Liver transplantation continues to be the most effective treatment of choice for patients with end-stage liver disease. Patients who go through that process experienced emotional stress and transplanted patients have a high rate of readmission.
AimsThis study aims to analyze the relation between mental health and hospital readmissions during the first year after liver transplantation.
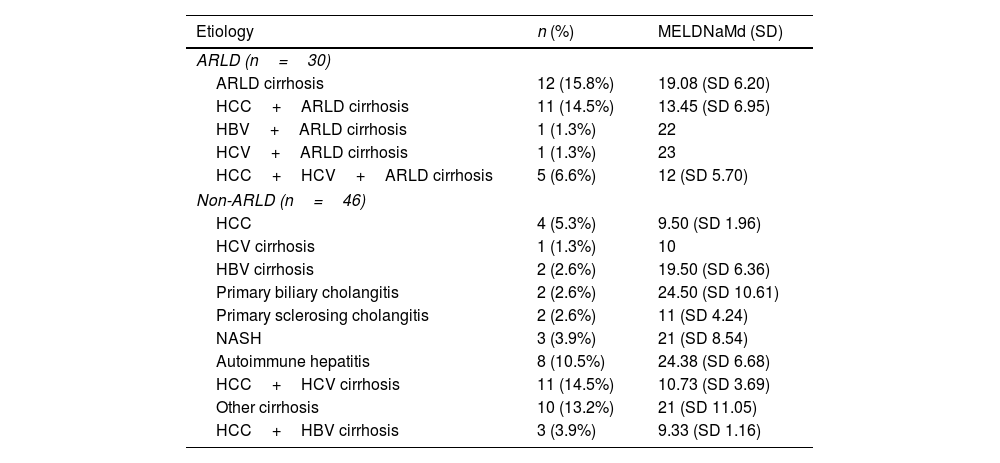
MethodA prospective study was conducted in a cohort of liver transplant patients in a tertiary hospital. Sociodemographic and clinical variables were collected. A descriptive analysis of the data and a multivariate study using a mixed linear model were performed.
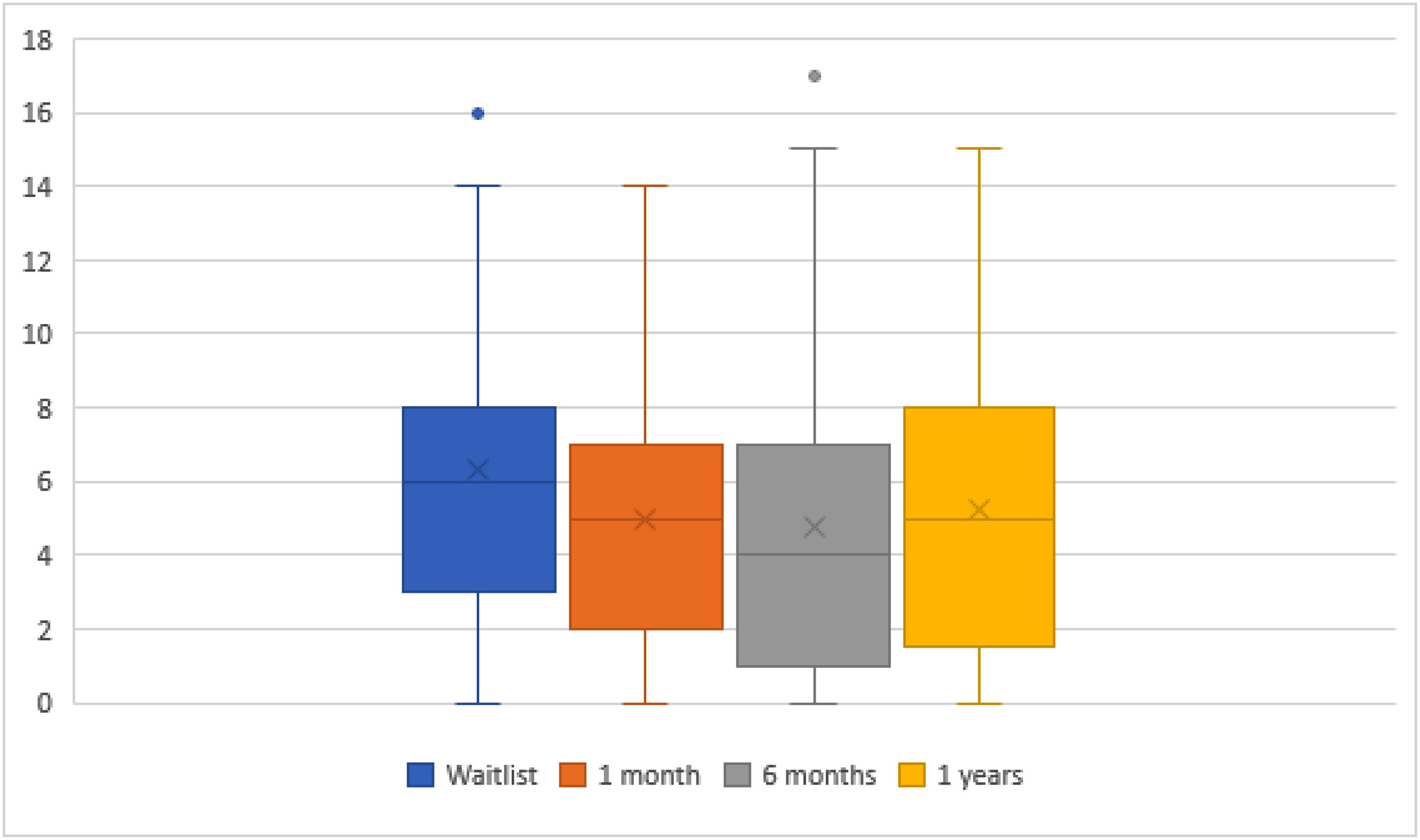
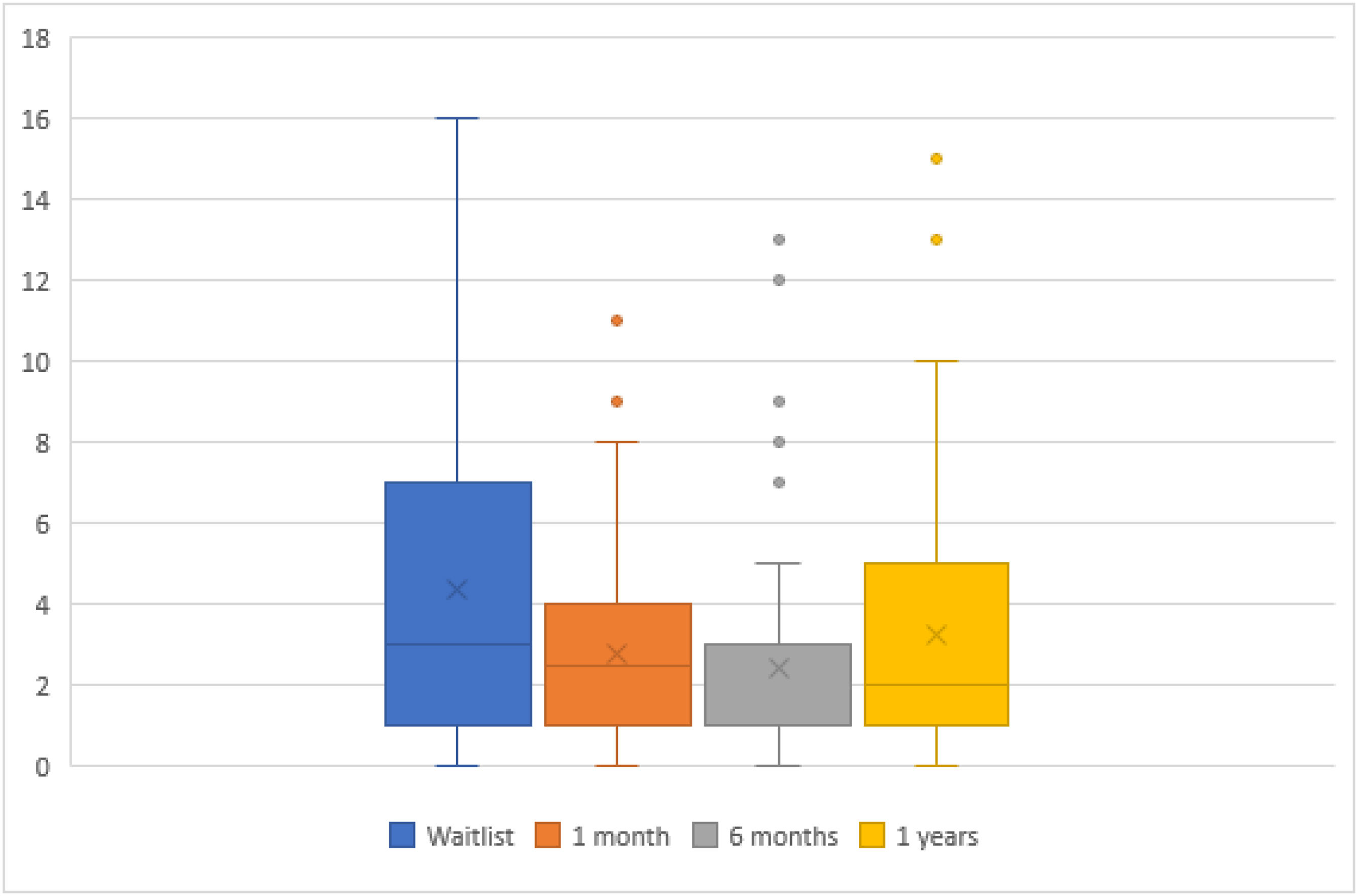
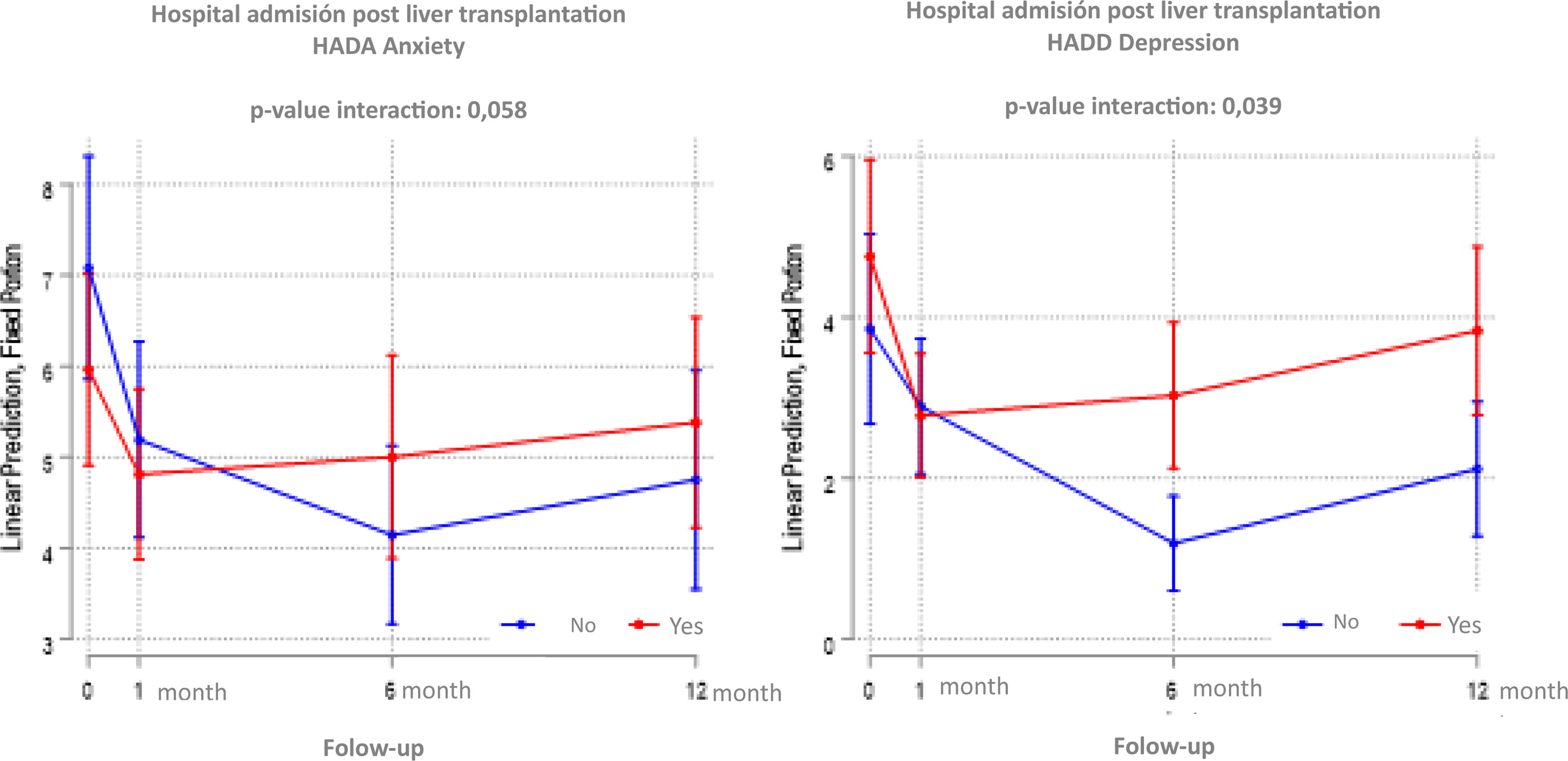
