To evaluate the orbital structures and to establish correlations with disease activity and severity in patients with Graves’ hyperthyroidism and orbitopathy (GO) using short-tau inversion-recovery (STIR) sequence magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
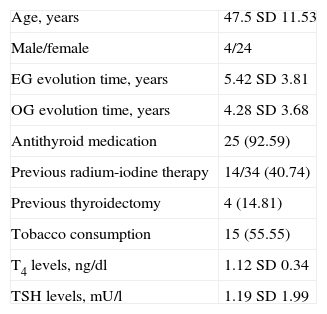
MethodsObservational, cross-sectional, case-control study. Twenty-eight patients with euthyroid status after treatment and GO (GO group) and 15 control subjects (control group) were included. Patients underwent a complete ophthalmologic examination and were then assessed according to the EUGOGO (European Group on Graves’ Orbitopathy) recommendations. Muscle cross-sectional areas, orbital tissue volumes and the signal intensity ratio (SIR) from the most inflamed extraocular muscle were calculated using a STIR-T2 weighted sequence MRI. Correlations between clinical and MRI measurements were analyzed.
ResultsEnlargements in the cross-sectional areas and volumes were significant for most EOMs (p<0.001), but not for the lateral rectus muscle cross-sectional area. A significant difference in SIR values between patients with GO and control subjects (p<0.001) was found. No significant correlations were found between muscle cross-sectional areas, orbital tissue volumes, SIR values and the clinical activity parameters.
ConclusionsGiven the small sample size of our study, with the obvious need for larger clinical trials, we were unable to demonstrate that the STIR sequences in MRI are a sensitive tool in assessing patients with longstanding GO in order to detect inflammatory changes and activity follow-up, possibly because it is in inactive phase. Meanwhile, it is still necessary to continue performing a thorough clinical evaluation in the therapeutic management of GO.
Evaluar las estructuras orbitarias mediante secuencias short-tau inversion-recovery (STIR) en resonancia nuclear magnética (RNM) y establecer correlaciones con los signos de actividad clínica (CAS) y severidad en pacientes con hipertiroidismo y orbitopatía Graves (OG).
MétodosEstudio clínico de casos y controles, observacional y transversal. Veintiocho pacientes en estatus eutiroideo postratamiento y OG (grupo OG) y 15 sujetos controles (grupo control) fueron evaluados. Se realizó una exploración oftalmológica completa a los participantes y se determinó la actividad y severidad de la OG, según recomendaciones EUGOGO (Grupo Europeo en Orbitopatía Graves). Áreas de sección transversal de los músculos extraoculares (MOE), volúmenes de los tejidos orbitarios y ratios (SIR) de intensidad de señal del MOE más inflamado fueron calculados usando secuencias STIR-T2 en RNM. Se establecieron correlaciones entre variables.
ResultadosLos incrementos en las áreas de sección transversal y volúmenes fueron significativos en la mayoría de los MOE (p<0,001), pero no en el área de sección transversal del recto lateral. Se encontraron diferencias significativas en valores SIR entre ambos grupos (p<0,001). No se establecieron correlaciones significativas entre el área total de sección transversal de los MOE, volúmenes de los tejidos orbitarios, valores SIR y signos de actividad clínica.
ConclusionesDado el tamaño muestral del estudio, con la necesidad obvia de estudios más amplios, no podemos demostrar que las secuencias STIR en RNM sean una herramienta sensible para evaluar cambios inflamatorios y actividad clínica en la OG de larga evolución, posiblemente debido a que se halle en fase inactiva.