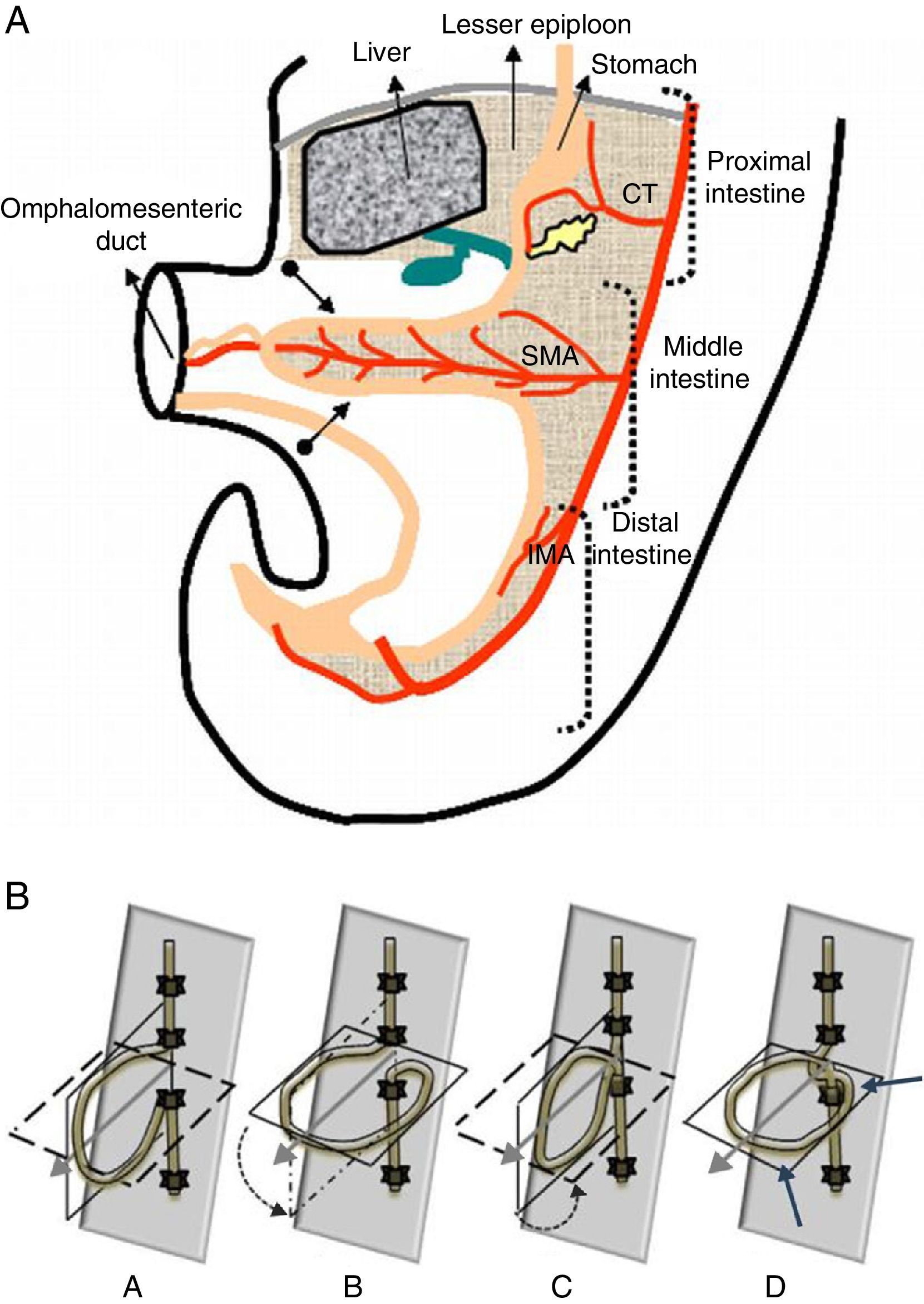
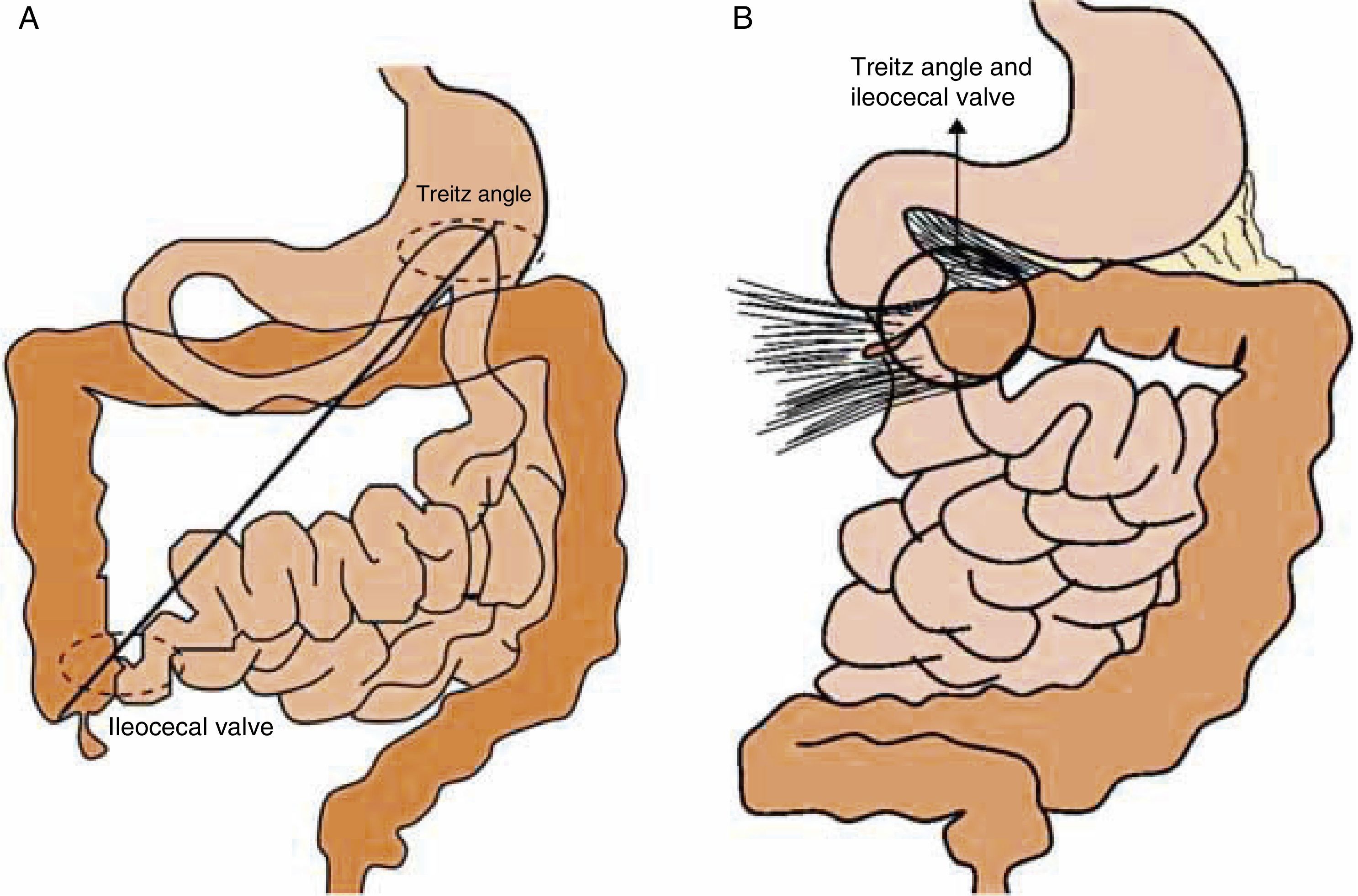
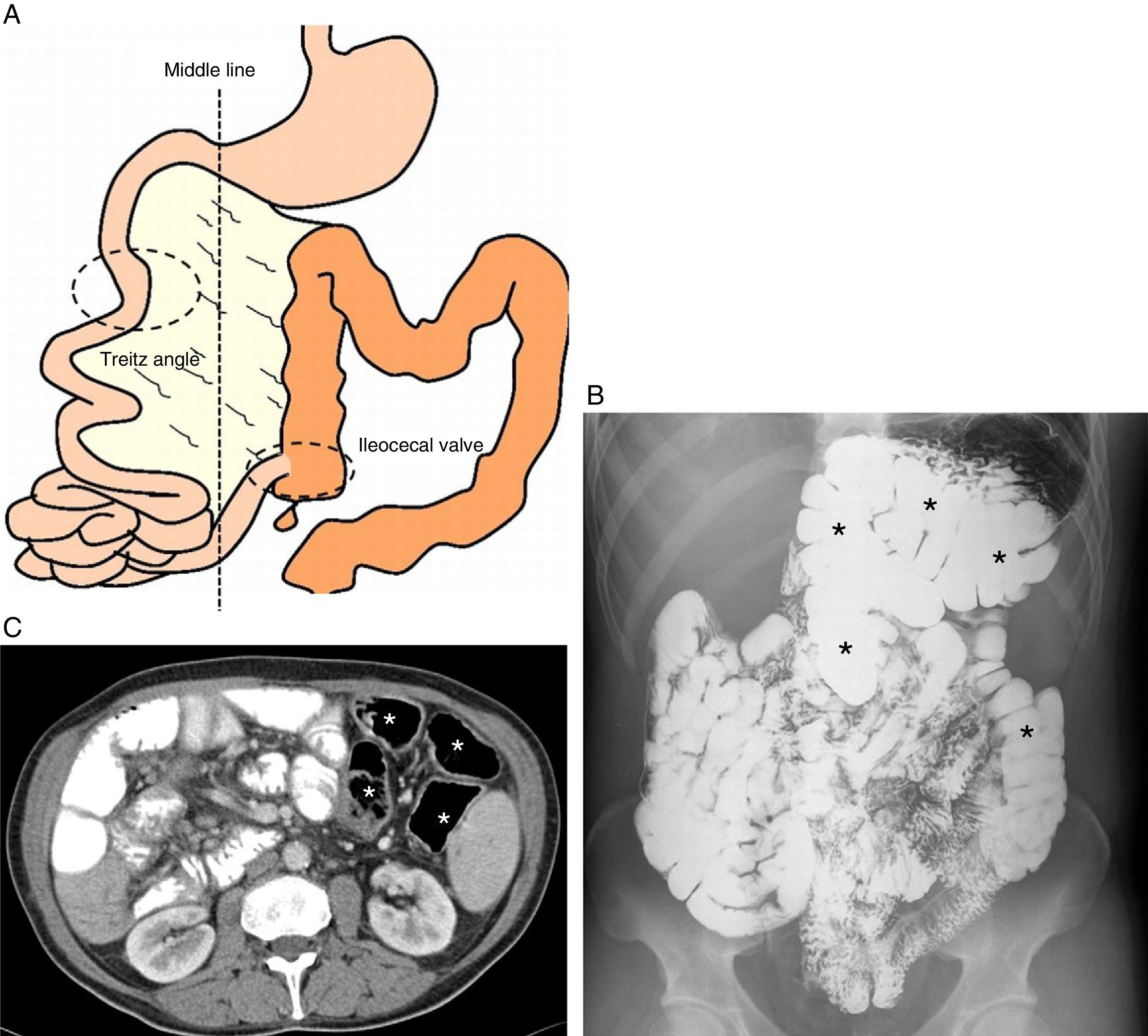
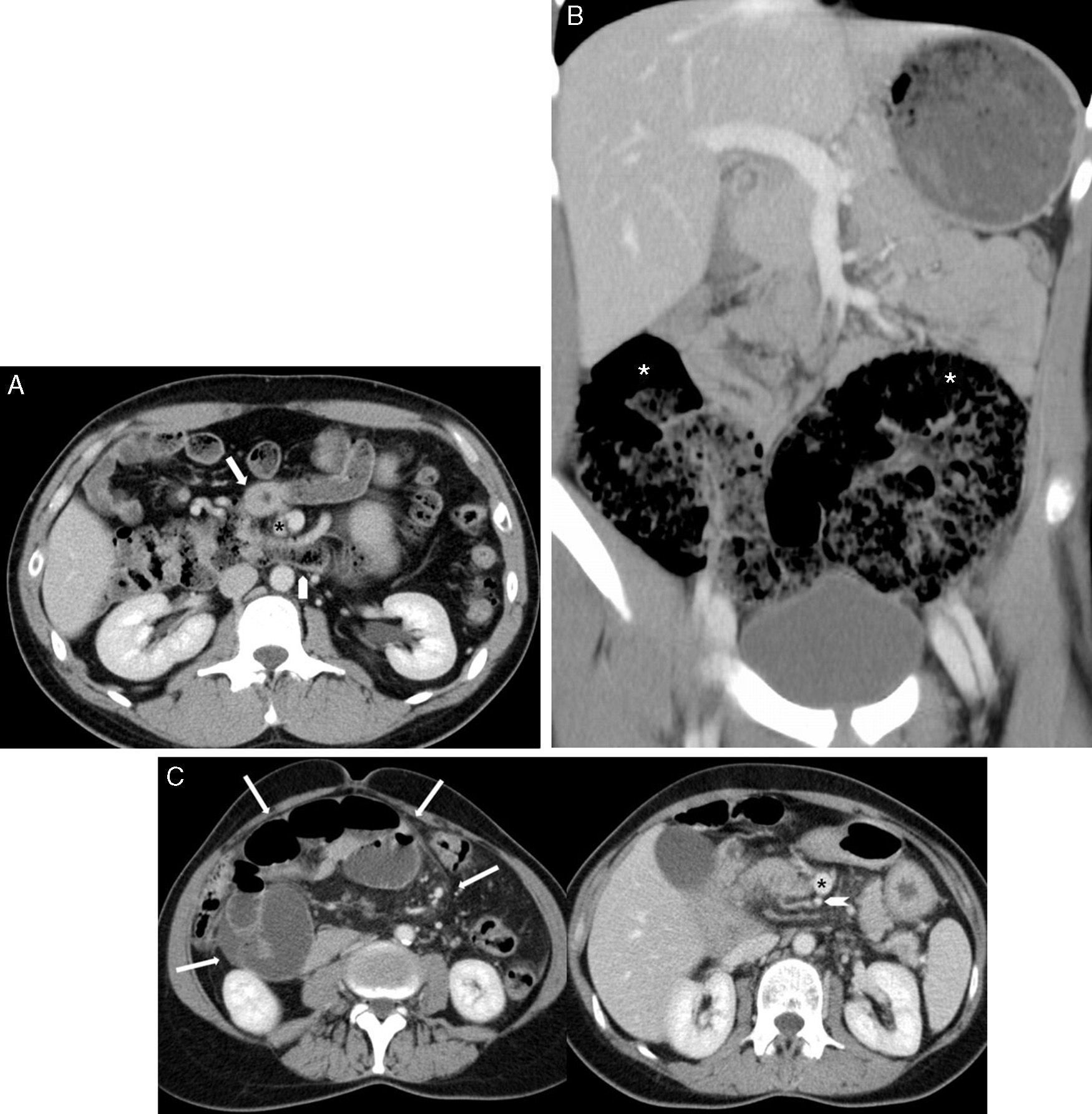
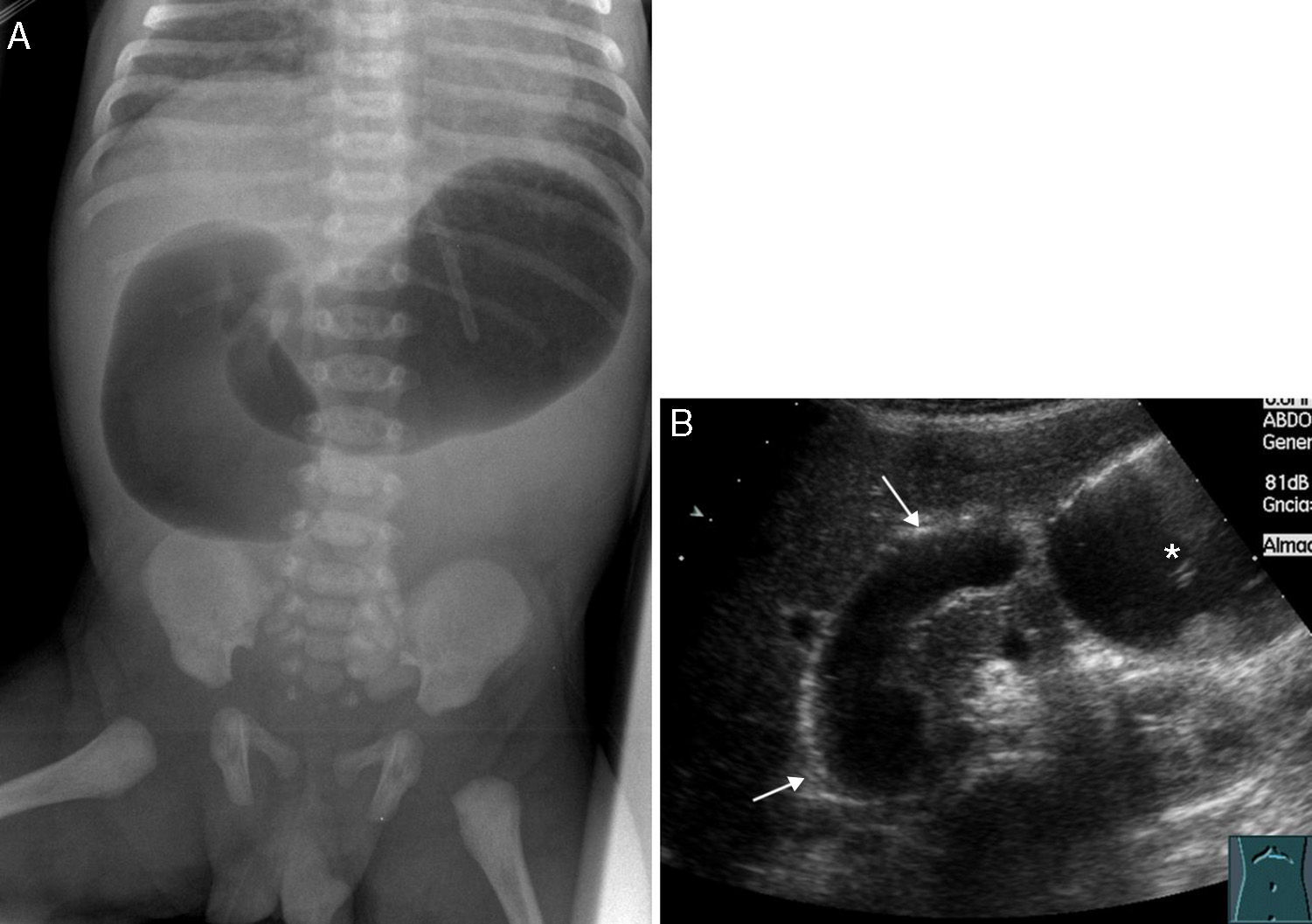
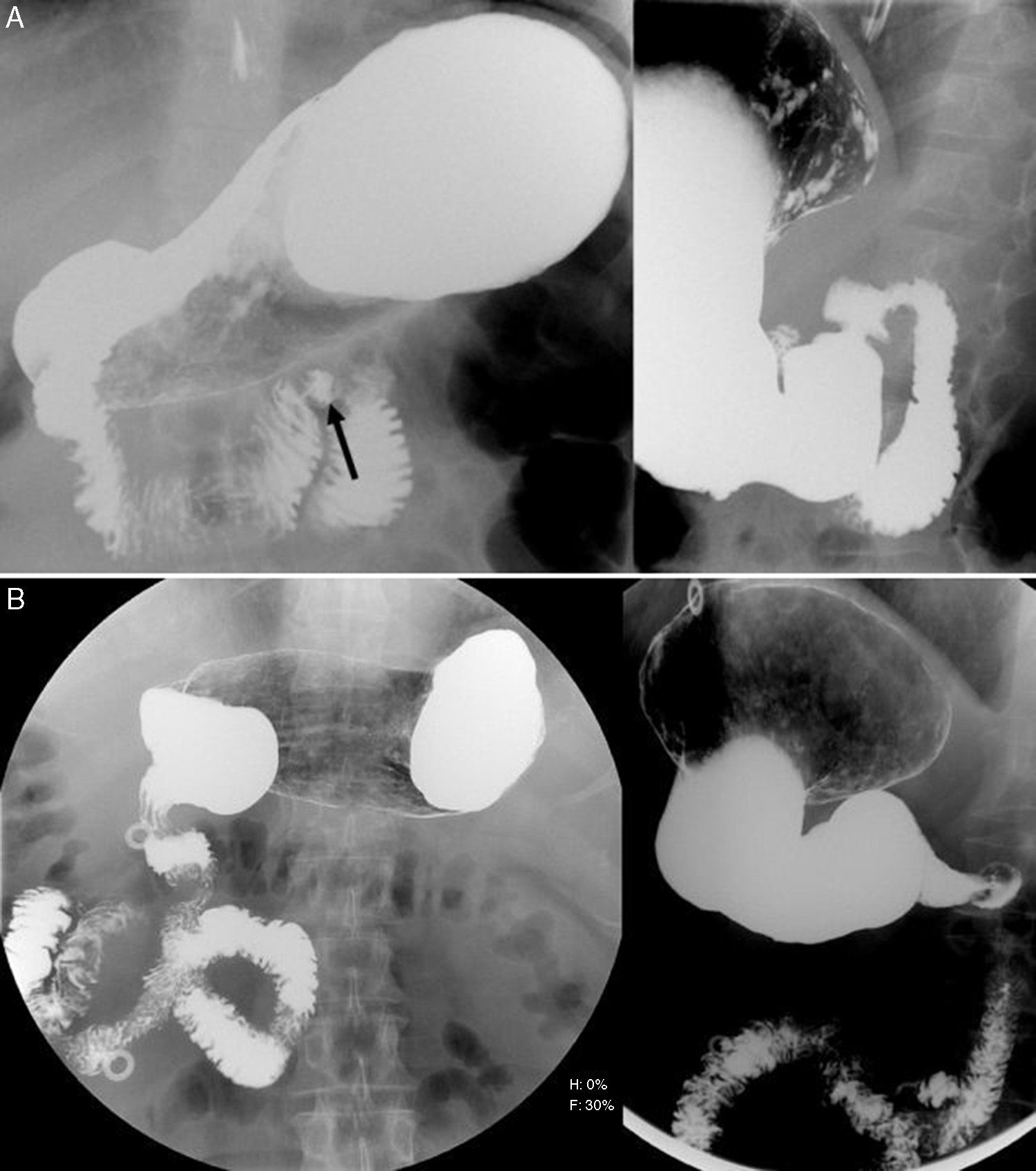
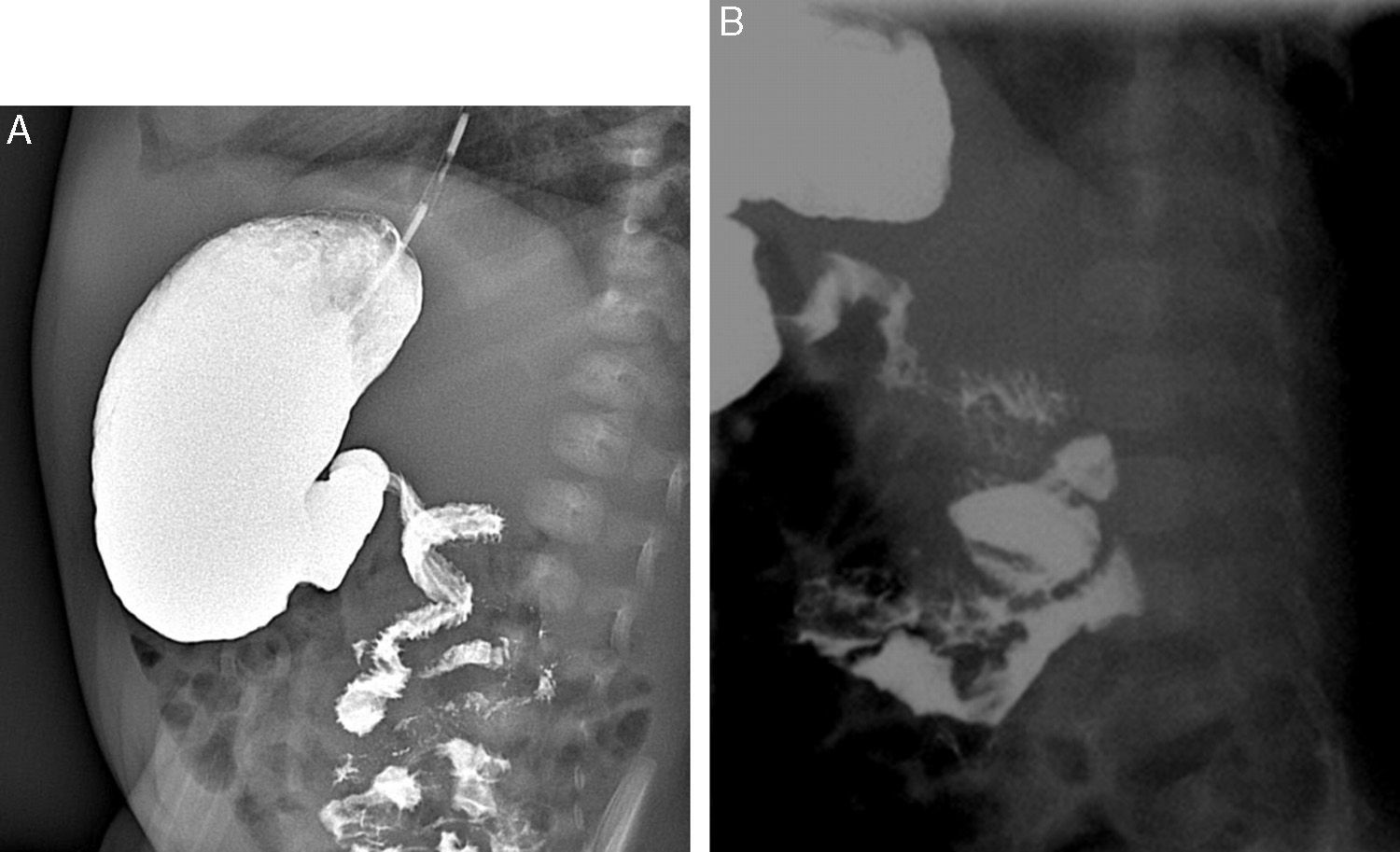