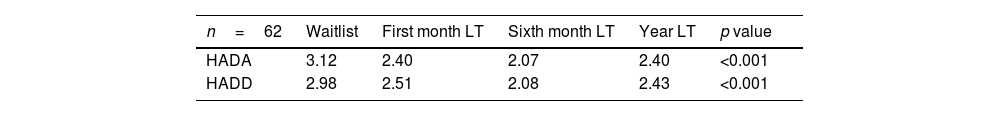
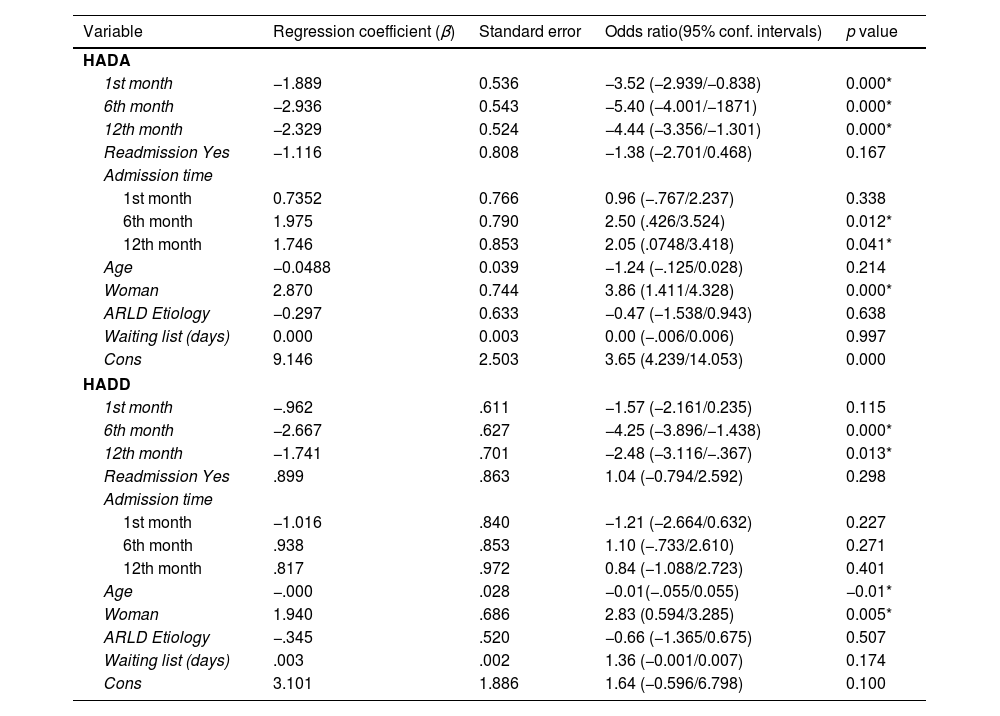
ResultsLiver transplant patients improve their mental health within the first year. Hospital admissions during the first-year impact negatively increasing anxiety and depression in liver transplant patients, especially in women.
ConclusionThe nurse must carry out a continuous psychological evaluation during the process and manage the necessary care, coordinating interdisciplinary care with the appropriate professionals to provide the emotional and psychological care. A multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary team should focus on the prevention of hospital admissions, controlling and managing cardiovascular risk, adherence to immunosuppressive treatment, adherence to the clinical follow-up prescribed by physicians, prevention of infections and promotion of healthy habits.
