To study the use of optical coherence tomography (OCT), for measuring the macular thickness variations produced over time in elderly pseudophakic subjects implanted with a clear intraocular lens (IOL) in one eye, and a yellow IOL in the other eye.
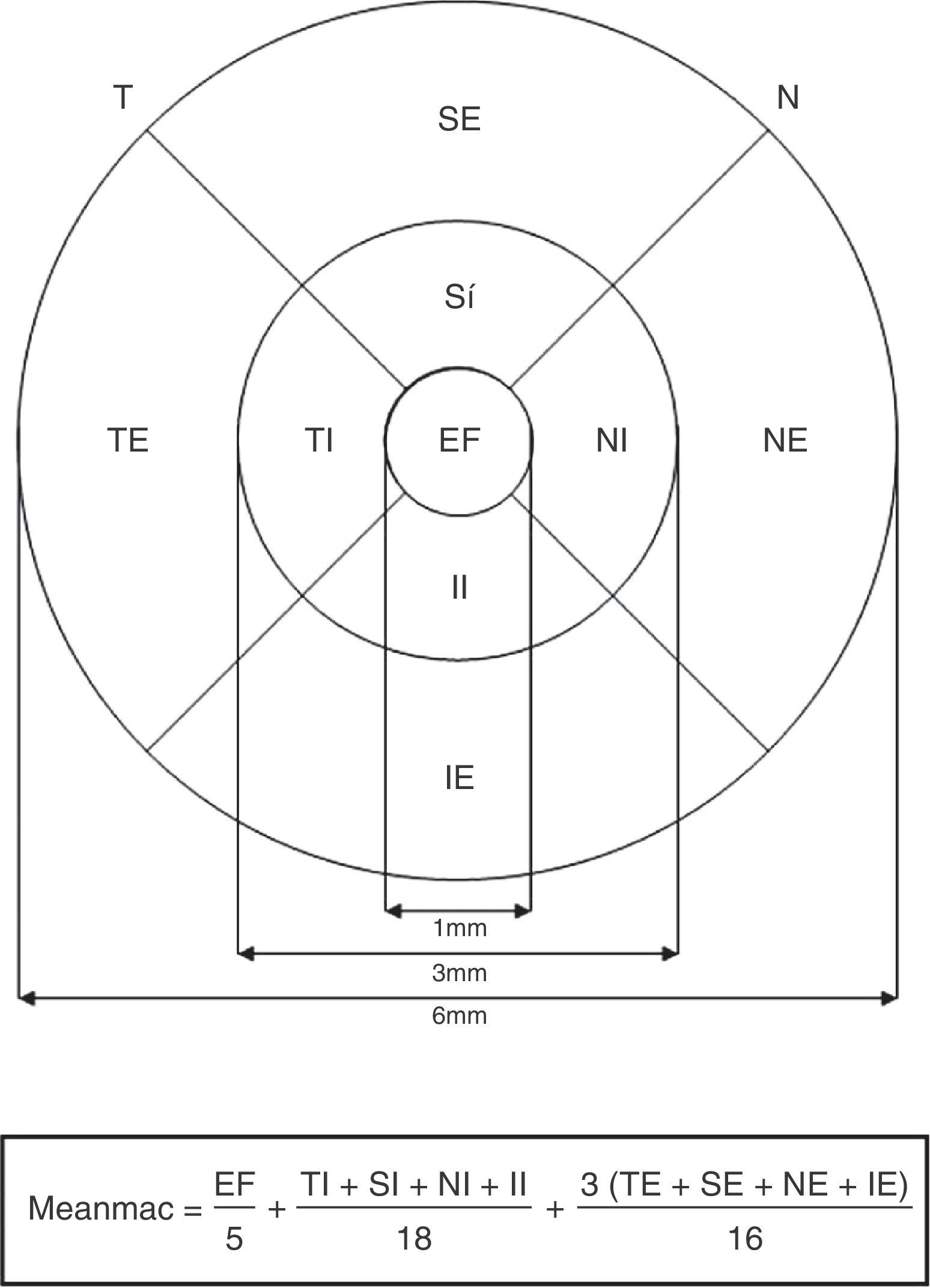
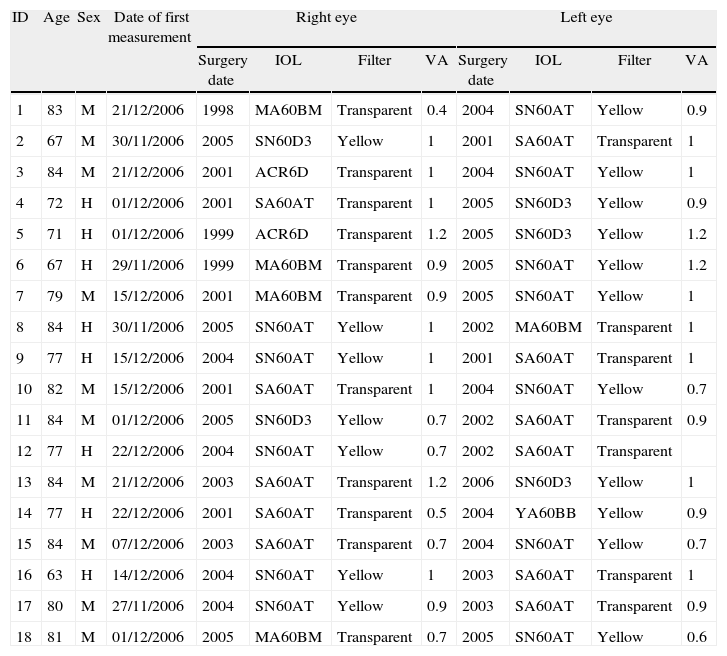
MethodsMacular thickness measurements were obtained in the 36 eyes of 18 subjects over 65 years, with cataracts surgically removed from both eyes and implanted with different absorbance (clear and yellow) IOLs in two separate surgeries. Stratus-OCT was used to determine the macular thickness in two sessions with 5 years of difference.
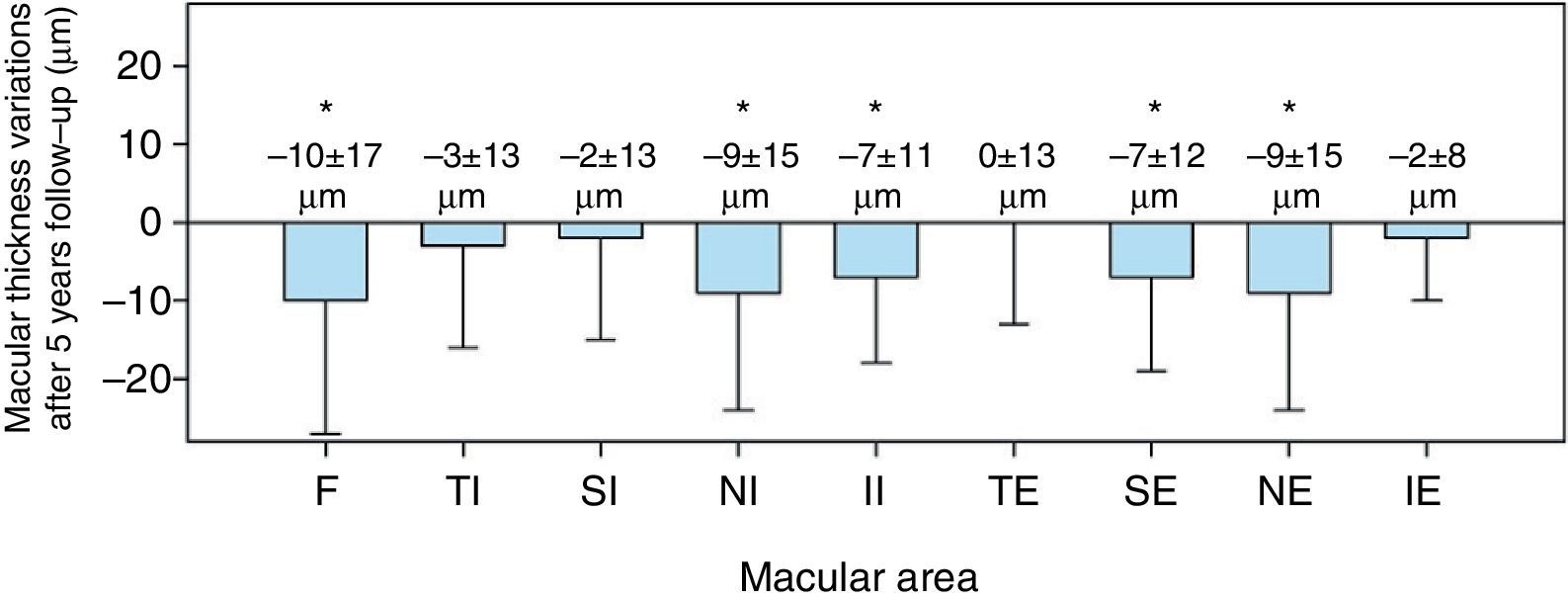
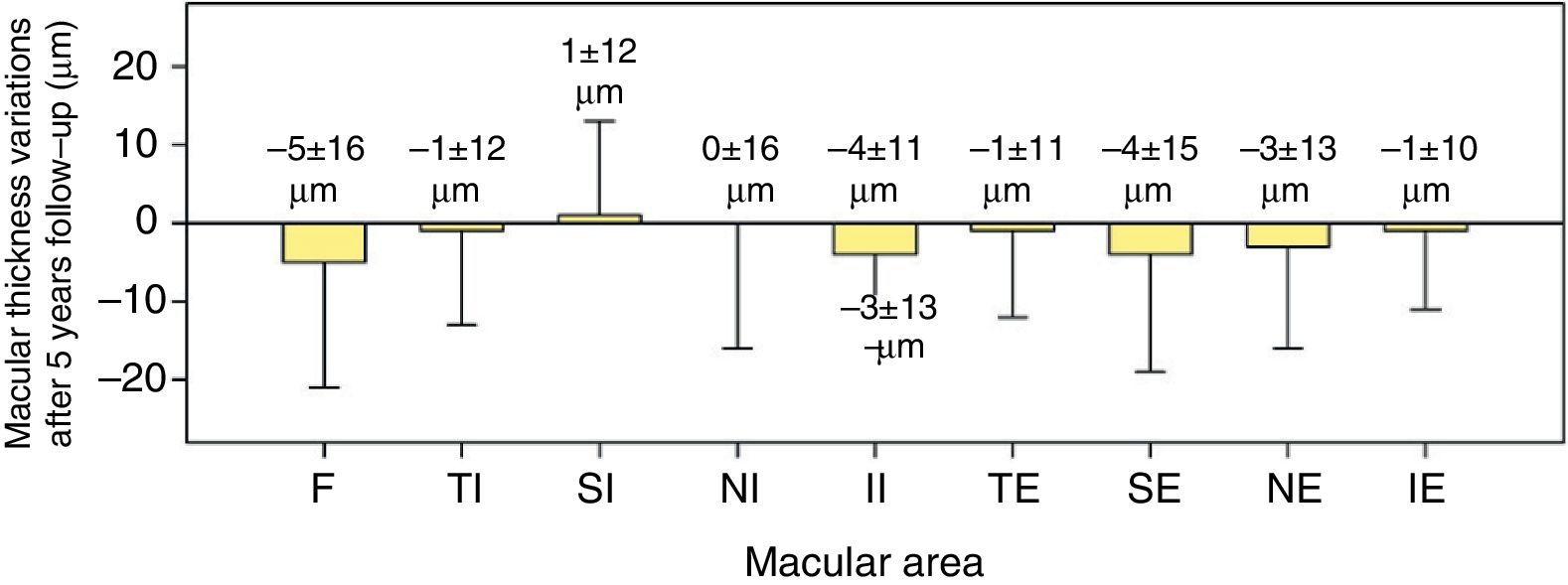
