La dilatación de la raíz aórtica (RaAo) es una condición que requiere monitorizar su crecimiento mediante estudios de imagen seriados a fin de definir el tratamiento. Se han reportado diferencias sistemáticas en las medidas de la RaAo entre la ecocardiografía transtorácica (ETT) y las técnicas seccionales. El objetivo de este estudio fue definir qué medición de la RaAo en válvulas aórticas tricúspides evaluada mediante angiotomografía computarizada cardíaca (ATCC) presentaba mejor correlación con la medición estándar por ETT.
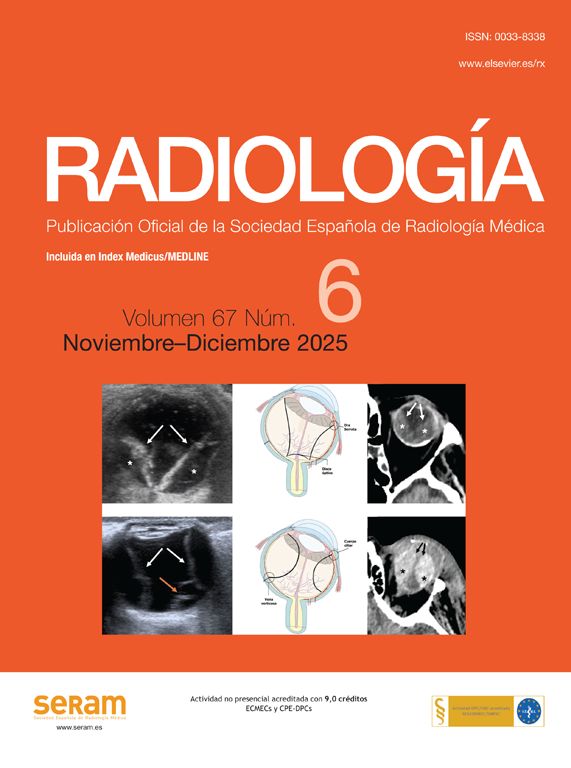
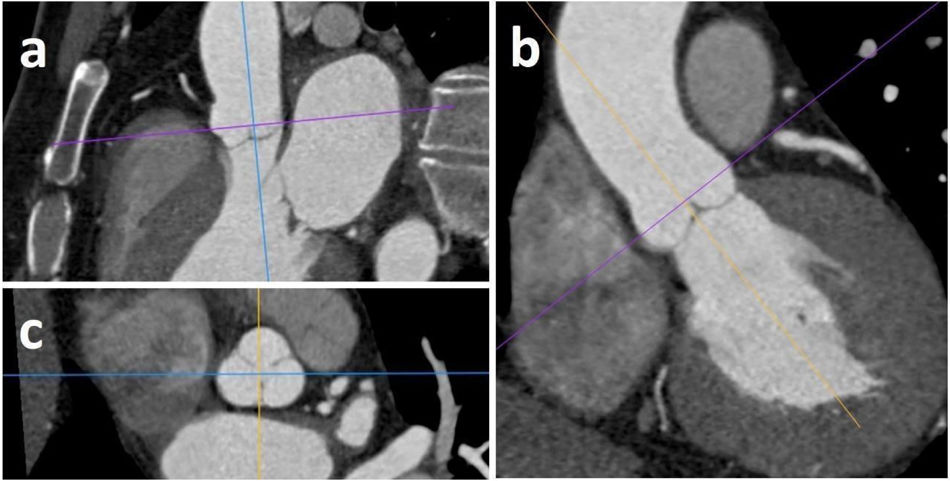
