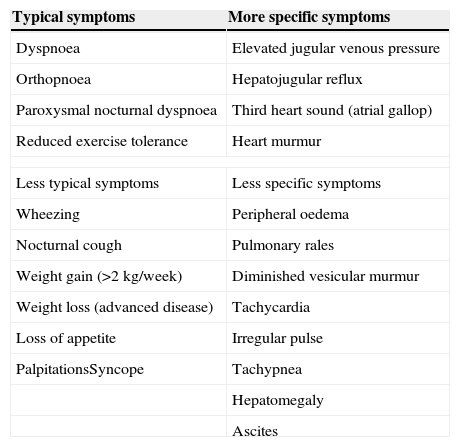
Table 2. Symptomatology of heart failure.
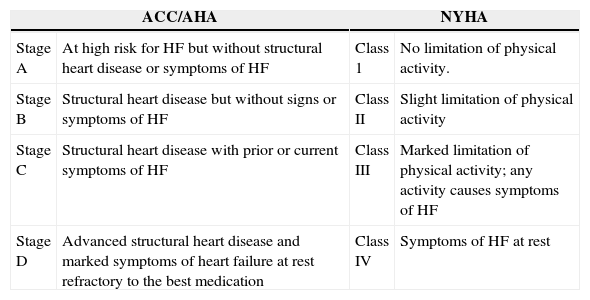
Table 3. Functional classification according to the American College of Cardiology/American heart Association (ACC/AHA) and of the New York Heart Association (NYHA) based on severity of symptoms and exercise.
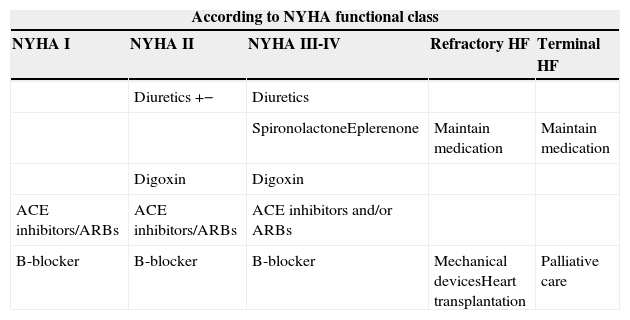
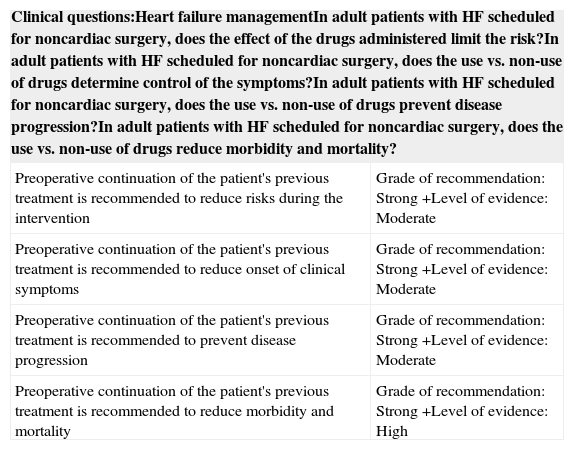
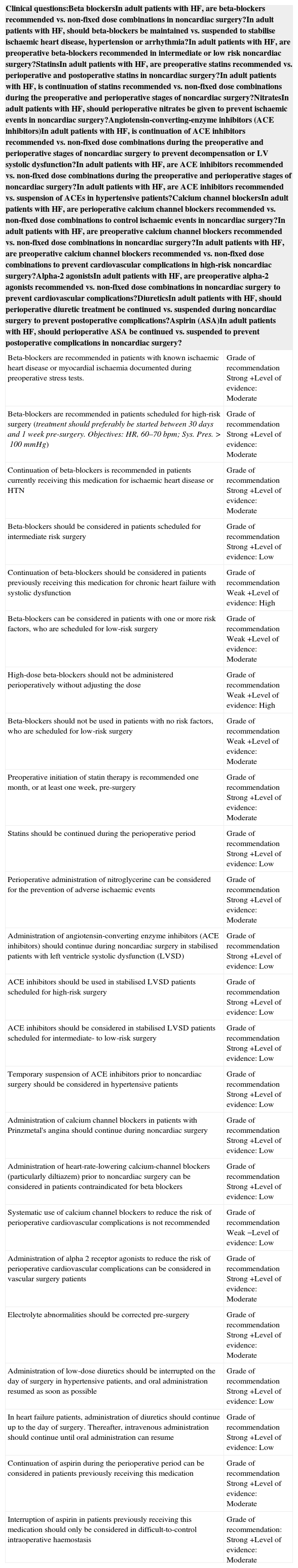
Table 4. Pharmacological therapy indicated in the treatment of heart failure.