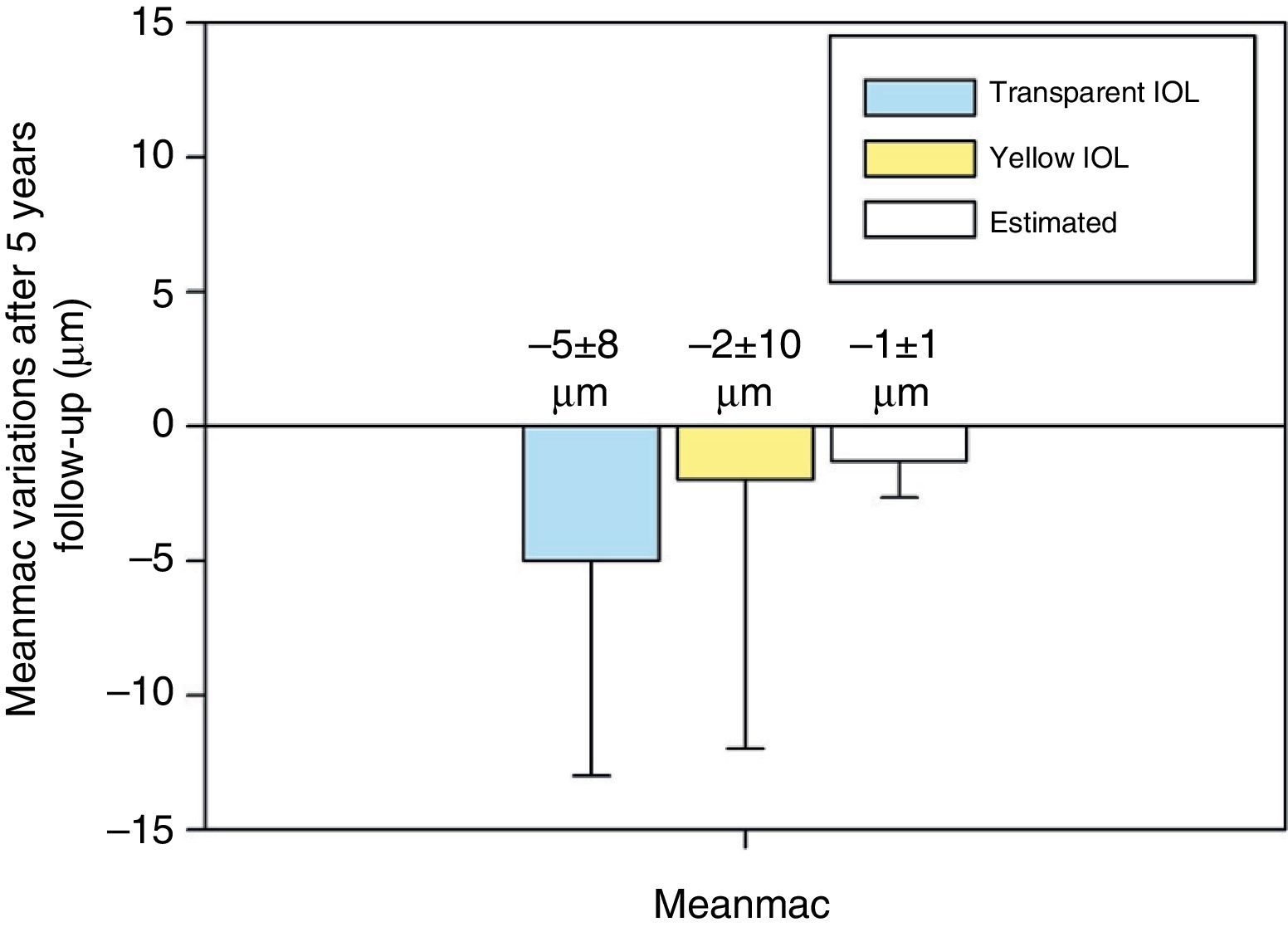
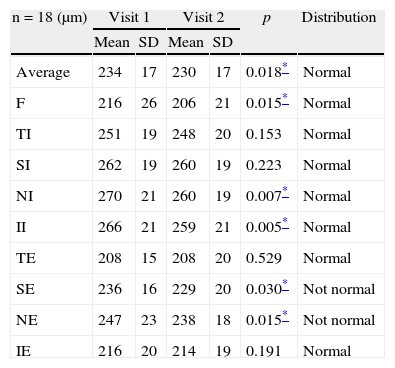
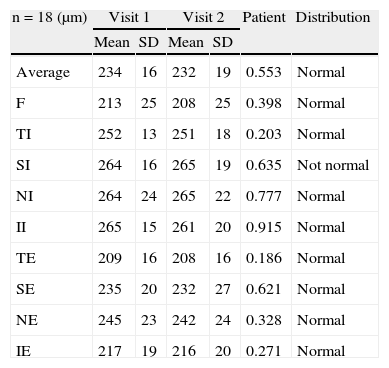
ResultsAfter 5 years of follow-up, the eyes implanted with clear IOLs revealed a significant decrease in macular thickness. However, in eyes implanted with yellow IOLs the macular thickness remained stable. The mean overall decrease in macular thickness in eyes implanted with clear IOLs was 5±8μm (p=0.02), and foveal thickness reduction was 10±17μm (p=0.02).
ConclusionsThe macular thickness changes produced in eyes implanted with a yellow IOL differ from those with a clear IOL. These observations point to a possible protective effect of yellow IOL against the harmful effects of light in elderly pseudophakic