El objetivo fue conocer la reproductibilidad en modelo murino de tumores renales de diferentes estirpes histológicas que podría ser útil para investigar la respuesta a fármacos diana.
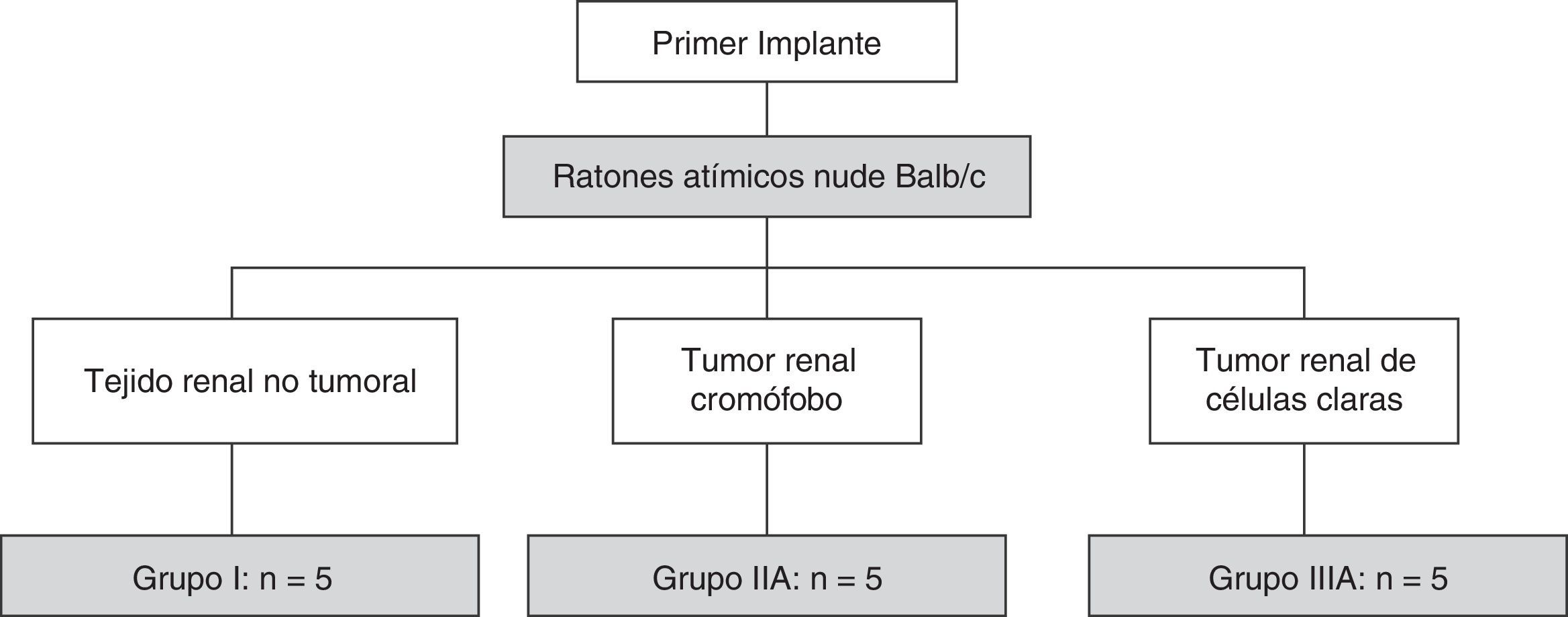
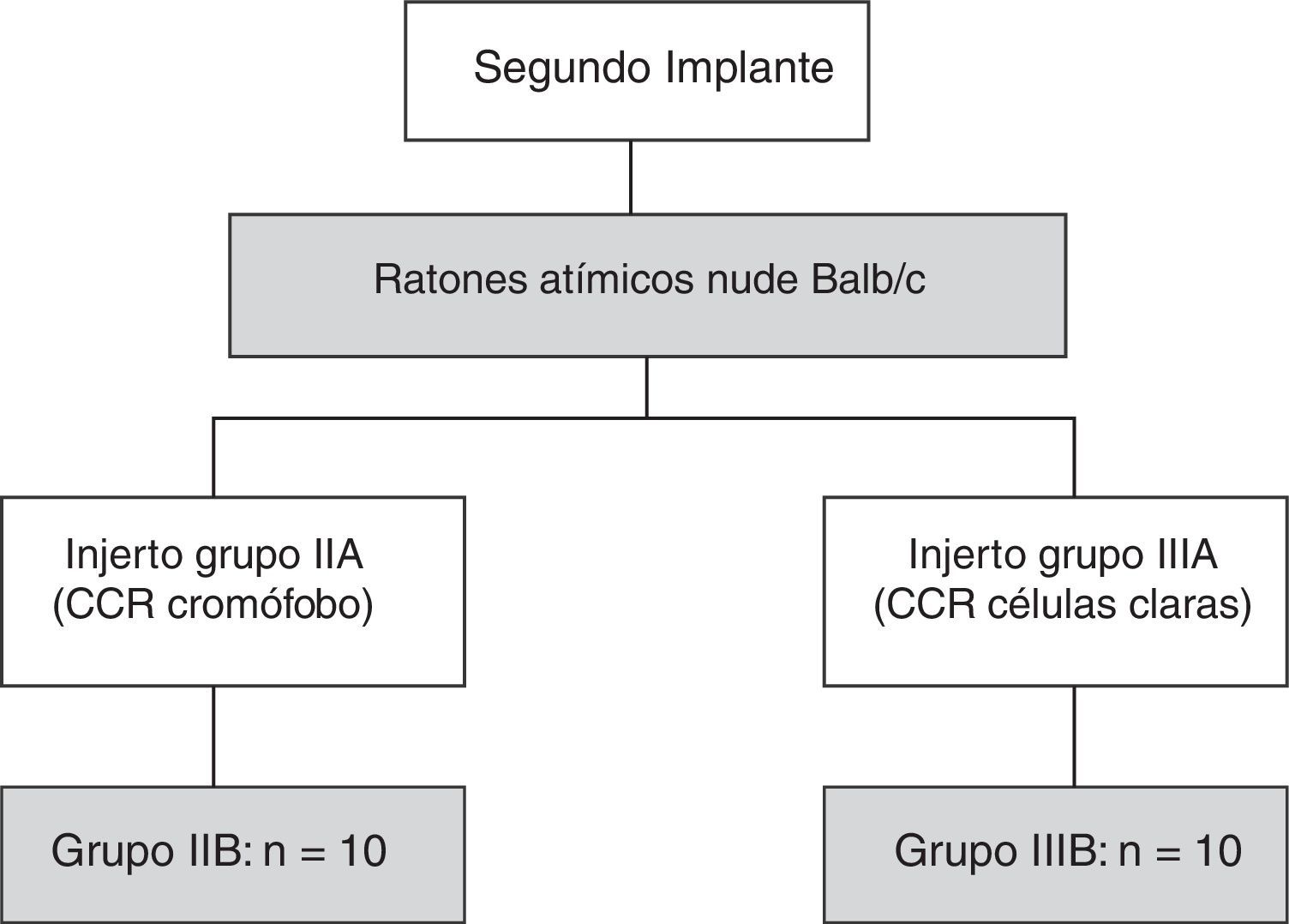
Material y métodosDesarrollo y análisis del modelo in vivo: xenoinjerto tumoral de carcinoma de células renales con ratones atímicos nude Balb/c. Se implanta tejido renal humano no tumoral en la región interescapular de 5 ratones, tumor renal tipo cromófobo en 5 ratones que tras comprobarse su crecimiento se preparó para implante en otros 10 ratones y tumor renal tipo carcinoma renal de células claras (CRCC) Fuhrman 2 en 5 ratones que también se implantó posteriormente en 10 ratones.
Se monitoriza el tamaño tumoral, la aparición de metástasis y el aumento de tamaño y número de las mismas. Cuando alcanza tamaño igual o superior a carcinoma localmente avanzado o metastásico los animales son sacrificados para estudio anatomopatológico, inmunohistoquímico y segunda fase de implante.
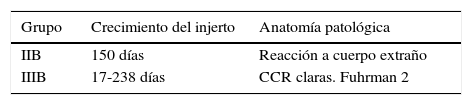
ResultadosEl xenoinjerto subcutáneo del tejido sano no creció, se sacrificaron a los 6 meses sin hallar tejido renal. El carcinoma renal de células cromófobas creció en la primera fase (100%), pero en la segunda fase se observó reacción inflamatoria crónica linfomonocitaria y a cuerpo extraño. El CRCC creció a los 5-8 meses, tanto en la primera como en la segunda fase (100%), manteniendo el tipo y el grado tumoral.
ConclusionesEl modelo con ratones atímicos nude Balb/c es útil para reproducir CRCC, con las mismas características y agresividad histológica al tumor humano nativo, alentando al desarrollo de la segunda fase experimental.