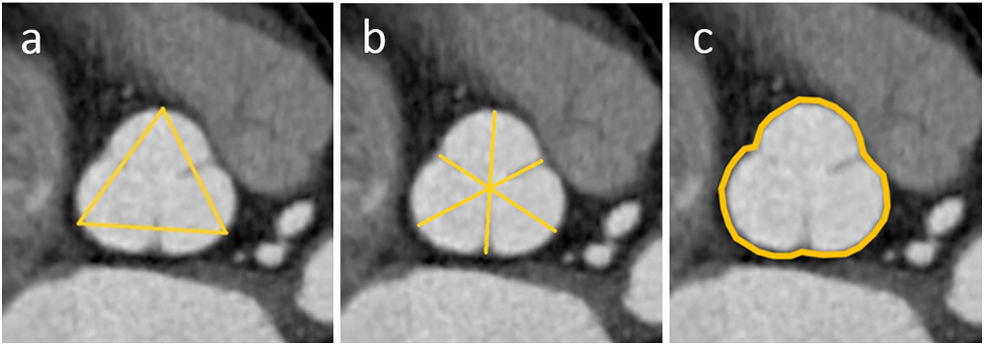
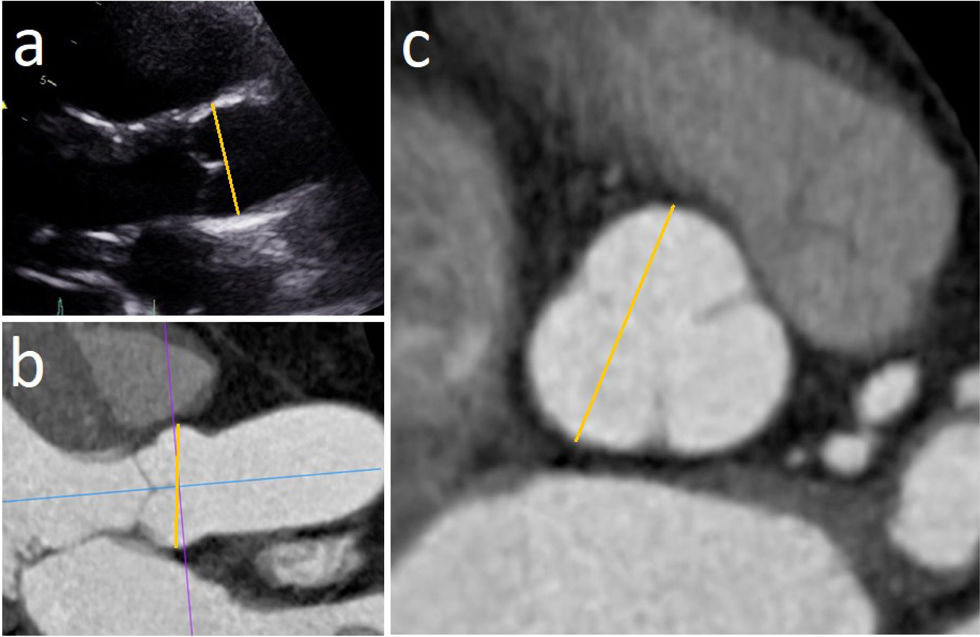
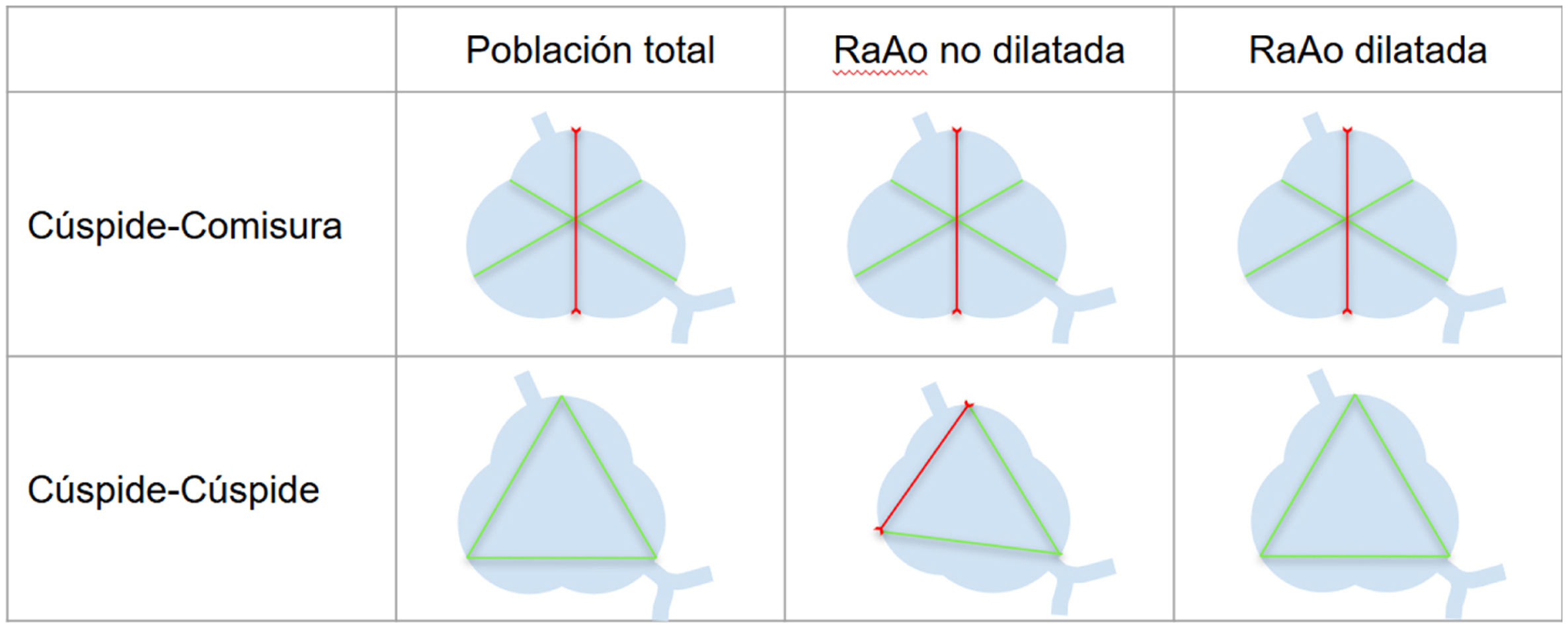
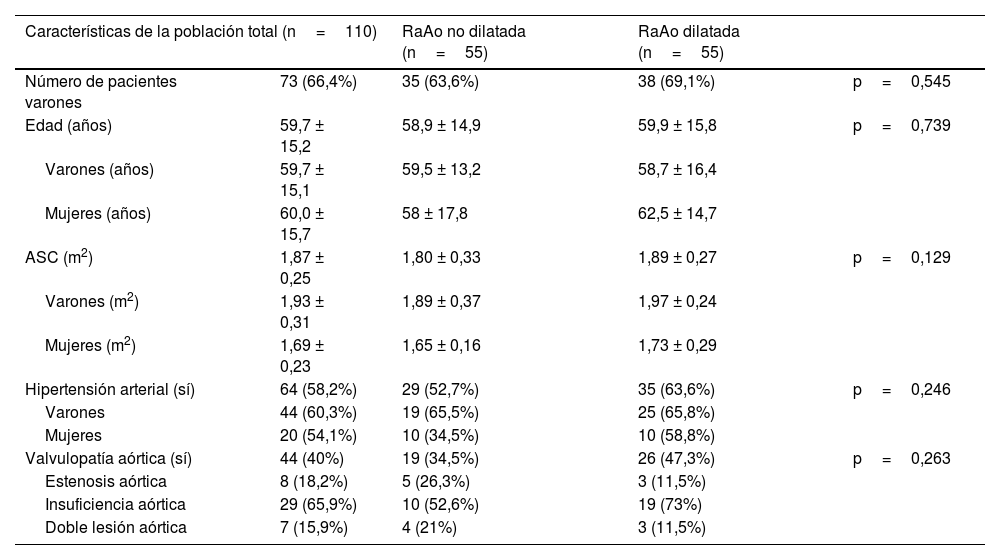
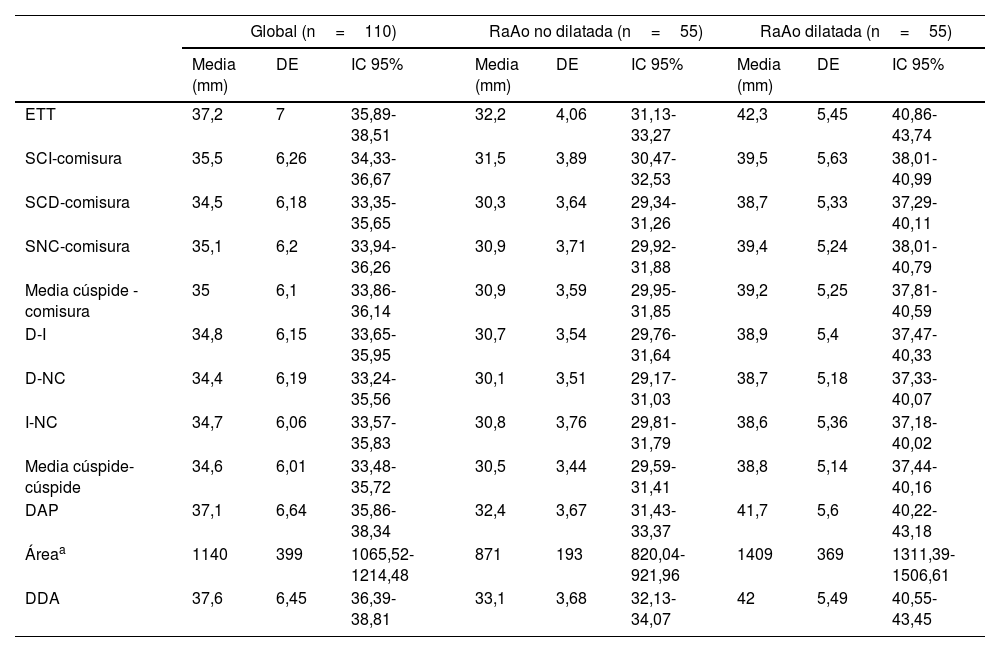
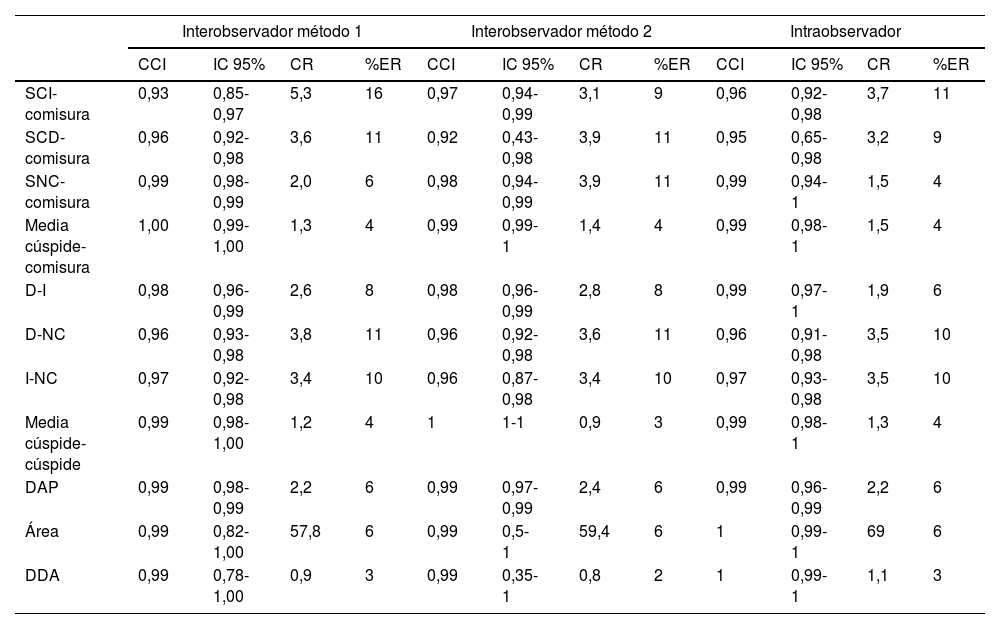
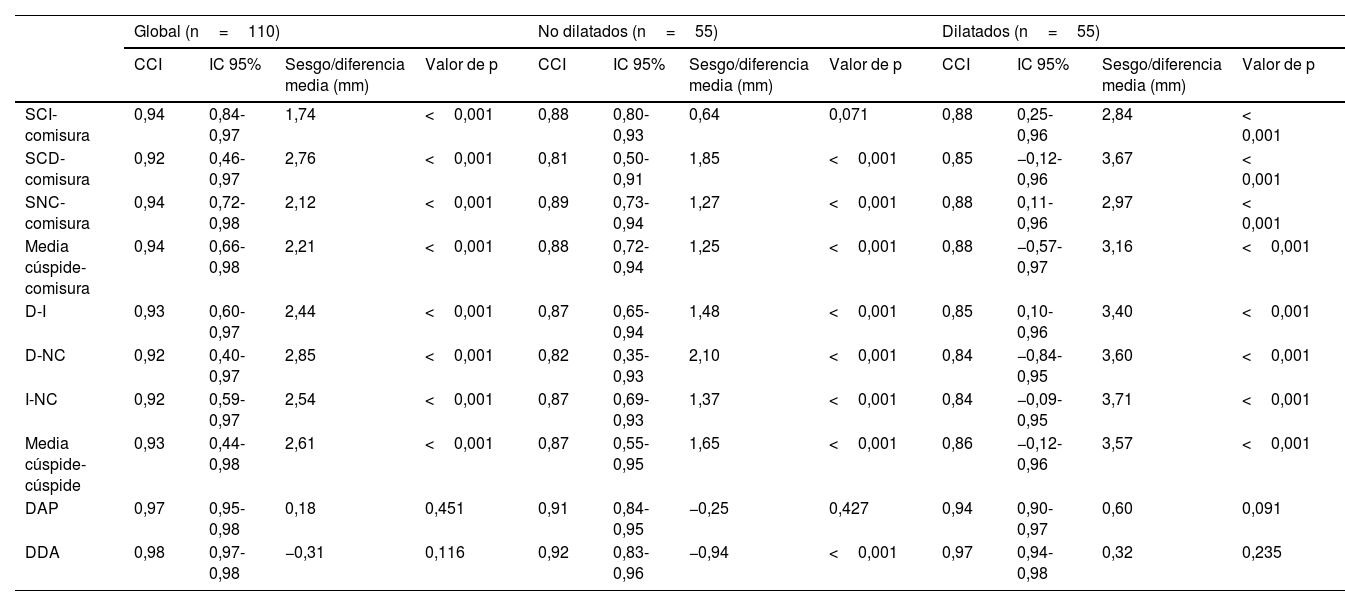
Material y métodosSe realizó un análisis retrospectivo de 110 pacientes que se sometieron a ATCC y ETT en un intervalo menor a 6 meses en nuestra institución, incluyendo de forma equilibrada pacientes con y sin dilatación de la RaAo. En el plano transversal de la RaAo en la ATCC se midieron distancias cúspide-comisura, cúspide-cúspide, el área y el diámetro derivado del área (DDA), así como la distancia anteroposterior (DAP). Las mediciones por ATCC mostraron excelente correlación con ETT (p<0,001), destacando el mejor grado de concordancia con el DDA y la DAP (ambos p<0,001).