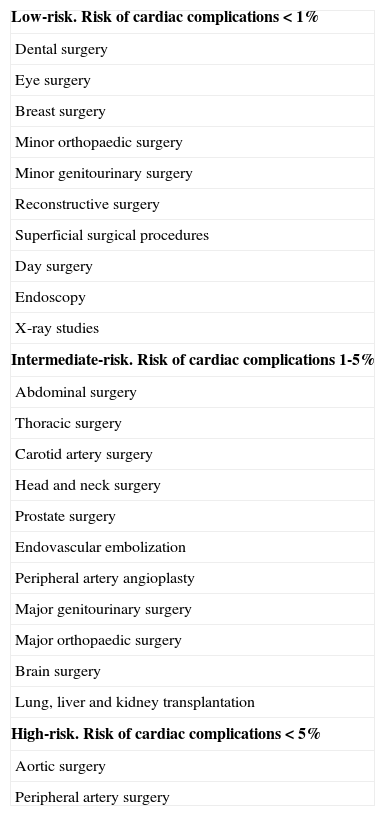
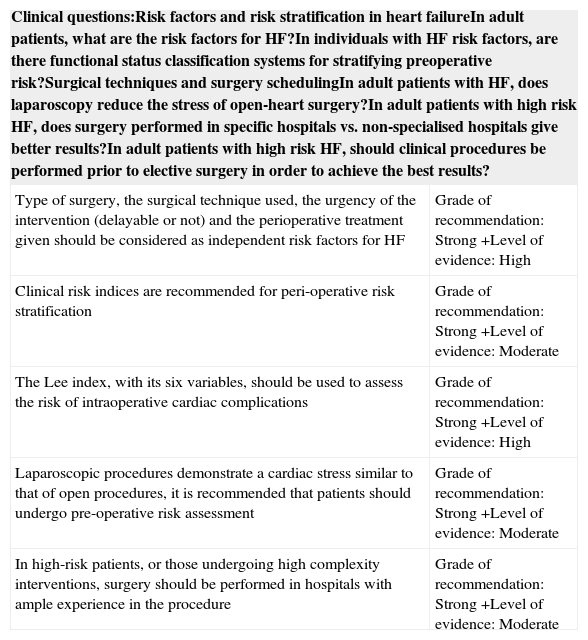
Table 5. Surgical risk in CHF patients based on the type of surgery.
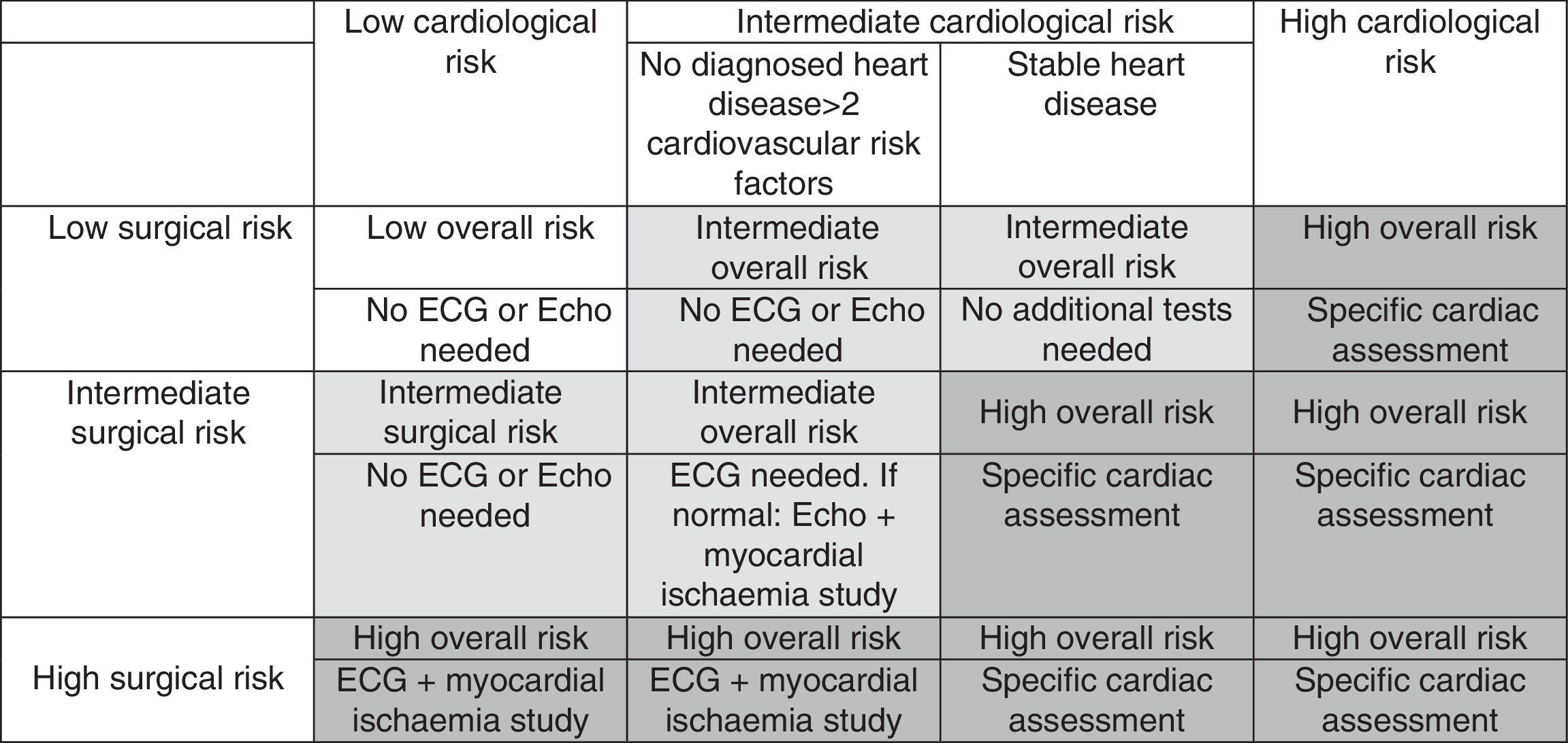
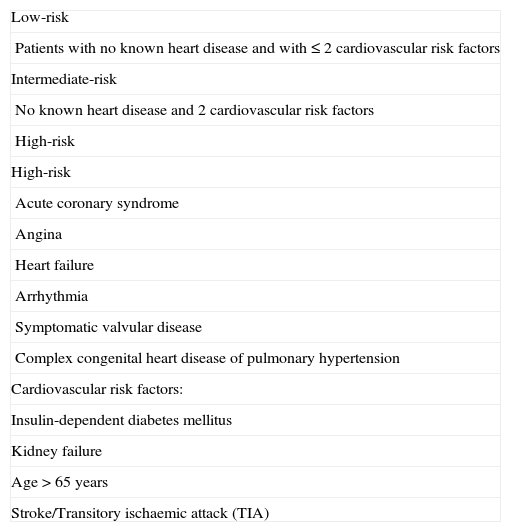
Table 6. Surgical risk based preoperative cardiac status.
