Optical coherence tomography (OCT) allows the measurement of the peripapillary optic nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness. The effect of ocular axial length (AL) on RNFL thickness measurement may be relevant in the interpretation of OCT results in diagnosing optic nerve diseases.
PurposeTo assess the influence of ocular AL on RNFL thickness and on optic disc topographic parameters (optic disc area, rim area and cup volume) measured by OCT, in healthy individuals.
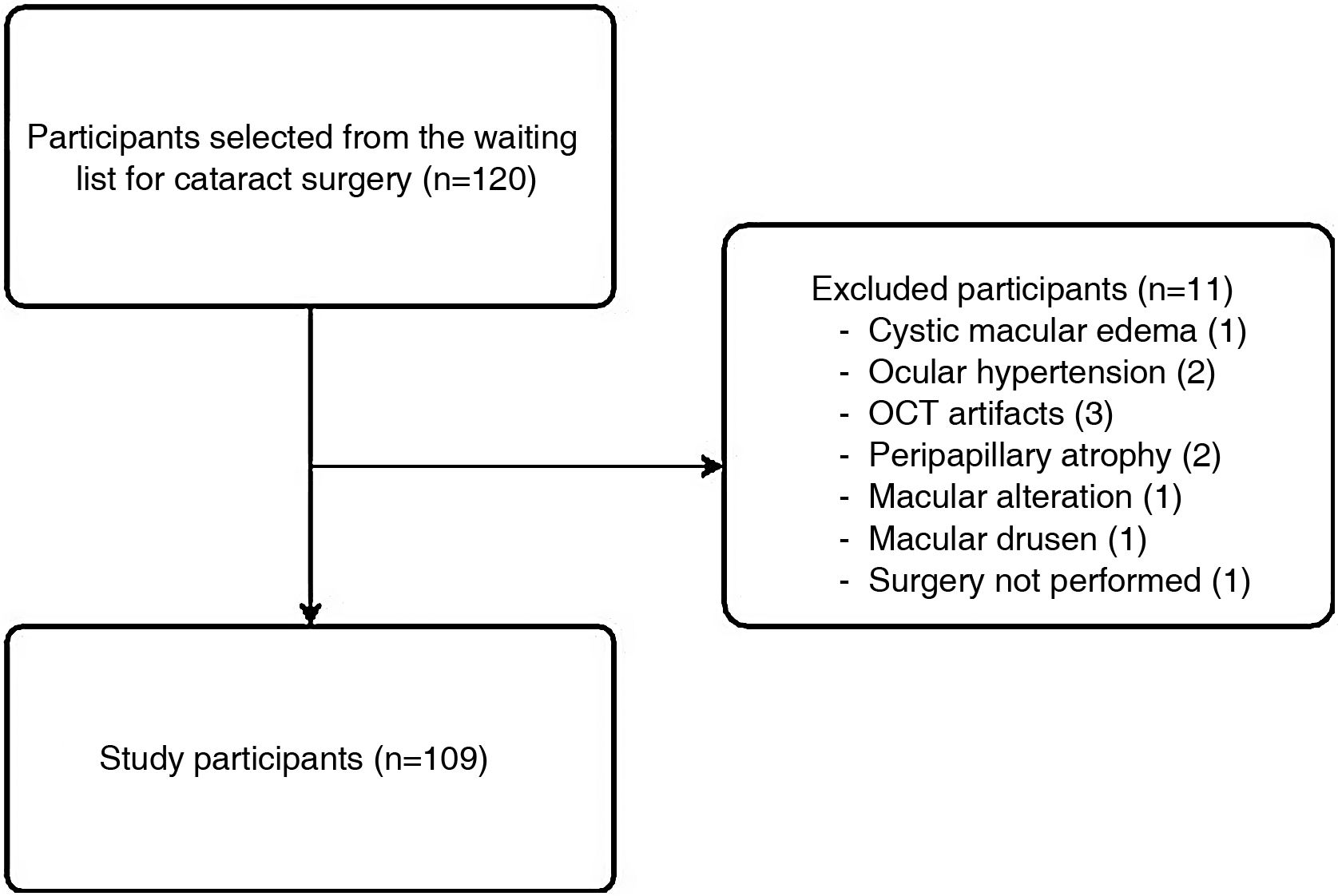
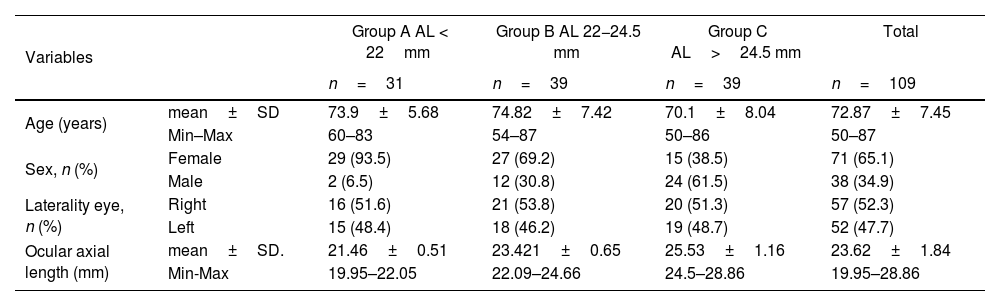
MethodsA sample of 109 healthy eyes classified into 3 groups according to AL (A: AL<22mm; B: AL 22−24.5mm; C: AL>24.5mm) was studied. RNFL thickness and optic disc topographic parameters were measured using Swept-Source OCT Triton (Topcon) and were compared between groups using a variance analysis. Correlation between the AL and the study variables was performed using a Pearson's correlation coefficient test.
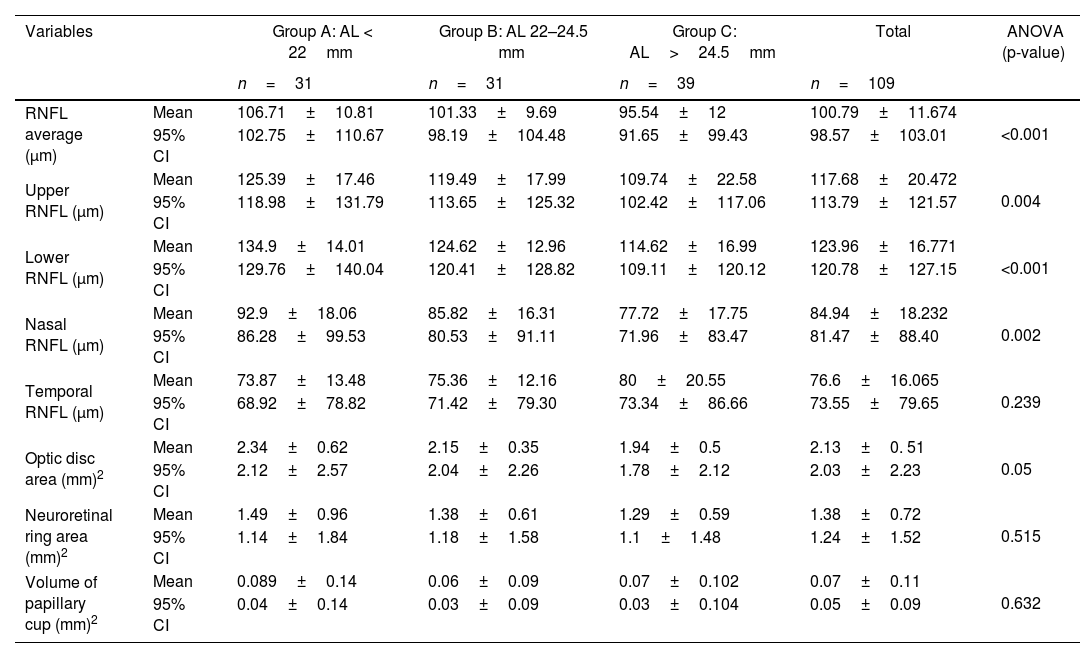
