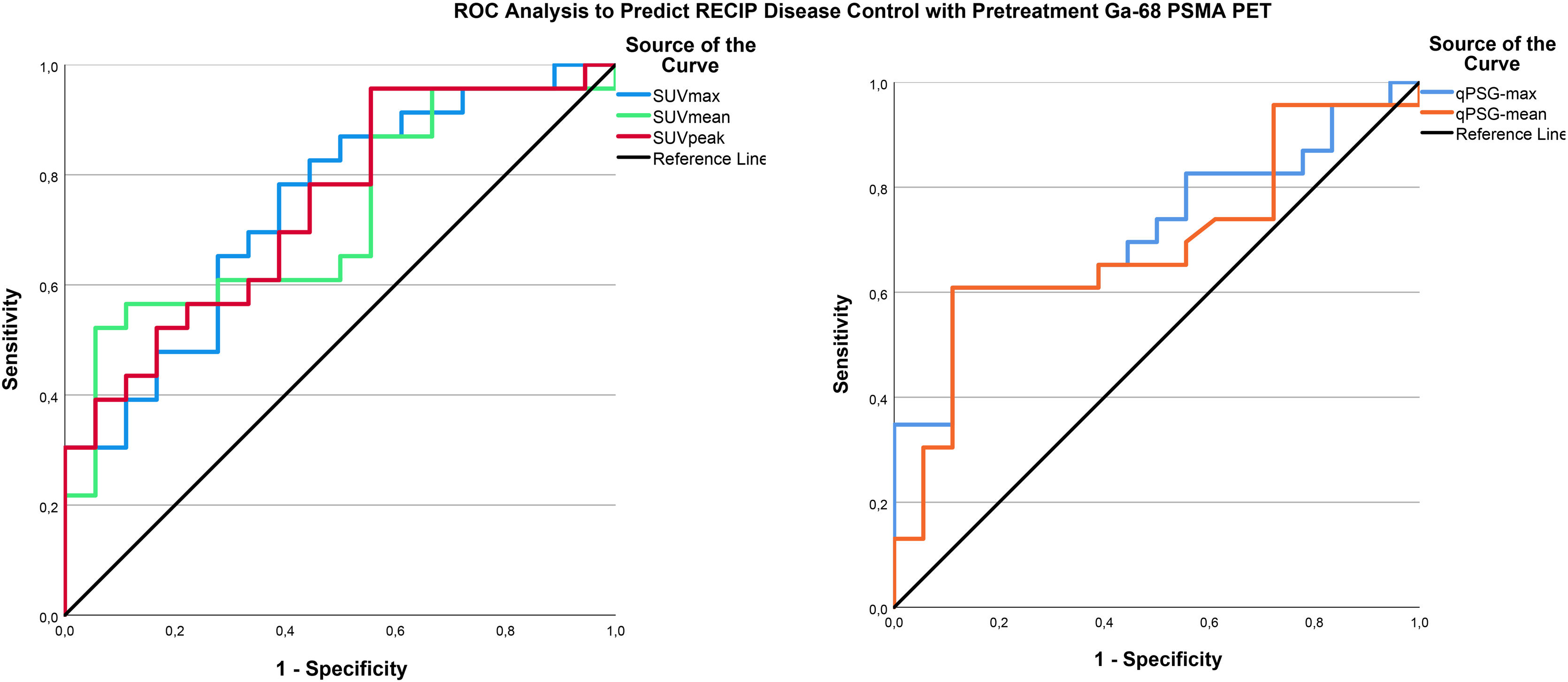
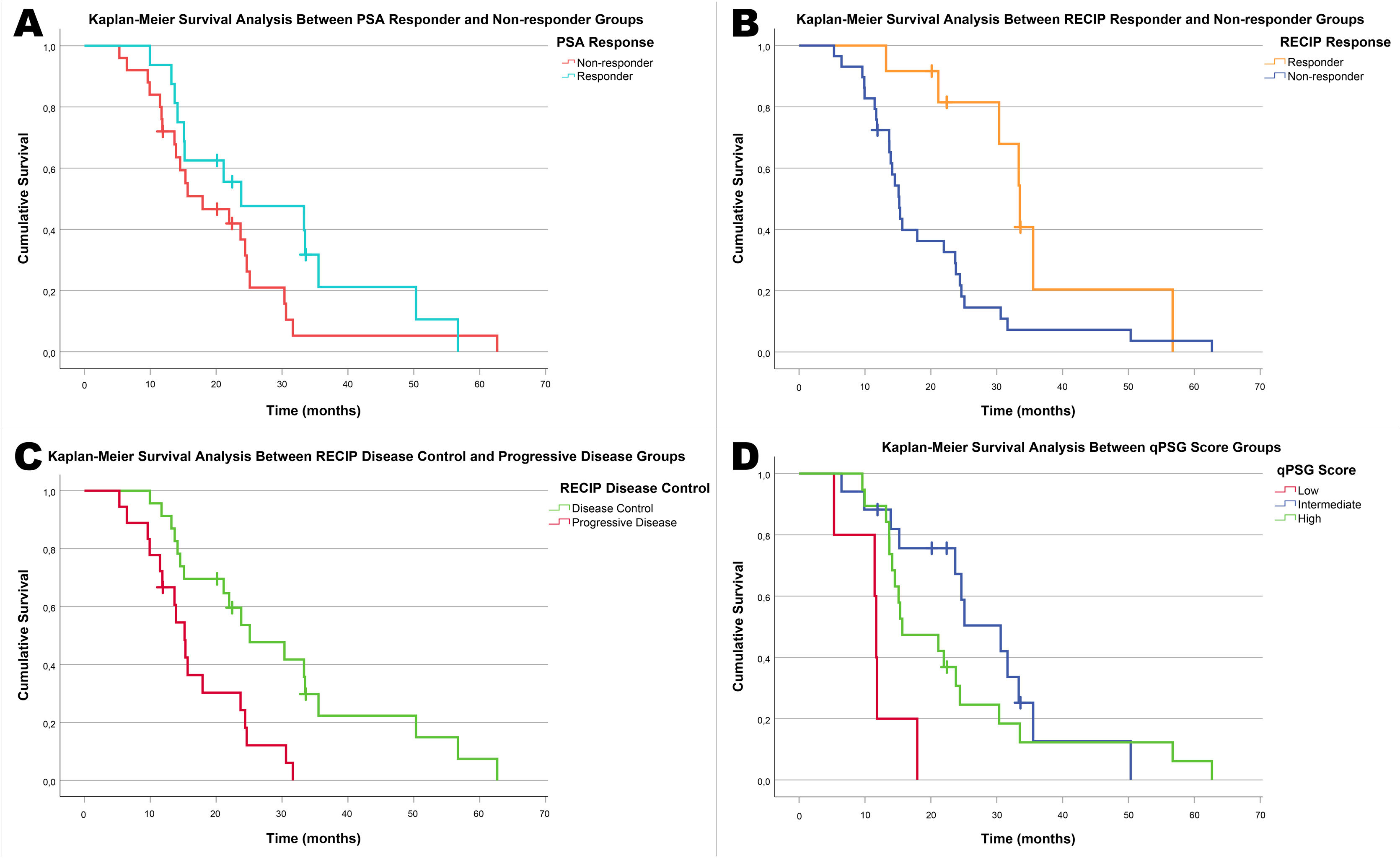
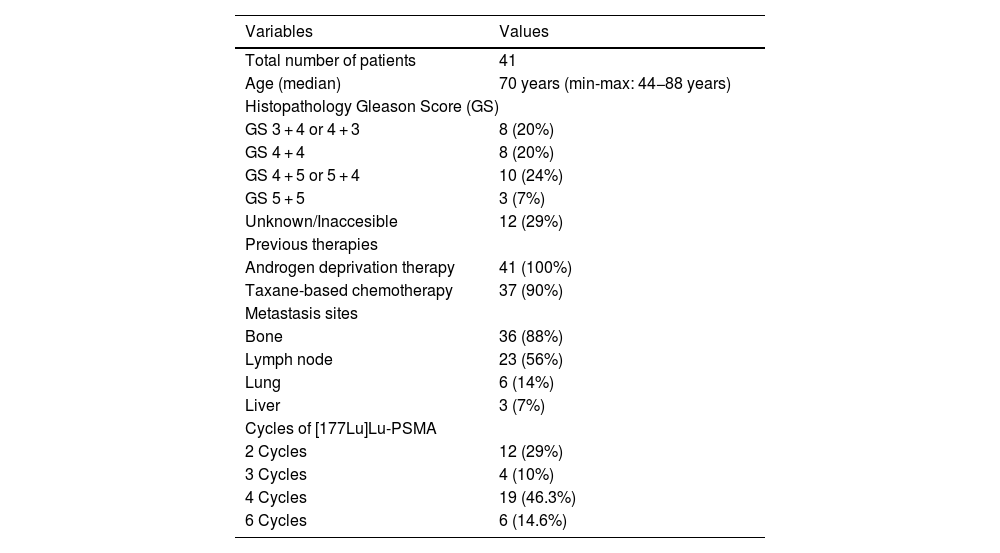
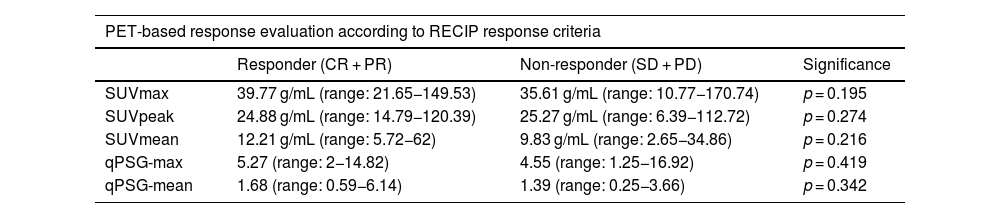
ResultsA total of 41 patients were included in the study. SUVmax, SUVpeak, SUVmean, qPSG-max and qPSG-mean values were significant factors in predicting PSA response. However, in predicting RECIP response (CR + PR), the AUC values for the SUV parameters were not significantly higher than 0.5. In predicting RECIP disease control (CR + PR + SD), the AUC values for SUVmax, SUVpeak, and SUVmean were 0.742(p = 0.002), 0.742(p = 0.002), and 0.722(p = 0.006). In the RECIP-responder and non-responder groups, the median survival was 33.5 and 15.2 months (p = 0.005). In patients with RECIP-disease control and progressive disease, the median survival was 25.1 and 15.2 months (p = 0.002). However, the survival difference between PSA-responder and non-responders groups did not reach significance (p = 0.127).