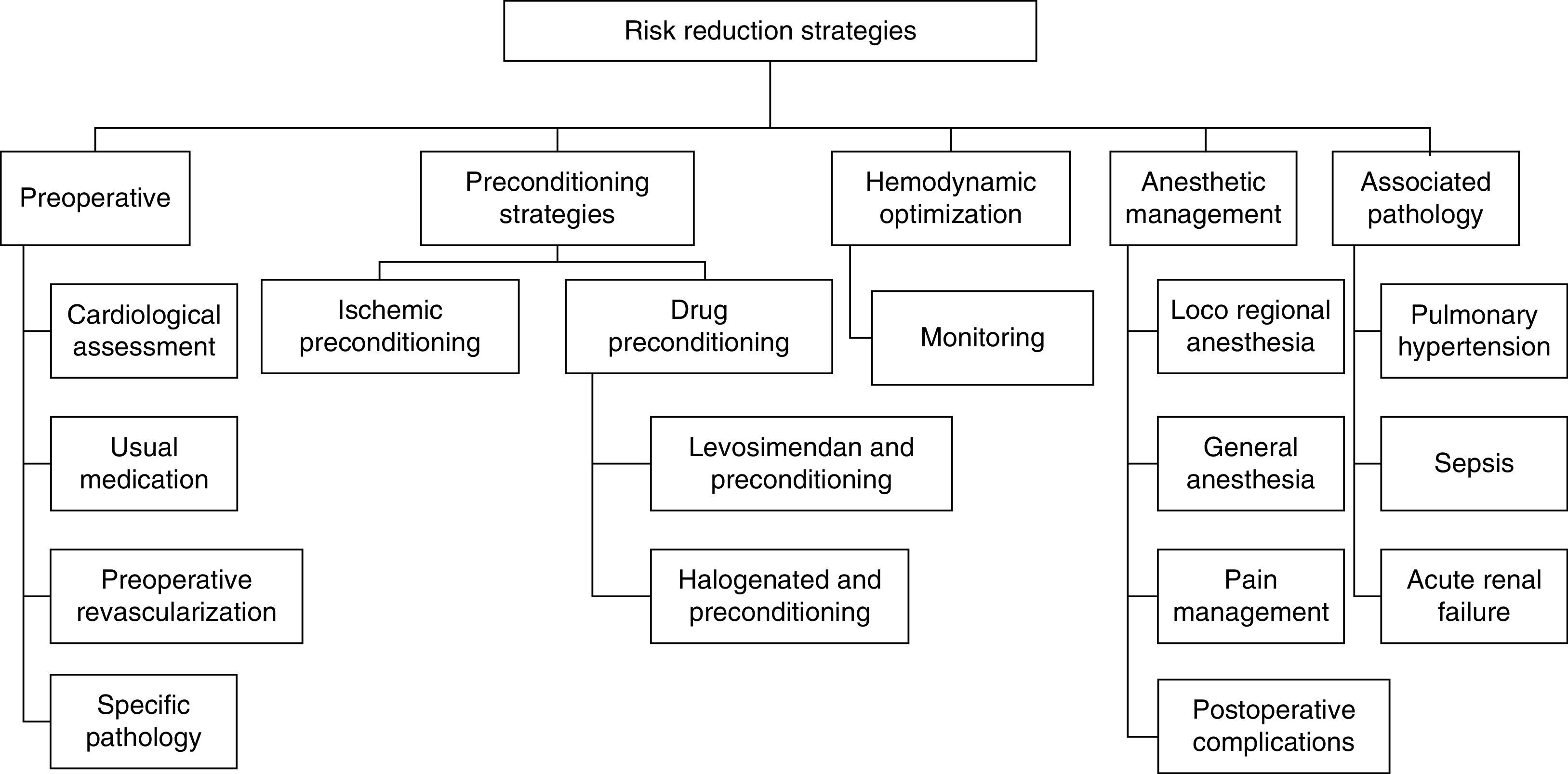
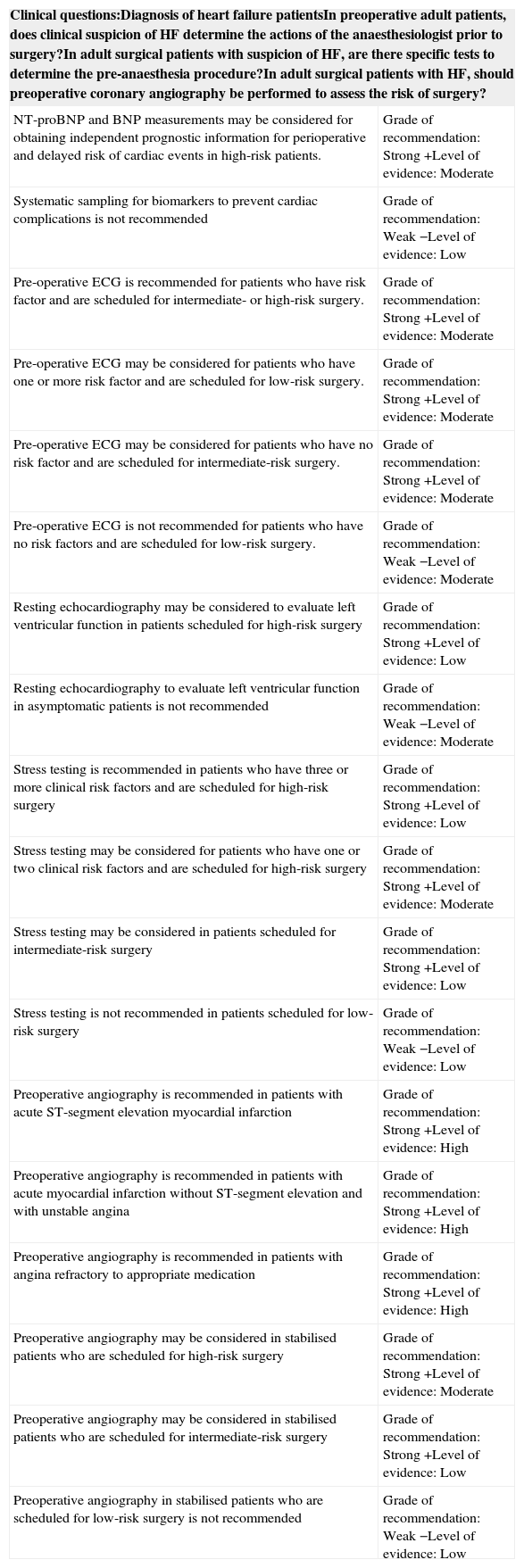
Table 7. Cardiological situation in which the patients must be evaluated using specific cardiological protocols.
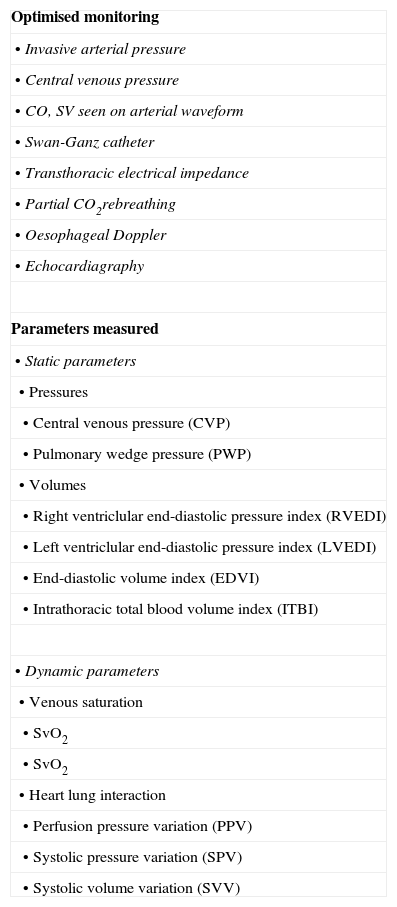
