A poor Nurse-to-Patient (N:P) ratio has a negative impact on the health of both patients and professionals. There are several tools to quantify the Nurse Workload (NW) and adjust nurse staffing. The use of such tools in the Intensive Care Units (ICU) can facilitate the adaptation of Nursing resources to patients’ real needs and improve working conditions.
ObjectiveTo determine the NW in a Surgical ICU.
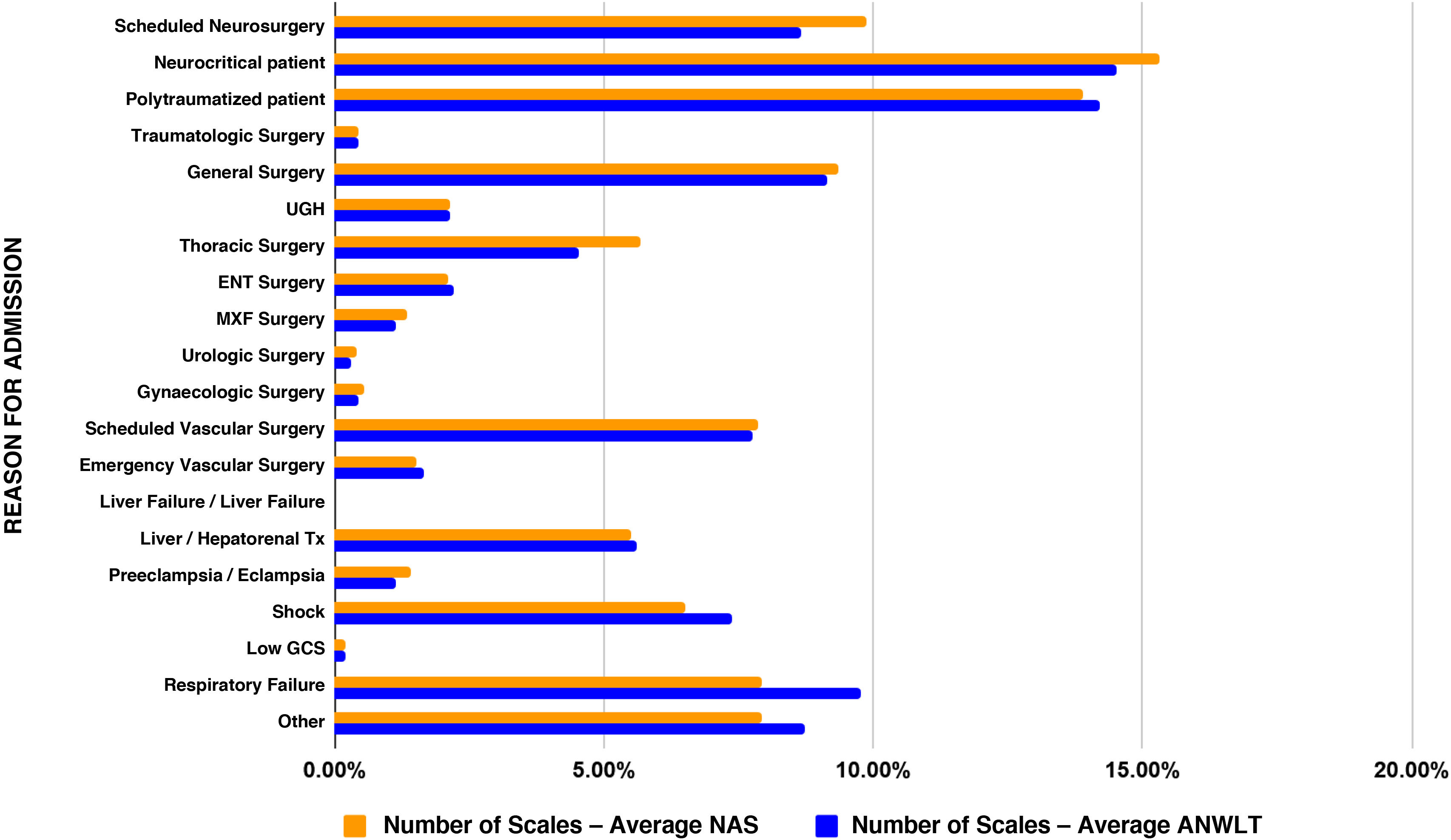
MethodologyDescriptive, transversal and unicentric study during March and April 2023. Determination of the operative N:P ratio adequated to the NW using the “Nursing Activities Score” (NAS). Measurement of the NW using NAS and “Valoración de Cargas de Trabajo y Tiempos de Enfermería” (VACTE) scales, together with the proposed NW indicators. Management and efficiency analysis of the Nursing Resources using the “Work Utilization Ratio” Index (WUR). Identification of work days and shifts with greater workload. Bivariate analysis relating NAS and VACTE to reason for admission. Calculation of the NW of each reason for admission relating the stay average and its NAS and VACTE average. Correlation analysis between scales.
