La edad y comorbilidad de los pacientes ingresados en Otorrinolaringología están aumentando, lo que incrementa las interconsultas a Medicina Interna, las cuales no alcanzan la efectividad requerida. Una alternativa es la asistencia compartida. El objetivo fue estudiar el efecto en los resultados clínicos de un programa de asistencia compartida en Otorrinolaringología.
MétodosEstudio observacional retrospectivo de los pacientes ≥16 años ingresados desde el 12/3/2017 hasta el 12/3/2019 en Otorrinolaringología; desde el 12/3/2018 con asistencia compartida con Medicina Interna. Analizamos las siguientes variables: edad, sexo, tipo de ingreso, si fue operado, peso administrativo asociado a GRD, número total de diagnósticos al alta, índice de comorbilidad de Charlson, éxitus, reingresos urgentes y estancia hospitalaria.
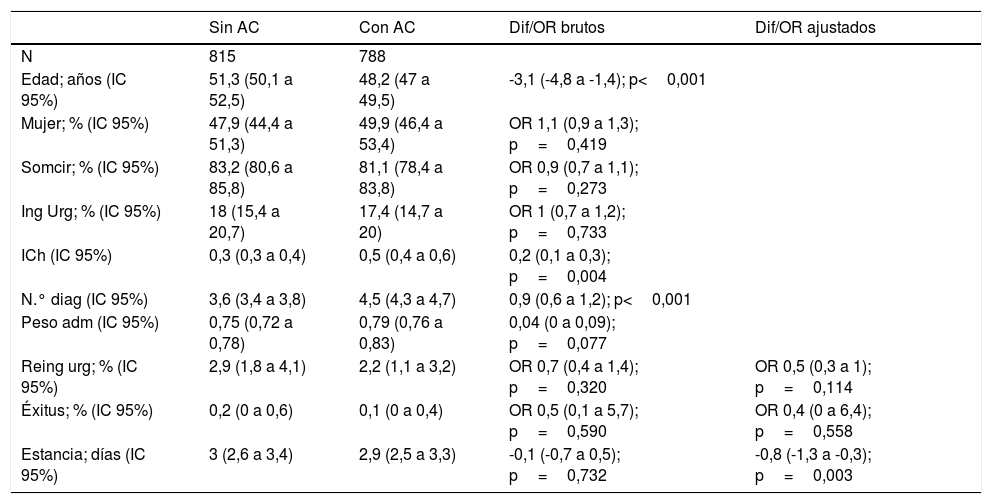
ResultadosLos pacientes con asistencia compartida fueron de menor edad (3,1 años; IC 95% 1,4 a 4,8), pero con mayor índice de comorbilidad de Charlson (0,2; IC 95% 0,1 a 0,3), mayor número de diagnósticos (0,9; IC 95% 0,6 a 1,2) y mayor peso administrativo (0,04; IC 95% 0 a 0,09). Al ajustar, observamos que la asistencia compartida redujo el 26,7% la estancia en Otorrinolaringología, 0,8 días (IC 95% 0,3 a 1,3), el 50% los reingresos urgentes y el 60% la mortalidad, ambos no significativos. El descenso de la estancia supone una disminución de costes de, como mínimo, 320.476,5€.
ConclusionesLos enfermos ingresados en Otorrinolaringología están aumentando su edad y comorbilidad. La asistencia compartida se asocia a una disminución de la estancia y los costes en Otorrinolaringología, en línea con lo observado en otros servicios quirúrgicos.
The age and comorbidity of patients admitted to Otolaryngology are increasing, leading to increased consultations/referrals to Internal Medicine, but do not reach the required effectiveness. An alternative is comanagement. A study is conducted on the effect of comanagement on Otolaryngology.
MethodsA retrospective observational study was conducted on patients ≥16 years old admitted in Otolaryngology between 03 December 2017 and 03 December 2019, since 03/12/2018 with comanagement with Internal Medicine since 03 December 2018. An analysis was performed on age, gender, type of admission, and whether the patient had surgery, administrative weight associated with (diagnosis-related group) DRG, total number of diagnoses at discharge, Charlson comorbidity index, deaths, urgent readmissions, and length of stay.
ResultsComanaged patients were younger (3.1 years, 95% confidence interval [95% CI] 1.4 to 4.8), but with higher Charlson comorbidity index (0.2; 95% CI; 0.1 to 0.3), number of diagnoses (0.9; 95% CI; 0.6 to 1.2), and administrative weight (0.04; 95% CI; 0 to 0.09). On adjustment, comanagement reduced Otolaryngology length of stay by 26.7%, 0.8 days (95% CI; 0.3 to 1.3), 50% of urgent readmissions, and 60% mortality, both non-significant. The decrease in length of stay implies an Otolaryngology savings of at least € 320,476.5.
ConclusionsPatients admitted to Otolaryngology are increasing in age and comorbidity. Comanagement is associated with reduced length of stay and costs similar to those observed in other surgical services.