Table 8. Recommended monitoring in patients undergoing preoperative haemodynamic optimisation with inotropic drugs such as levosimendan.
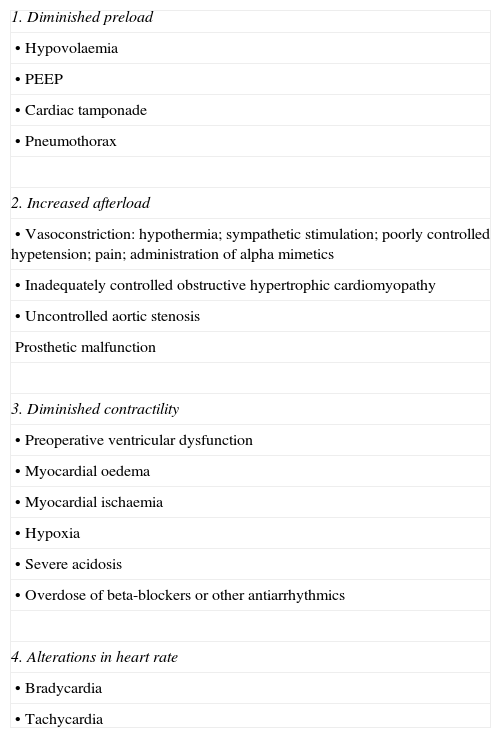
Table 9. Most common causes of postoperative low output.