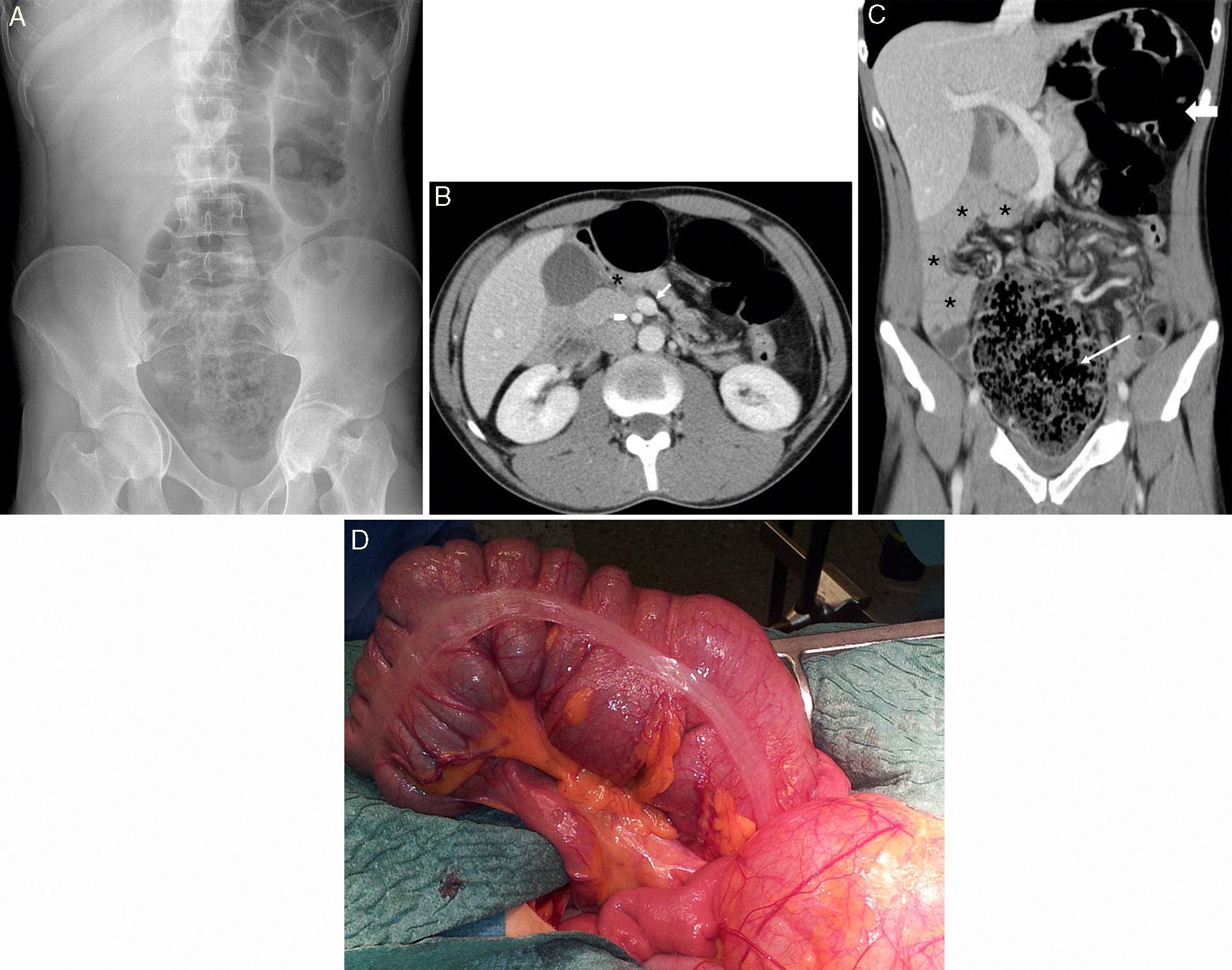
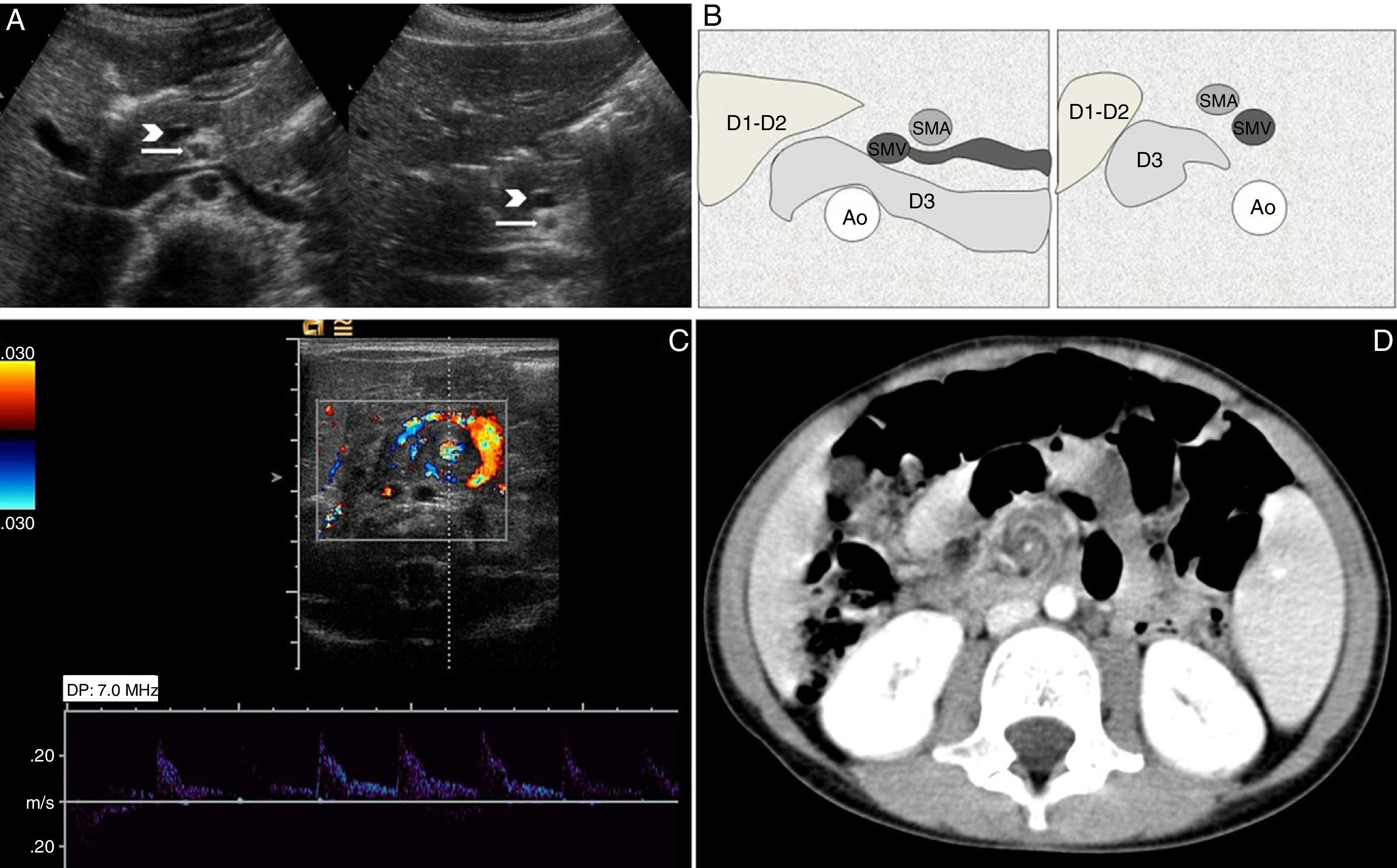
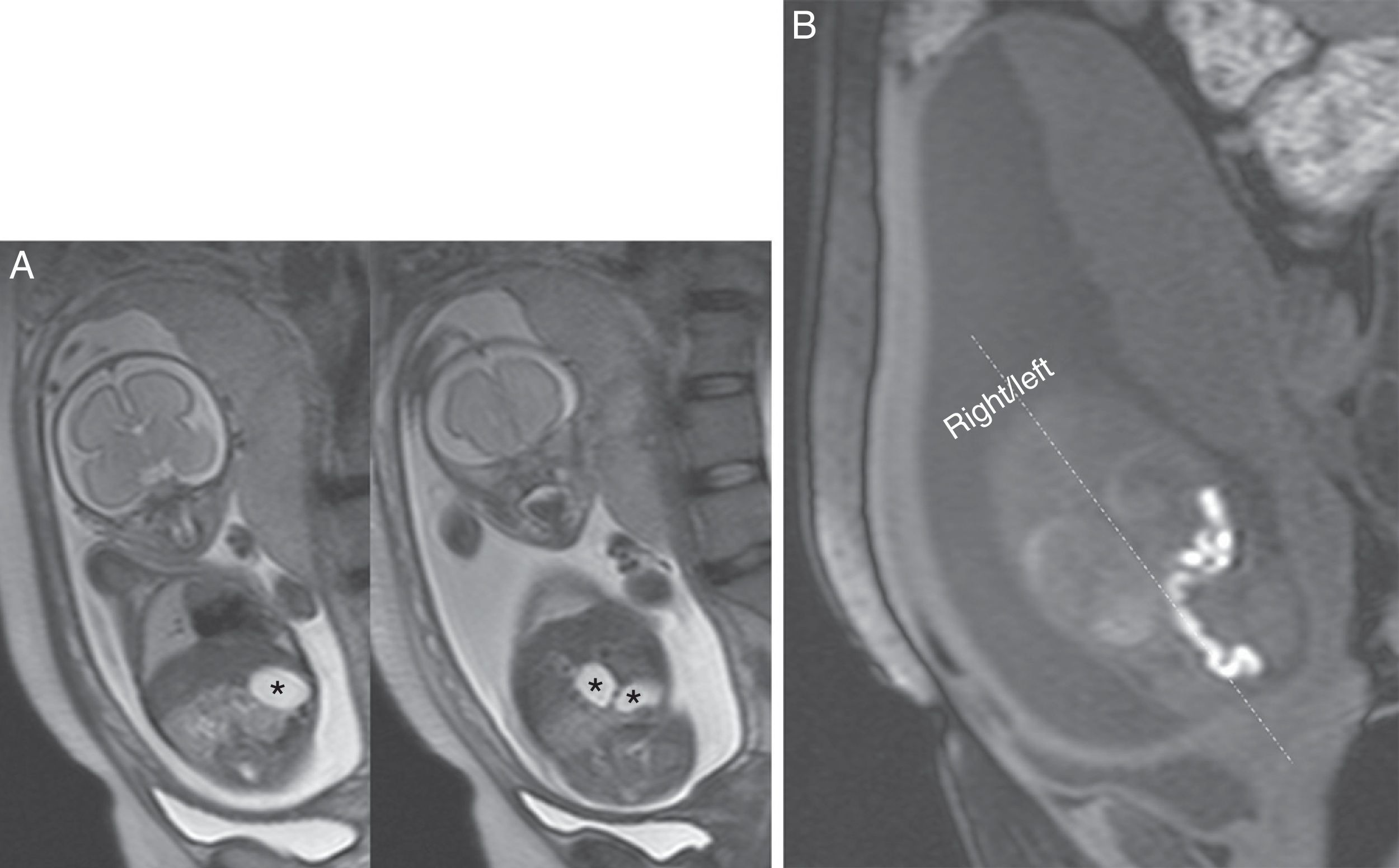
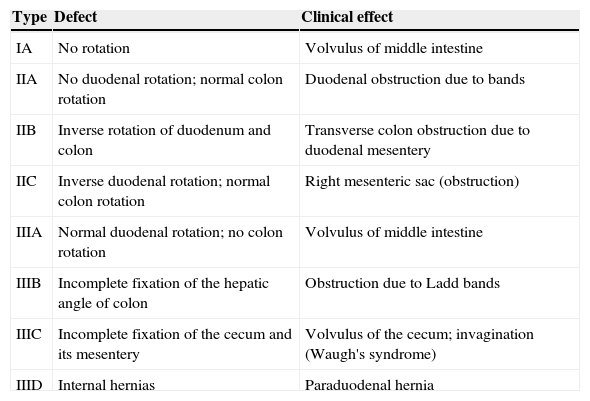
Radiologists must be able to recognize the imaging signs of intestinal malrotation because this