ConclusionPSMA PET imaging is a useful method to select patients who will most likely to benefit from [177Lu]Lu-PSMA treatment. Also, it has been shown that RECIP has significantly performed better than PSA-based response evaluation in terms of predicting overall survival.
En este estudio, se evaluó la capacidad de predicción de respuesta mediante parámetros derivados de PET con [68Ga]Ga-PSMA y la eficacia de los criterios RECIP y la respuesta del PSA en la predicción de la supervivencia tras la terapia con [177Lu]Lu-PSMA.
MétodosSe incluyeron retrospectivamente pacientes que recibieron al menos dos ciclos de terapia con [177Lu]Lu-PSMA. Todas las lesiones en las imágenes PET fueron segmentadas y se extrajeron los parámetros cuantitativos basados en PSMA. La respuesta al tratamiento se evaluó según los criterios RECIP y PSA. Se realizaron análisis ROC para evaluar su capacidad discriminatoria en la predicción de la respuesta. La correlación con la supervivencia global se analizó mediante curvas de Kaplan-Meier.
ResultadosSe incluyó un total de 41 pacientes. Los valores de SUVmax, SUVpeak, SUVmean, qPSG-max y qPSG-mean fueron factores significativos en la predicción de la respuesta del PSA. En la predicción del control de la enfermedad según RECIP (CR + PR + SD), los valores del AUC para SUVmax, SUVpeak y SUVmean fueron 0.742 (p = 0.002), 0.742 (p = 0.002) y 0.722 (p = 0.006), respectivamente. En los grupos de respondedores y no respondedores según RECIP, la supervivencia mediana fue de 33.5 y 15.2 meses (p = 0.005). En pacientes con control de la enfermedad y enfermedad progresiva según RECIP, la supervivencia mediana fue de 25.1 y 15.2 meses (p = 0.002). Sin embargo, la diferencia en la supervivencia entre los grupos de respondedores y no respondedores según PSA no alcanzó significación estadística (p = 0.127).
ConclusiónLa PET con PSMA es una herramienta útil para seleccionar a los pacientes con mayor probabilidad de beneficiarse de la terapia con [177Lu]Lu-PSMA. Además, se ha demostrado que los criterios RECIP tienen un mejor rendimiento que la evaluación basada en PSA para predecir la supervivencia global.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)