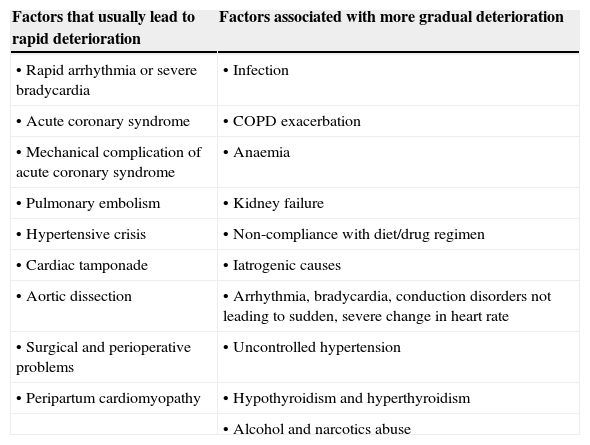
Table 10. Trigger factors for acute heart failure (AHF).
Table 11. Therapeutic goals in acute postoperative heart failure.
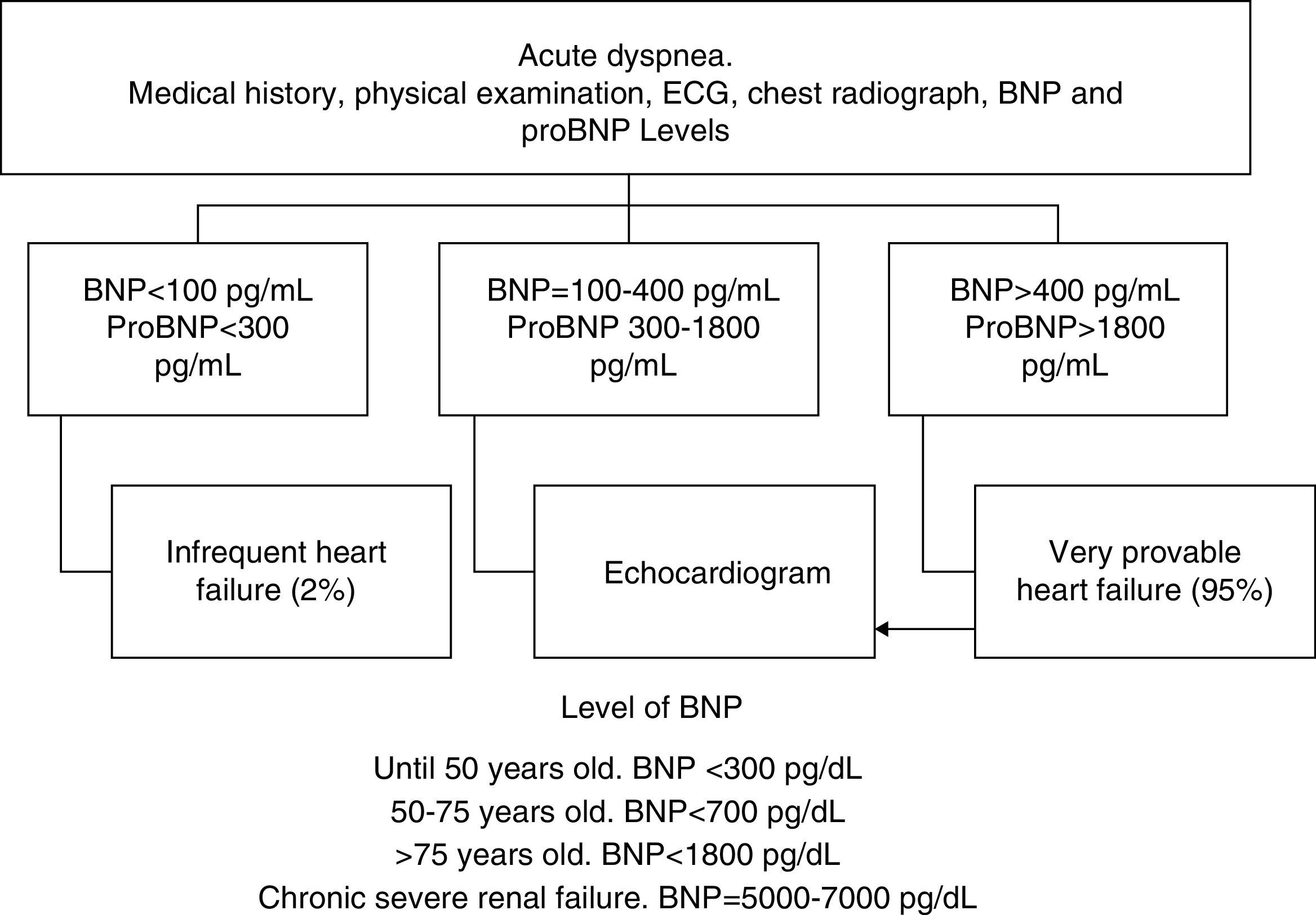
Table 12. Differential diagnosis of postoperative dyspnoea.