subjects. However, studies with a longer follow-up are still needed to confirm that the protection provided by this IOL model is clinically significant.
Evaluar mediante tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT) las variaciones de espesor macular producidas a lo largo del tiempo en ojos pseudoafáquicos implantados con una lente intraocular (LIO) transparente en comparación con sus respectivos ojos contralarerales implantados con LIO amarilla.
MétodosEl espesor macular de 36 ojos de 18 sujetos fue evaluado mediante OCT. Los sujetos presentaban edades superiores a 65 años y habían sido intervenidos de cataratas en ambos ojos en 2 cirugías independientes. La principal característica de los individuos es que llevaban implantada una LIO con diferente absorción en cada ojo: transparente (absorbente de la radiación ultravioleta) y amarilla (con filtro adicional absorbente de las radiaciones violeta-azul del espectro visible). El espesor macular se evaluó en 2 sesiones separadas en el tiempo por un intervalo de tiempo de 5 años, mediante el sistema Stratus-OCT (protocolo fast macular thickness). Se analizaron estadísticamente las diferencias en la evolución del espesor macular entre ojos con diferente tipo de LIO.
ResultadosTras 5 años de seguimiento, se observó que los ojos implantados con LIO transparente manifestaban una reducción del espesor macular estadísticamente significativa, superior a la esperada por el aumento de la edad. Sin embargo, los ojos implantados con LIOs amarillas mantuvieron su espesor macular estable. La disminución del espesor macular promedio en ojos implantados con LIO transparente fue de 5±8μm (p=0,02) y la reducción del espesor foveal fue de 10±17μm (p=0,02).
ConclusionesLos cambios de espesor macular producidos en ojos implantados con una LIO amarilla difieren de los cambios manifestados en ojos con LIO transparente. Estas observaciones apuntan a un posible efecto protector de las LIOs amarillas contra los efectos dañinos de la luz en sujetos pseudoafáquicos. Sin embargo, estudios con un mayor tamaño muestral y mayor tiempo de seguimiento son necesarios para confirmar que la protección inducida por este tipo de LIO es clínicamente significativa.