condition can lead to potentially lethal complications such as midgut volvulus. The correct diagnosis depends on both high clinical suspicion and the radiologist's ability to recognize the specific signs of malrotation and the normal variants that can lead to the wrong diagnosis. Although the location of the third portion of the duodenum outside the retroperitoneal area on ultrasonography, CT, or MRI seems to be a reliable sign of malrotation, the gold standard for determining whether the duodenojejunal flexure is in an abnormal location continues to be the upper gastrointestinal series. In this article, we review the most important imaging signs of malrotation and emphasize the role of ultrasonography in diagnosing midgut volvulus.
El radiólogo debe ser capaz de reconocer los signos de la malrotación intestinal en la imagen al tratarse de una entidad patológica con complicaciones potencialmente letales, como el vólvulo de intestino medio. Para diagnosticarla correctamente, es tan importante que exista un índice de sospecha clínica elevado como que el radiólogo sepa reconocer los signos específicos de malrotación y las variantes de la normalidad que pueden conducir a un diagnóstico erróneo. Aunque la posición no retroperitoneal de la tercera porción duodenal en ecografía, TC o RM parece ser un signo fiable para el diagnóstico, el tránsito gastrointestinal continúa siendo el estándar de referencia para ver la unión duodeno-yeyunal en una posición anómala. Nuestro objetivo es revisar los principales signos radiológicos de esta enfermedad y hacer hincapié en el papel de la ecografía para diagnosticar el vólvulo de intestino medio.