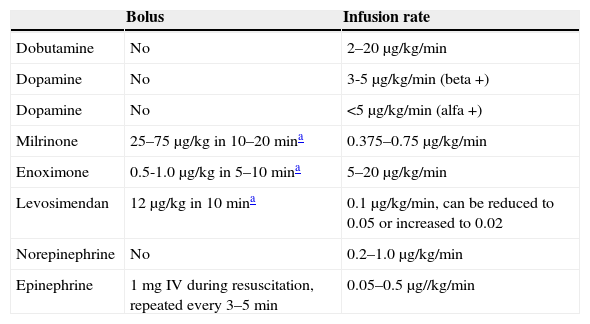
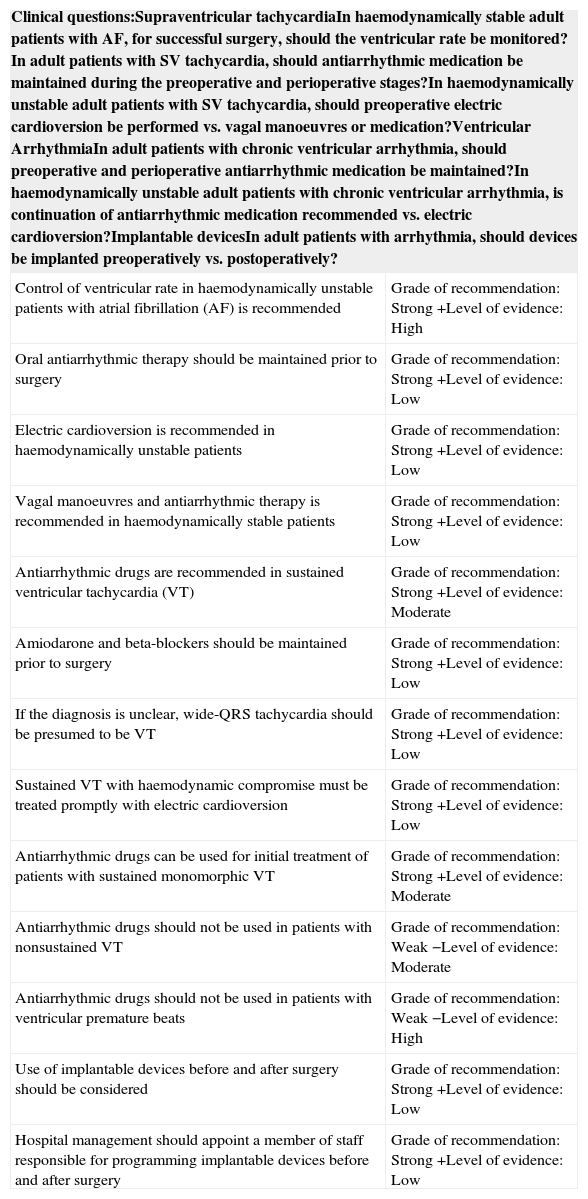
Table 13. Positive inotropic or vasopressor drugs, or both, used to treat acute HF.
Table 14. Diagnosis of cardiogenic shock.
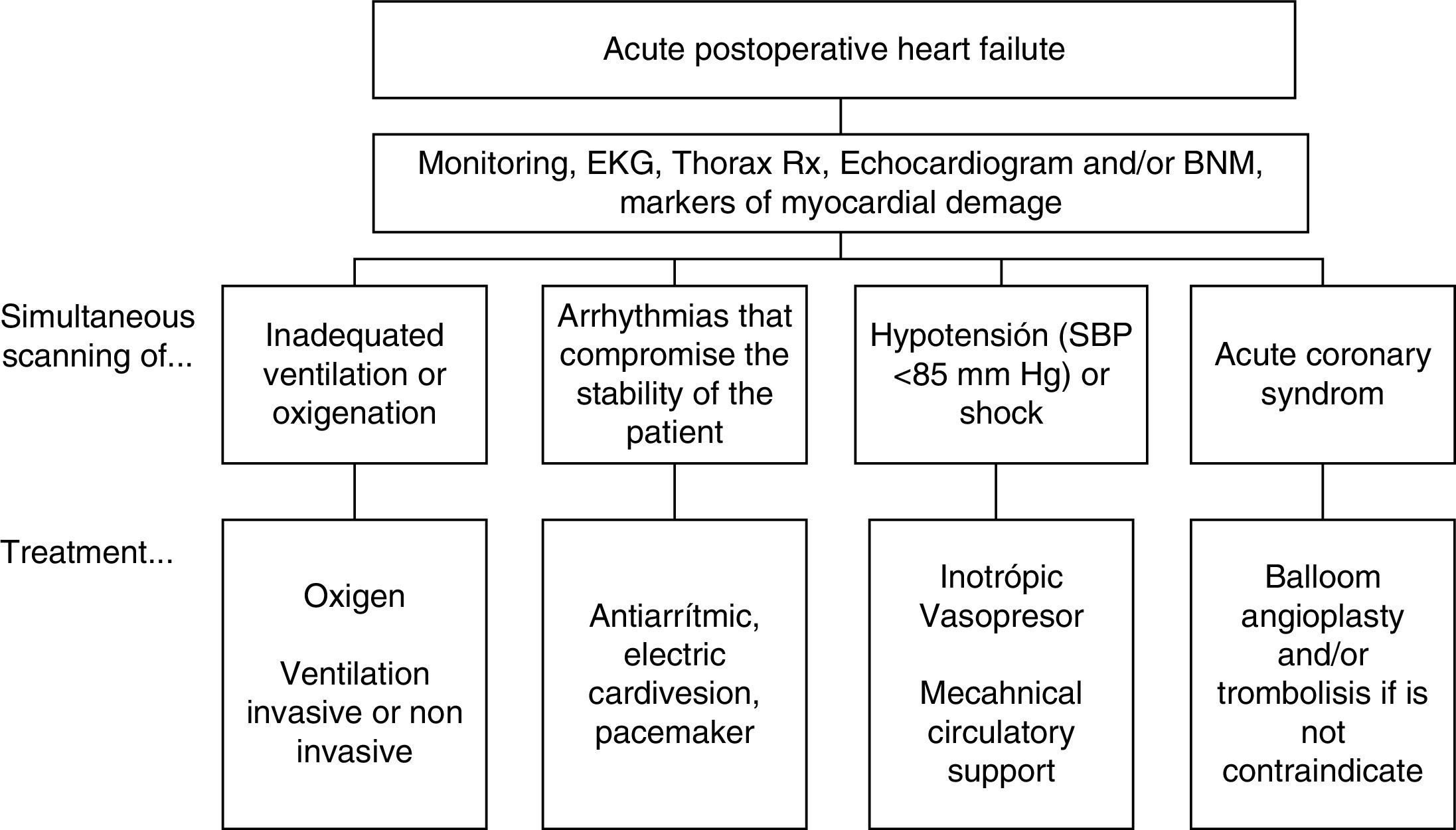
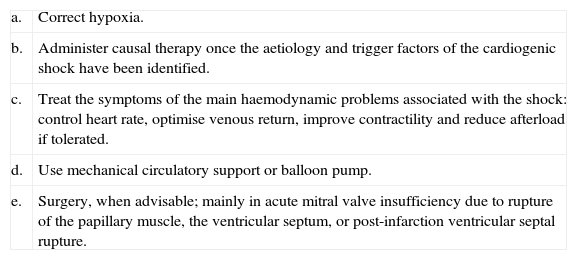
Table 15. Basic therapeutic manoeuvres in left ventricle failure.