El trasplante de hígado sigue siendo el tratamiento más efectivo para los pacientes con enfermedad hepática en la etapa terminal. Los pacientes que atraviesan este proceso experimentan estrés emocional y presentan una alta tasa de readmisión hospitalaria.
ObjetivoEste estudio tiene como objetivo analizar la relación entre la salud mental y las readmisiones hospitalarias durante el primer año después del trasplante de hígado.
MétodoSe llevó a cabo un estudio prospectivo en una cohorte de pacientes trasplantados en un hospital terciario. Se recopilaron las variables sociodemográficas y clínicas. Se realizó un análisis descriptivo de los datos y un estudio multivariado utilizando un modelo lineal mixto.
ResultadosLos pacientes trasplantados de hígado mejoran su salud mental dentro del primer año. Sin embargo, las hospitalizaciones durante este período impactan negativamente, aumentando la ansiedad y la depresión, especialmente en las mujeres.
ConclusiónLa enfermería debe realizar una evaluación psicológica continua a lo largo del proceso y brindar la atención necesaria, coordinando cuidados interdisciplinarios con los profesionales adecuados para proporcionar apoyo emocional y psicológico. Además, un equipo multidisciplinario e interdisciplinario debe enfocarse en la prevención de readmisiones hospitalarias mediante el control y la gestión del riesgo cardiovascular, la adherencia al tratamiento inmunosupresor, el seguimiento clínico indicado por los médicos, la prevención de infecciones y la promoción de hábitos saludables.