The objective of this study was to determine the reproducibility in a murine model of renal tumours of various histological strains that could be useful for investigating the response to target drugs.
Material and methodsDevelopment and analysis of the “in vivo” model: tumour xenograft of renal cell carcinomas with Balb/c nude athymic mice. Nontumourous human renal tissue was implanted in the interscapular region of 5 mice, chromophobe renal cell carcinoma was implanted in 5 mice (which, after checking its growth, was prepared for implantation in another 10 mice) and Fuhrman grade 2 clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) was implanted in 5 mice (which was also subsequently implanted in 10 mice).
We monitored the tumour size, onset of metastases and increase in size and number of tumours. When the size had reached a point greater than or equal to locally advanced or metastatic carcinoma, the animals were euthanised for a pathological and immunohistochemical study and a second phase of implantation.
ResultsThe subcutaneous xenograft of the healthy tissue did not grow. The animals were euthanised at 6 months and no renal tissue was found. The chromophobe renal cell carcinoma cells grew in the initial phase (100%); however, in the second phase, we observed a chronic lymphomonocyte inflammatory reaction and a foreign body reaction. The CCRCC grew at 5-8 months both in the first and second phase (100%), maintaining the tumour type and grade.
ConclusionsThe model with athymic Balb/c nude mice is useful for reproducing CCRCC, with the same histological characteristics and aggressiveness as native human tumours, promoting the development of the second experimental phase.