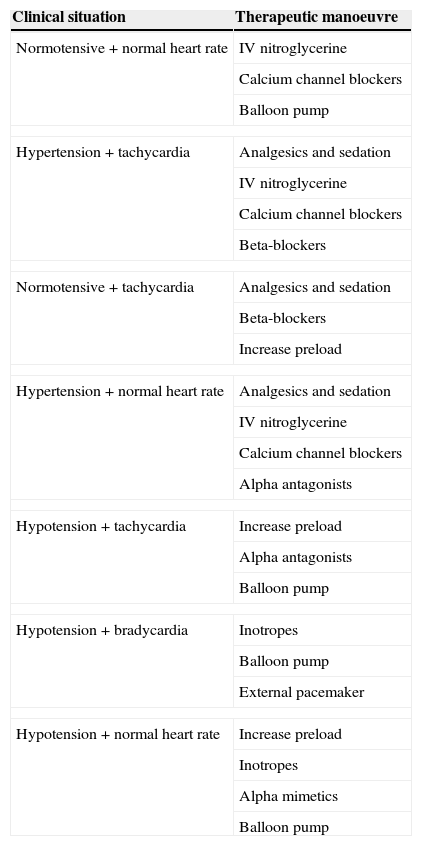
Table 16. Basic therapeutic manoeuvres in postoperative myocardial ischaemia.
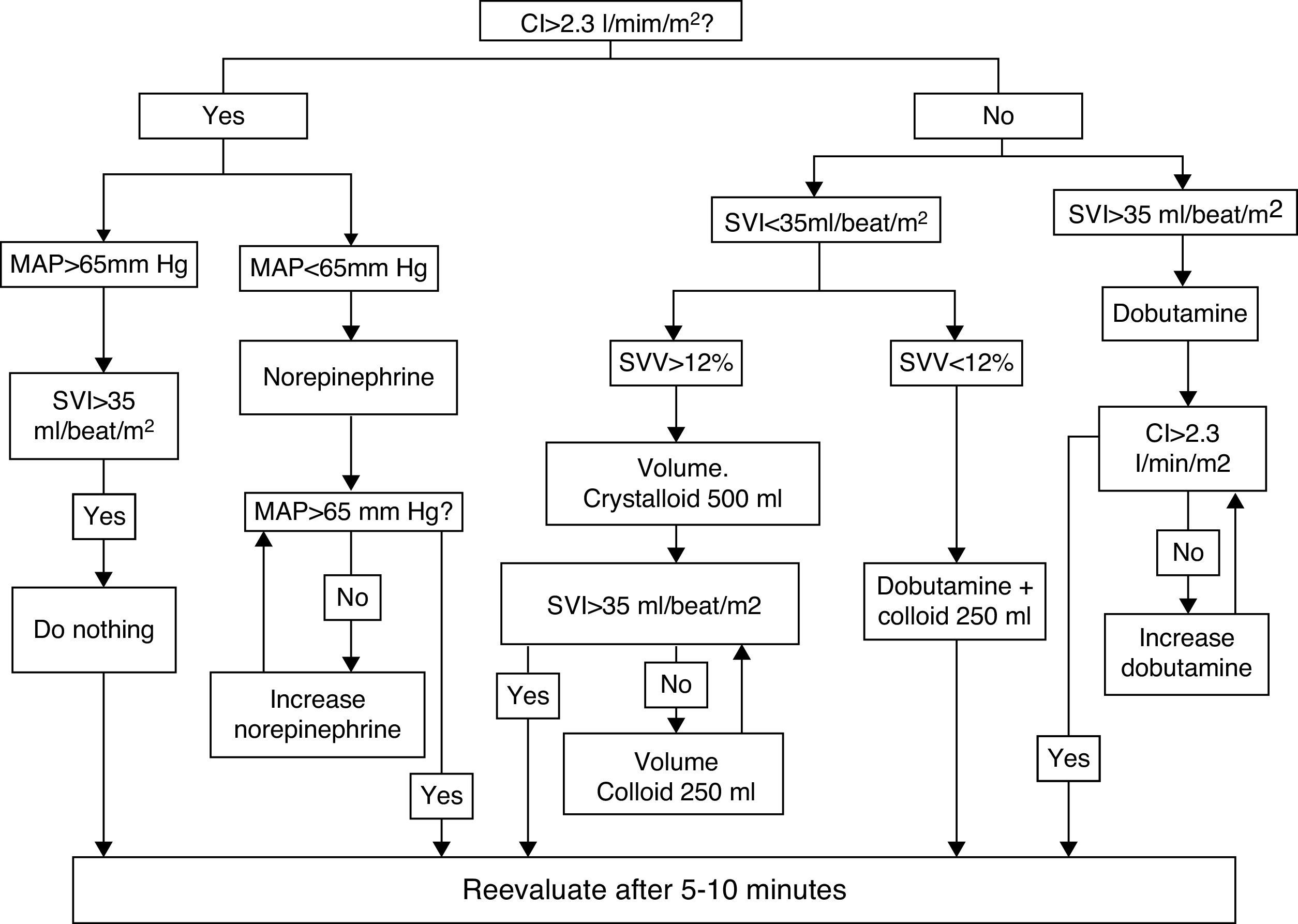
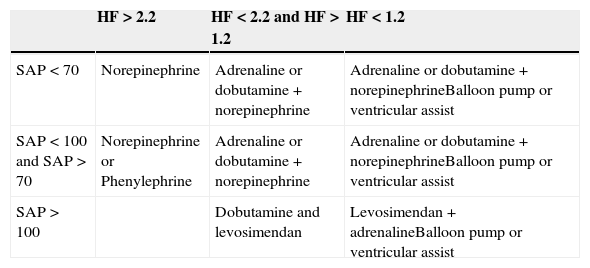
Table 17. Use of inotropes and ventricular assist devices according to haemodynamic status.
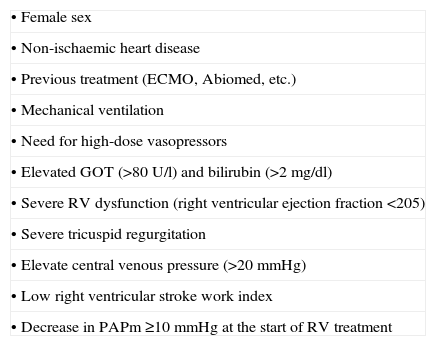