Results1705 records per scale were collected. NAS per patient median: 55.70 (IR: 51.30−60.38), (95%CI: 54.74−56.66). NAS per patient mean: 56,67 (SD: ±8,28), (95%CI: 55.72–57.63). NW per bed NAS: 63.39, VACTE: 652.93. NAS per nurse: 135.23%. B:P Ratio: 1:1.09. Operative N:P Ratio: 1:1.76. WUR > 1. Correlation coefficient between scales: 0.45.
ConclusionsThere is a shortage of nurses in relation to the work generated. An update in the scales is required. The NAS per nurse is more effective than the NAS per patient for the adequacy of the Nursing workforce. The new proposed indicators might be suitable to determine the NW and to optimize the calculation of Nursing resources.
Un deficiente ratio Enfermera:Paciente (E:P) conlleva un impacto negativo en la salud tanto de pacientes como de profesionales. Existen diferentes instrumentos para cuantificar la Carga de Trabajo Enfermero (CTE) y adecuar su dotación. El uso de estos en las Unidades de Cuidados Intensivos (UCI) puede facilitar la adecuación de Recursos Enfermeros (RREE) a las necesidades reales de los pacientes y mejorar las condiciones laborales.
ObjetivoDeterminar la CTE en una UCI Quirúrgica.
MétodoEstudio descriptivo, transversal y unicéntrico durante marzo y abril de 2023. Determinación del ratio E:P operativo con la escala “Nursing Activities Score” (NAS). Medición de la CTE mediante las escalas NAS y “Valoración de Cargas de Trabajo y Tiempos de Enfermería” (VACTE), junto con los indicadores de CTE propuestos. Análisis de gestión y eficiencia de los RREE mediante el índice “Work Utilization Ratio” (WUR). Identificación de los días y turnos de trabajo con mayor CTE. Análisis bivariado relacionando NAS y VACTE con Motivo de Ingreso (MI). Cálculo de la CTE de cada MI relacionando su estancia media y su media NAS y VACTE. Análisis de correlación entre las escalas.
ResultadosSe recopilaron 1705 registros por escala. Mediana NAS paciente: 55,70 (RI: 51,30–60,38), (IC95%: 54,74−56,66). Media NAS paciente: 56,67 (DE: ±8,28), (IC95%: 55,72−57,63). CTE por cama: NAS: 63,39, VACTE: 652,93. NAS enfermera: 135,23%. Ratio C:P 1:1,09. Ratio E:P operativo 1:1,76. WUR > 1. Coeficiente de correlación entre escalas: 0,45.
ConclusionesLos RREE son deficitarios respecto al trabajo generado. Se precisa una actualización de escalas. La NAS enfermera es más eficaz que la NAS paciente para la adecuación de los RREE. Los nuevos indicadores propuestos podrían ayudar a determinar la CTE y optimizar el cálculo de RREE.
Article
Diríjase al área de socios de la web de la SEEIUC, (https://seeiuc.org/mi-cuenta/iniciar-sesion/) y autentifíquese.