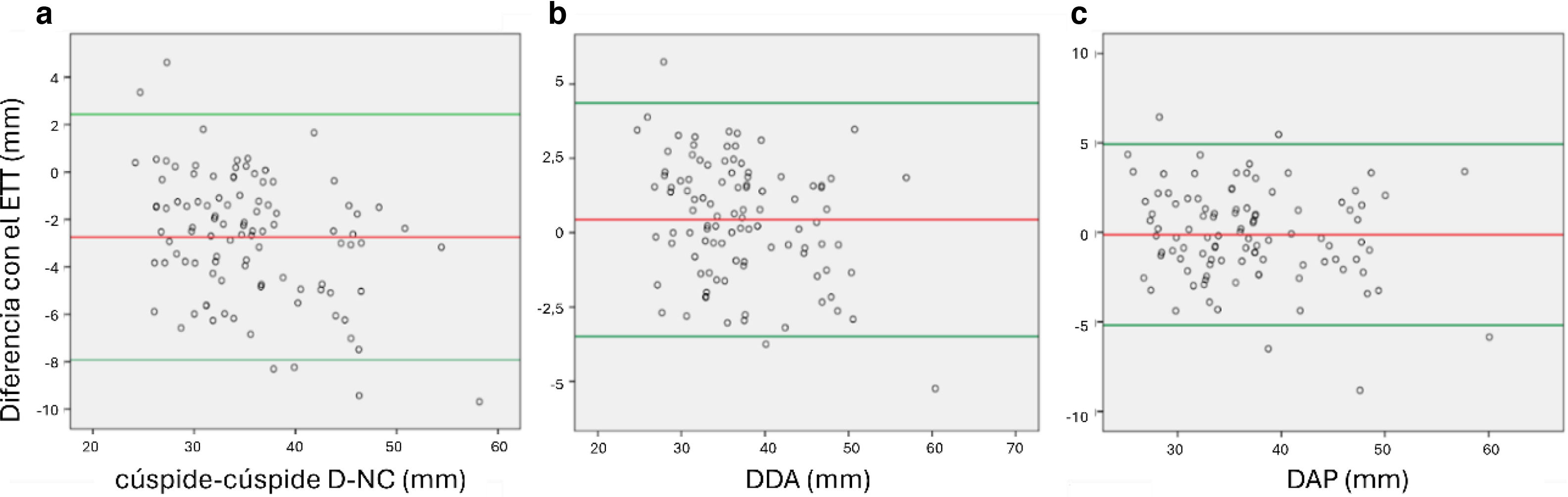
ResultadosLas mediciones de DAP no difirieron significativamente de las obtenidas por ETT en ningún grupo (global p=0,451; RaAo no dilatada p=0,427; RaAo dilatada p=0,091), a diferencia del resto de mediciones, incluido el DDA.
ConclusiónLa medición DAP mediante ATCC resultó equivalente a la obtenida por ETT, fácil de obtener y altamente reproducible. Investigaciones futuras podrían confirmar el DAP como la medida de referencia para comparar resultados entre ambas técnicas.
Aortic root (AoR) dilatation is a condition that requires monitoring of its growth through serial imaging studies in order to determine appropriate treatment. Systematic differences in AoR measurements have been reported between transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) and cross-sectional imaging techniques. The aim of this study was to determine which AoR measurement-performed using cardiac computed tomography angiography (CCTA) in patients with tricuspid aortic valves-shows the best correlation with the standard measurement obtained by TTE.
Material and methodsA retrospective analysis was conducted on 110 patients who underwent both CCTA and TTE within a six-month interval at our institution, including an equal number of patients with and without AoR dilatation. On the transverse plane of the AoR in CCTA, the following measurements were taken: cusp-to-commissure, cusp-to-cusp, area, area-derived diameter (ADD) and anteroposterior diameter (APD). CCTA measurements showed excellent correlation with TTE (p<.001), with the highest degree of agreement observed for ADD and APD (both p<.001).
ResultsAPD measurements did not differ significantly from those obtained by TTE in any group (overall p=.451; non-dilated AoR p=.427; dilated AoR p=.091), in contrast to the other measurements, including ADD.
ConclusionThe APD measurement obtained by CCTA proved to be equivalent to that obtained by TTE, easy to perform and highly reproducible. Future research may establish APD as the reference measurement for comparing results between both techniques.