Table 18. Main predisposing factors for right ventricle failure.
Table 19. Pharmacological therapy in right ventricle failure.
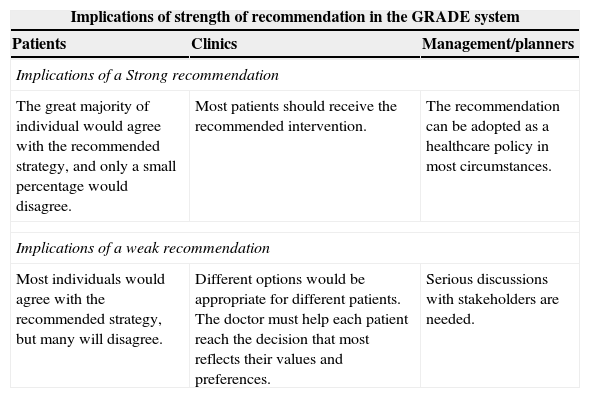
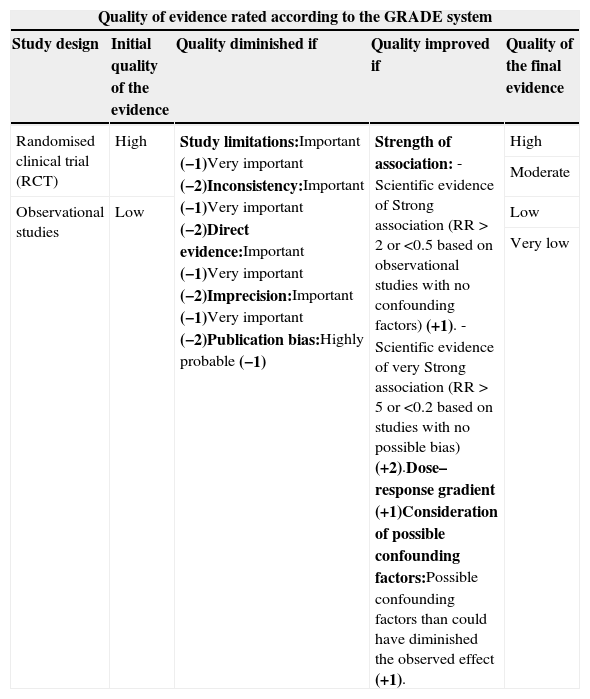
Levels of evidence and grades of recommendation (GRADE).
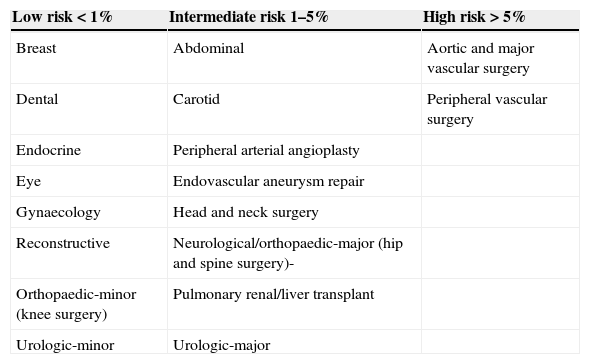
Surgical riska estimate.