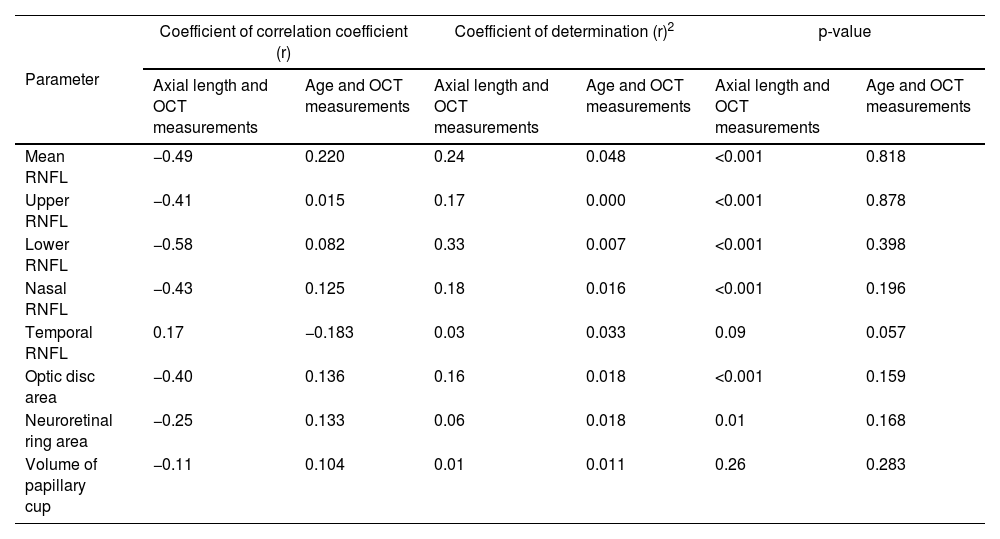
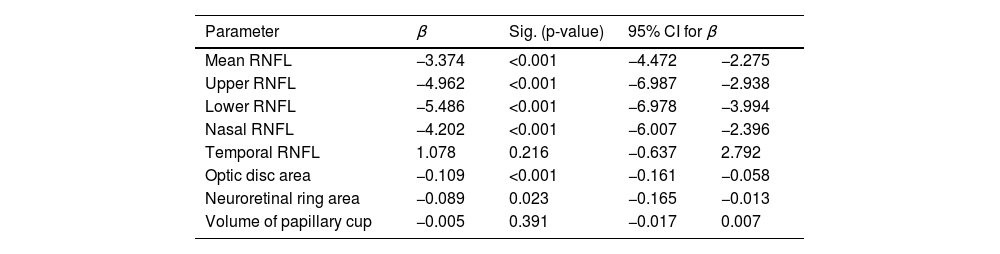
ResultsThe RNFL thickness was lower in eyes with higher AL in the superior (r=−0.41; p<0.001), inferior (r=0.58; p<0.001) and nasal (r=−0.43; p<0.001) quadrants, in the mean value of the RNFL (r=−0.49; p<0.001), optic disc area (r=−0.40; p<0.001) and rim area (r=−0.25; p=0.01).
ConclusionsAL is negatively correlated with RNFL thickness and optic disc topographic parameters measured by Swept-Source OCT Triton (Topcon).
La tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT) permite la medición del grosor de la capa de fibras del nervio óptico (CFNR) peripapilar. El efecto de la longitud axial ocular (LA) sobre el grosor de la CFNR puede ser relevante en la interpretación de los resultados de OCT en el diagnóstico de enfermedades del nervio óptico.
ObjetivosEvaluar la influencia de la longitud axial ocular en el grosor de la CFNR y en los parámetros topográficos del disco óptico (área del disco óptico, área del anillo neurorretiniano y volumen de la excavación papilar) medidos por OCT, en individuos sanos.
MétodoSe estudió una muestra de 109 ojos sanos clasificados en 3 grupos según la LA (A:LA<22mm; B:LA 22-24,5mm; C:LA>24,5mm). La medición del grosor de la CFNR y de los parámetros topográficos del disco óptico se realizó mediante Swept-Source OCT Triton (Topcon), y se compararon entre grupos mediante análisis de la varianza. La correlación entre la longitud axial y las variables de estudio se realizó mediante correlación de Pearson.
ResultadosEl grosor de la CFNR fue menor en ojos con longitud axial más alta en el cuadrante superior (r=-0,41; p<0,001)), inferior (r=-0,58; p<0,001) y nasal (r=-0,43; p<0,001), en el valor medio de la CFNR (r=-0,49; p<0,001), área del disco óptico (r=- 0,40;p<0,001) y área del anillo neurorretiniano (r=-0,25; p=0,01).
ConclusiónLa longitud axial se correlaciona negativamente con el grosor de la CFNR y los parámetros topográficos del disco óptico medidos mediante SS OCT Triton (Topcon).