Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a frequent complication in Intensive Care Unit (ICU) patients with high morbidity and mortality.
ObjectiveTo analyze the incidence of mechanical and metabolic adverse events associated with continuous renal replacement therapy using sodium citrate as a regional anticoagulant.
Material and methodsObservational, descriptive and prospective study performed in a polyvalent ICU during three years. Patients with AKI treated with renal replacement therapy and sodium citrate (Prismocitrate 18/0 mmol/L [0.5%]) were included. Patients with liver failure, active bleeding, severe thrombocytopenia, ICU stay of less than 24 h or treated with other anticoagulants were excluded. Demographic variables, severity index (APACHE II), vasoactive drug use, adverse events, and catheter characteristics were recorded. Anticoagulation efficacy was assessed with filter duration. Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS v.28.0, with P < .05 as the significance level. The study was approved by the ethics committee and informed consent was obtained from the patients or their relatives.
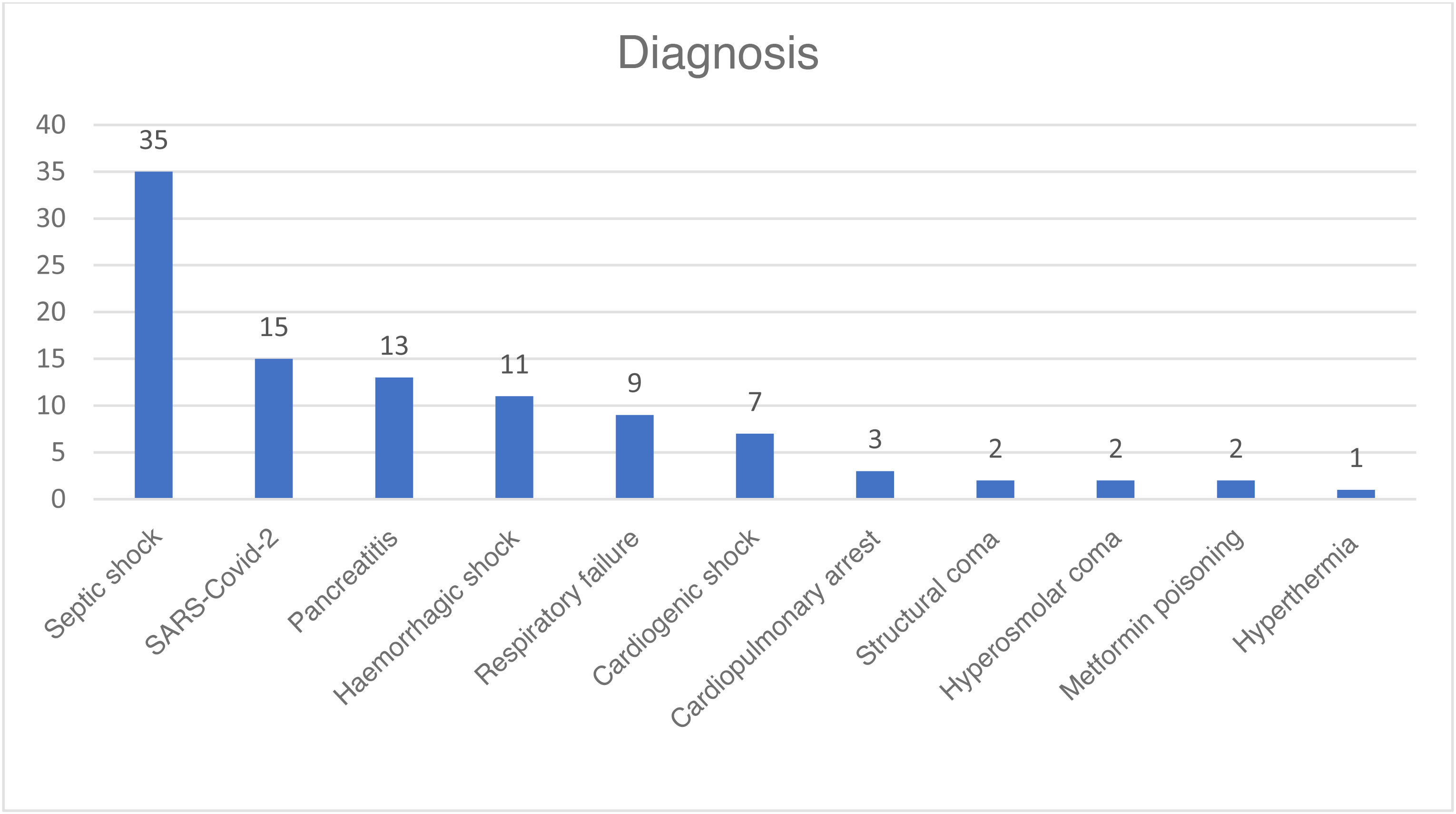
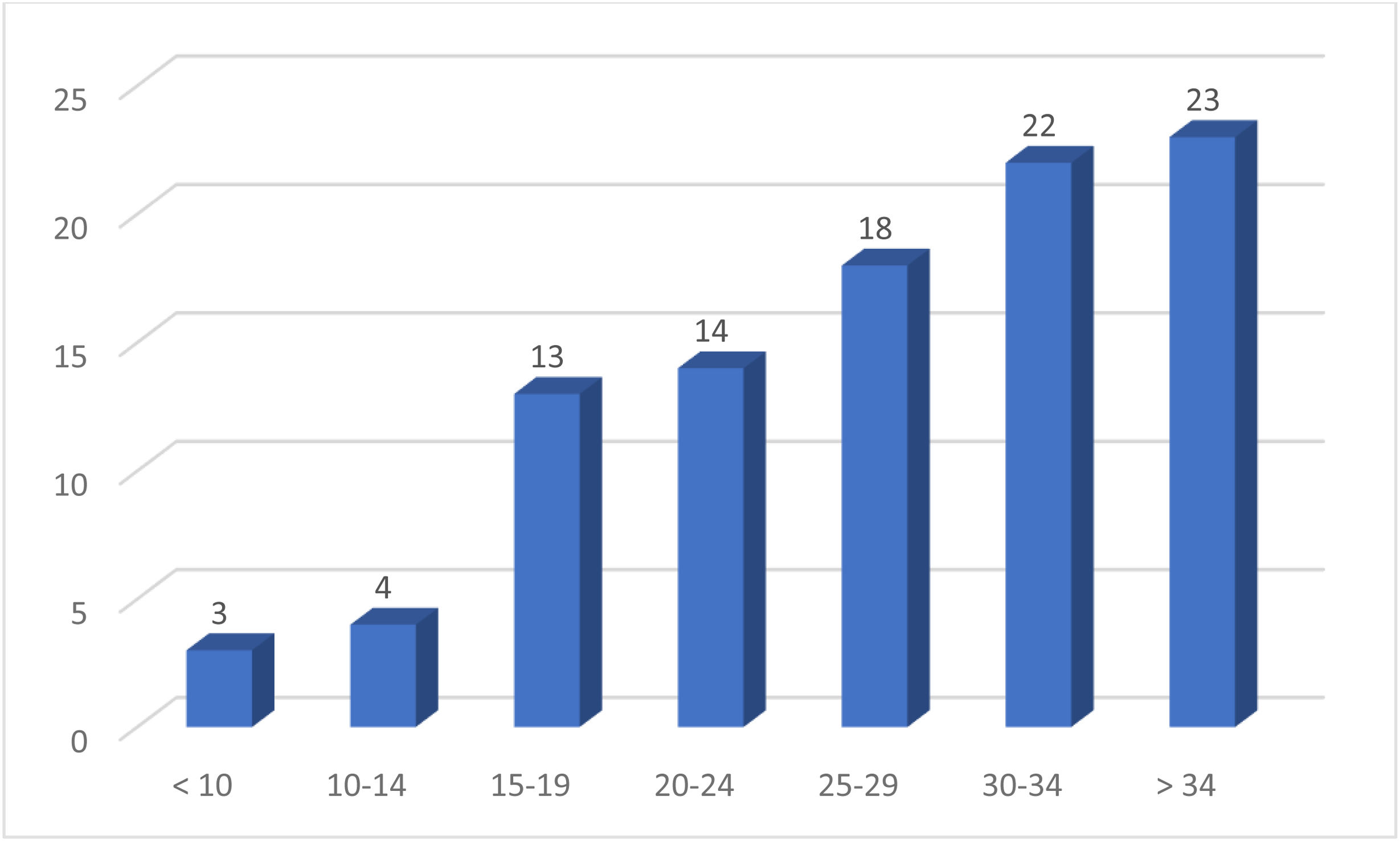
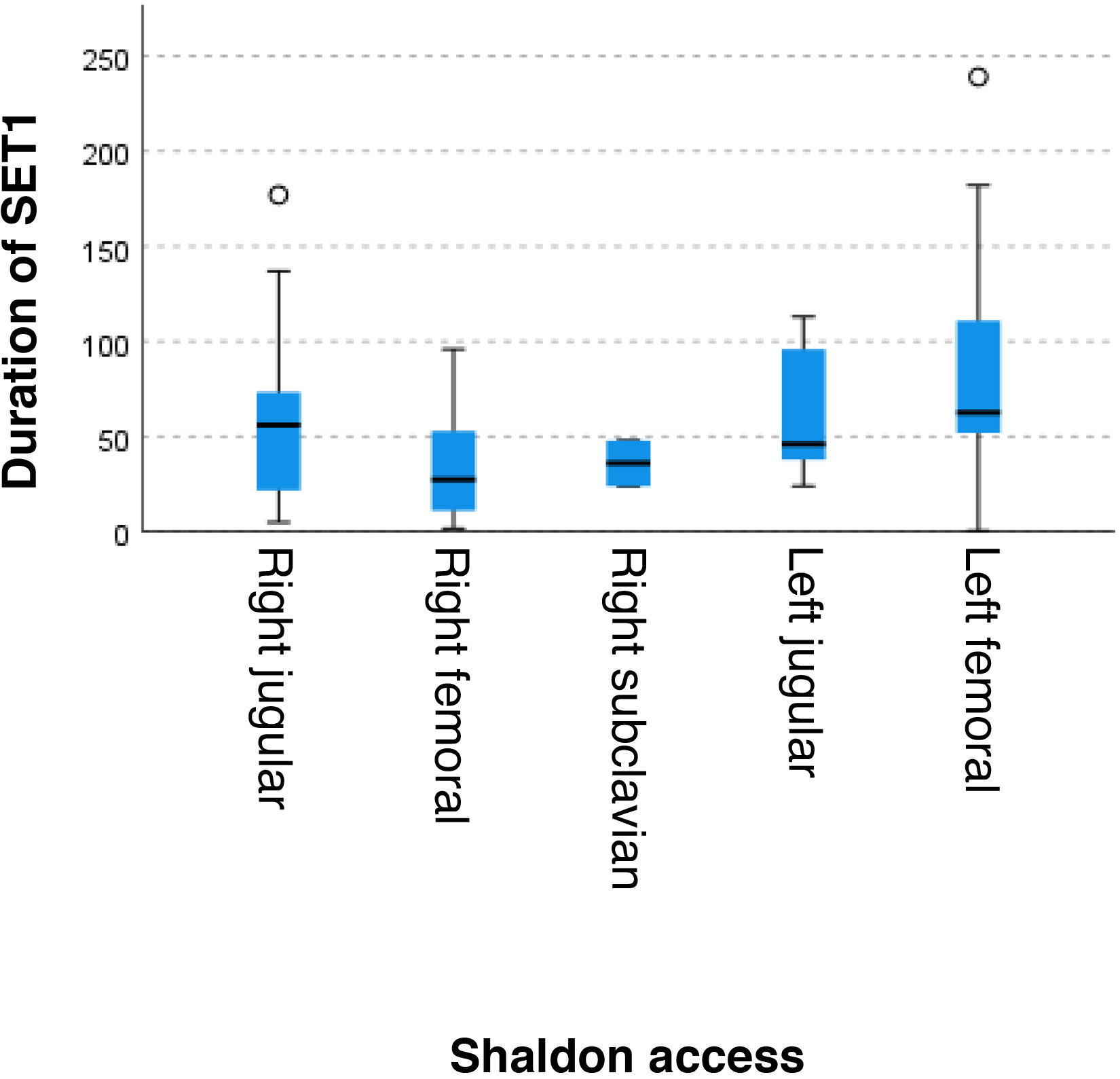
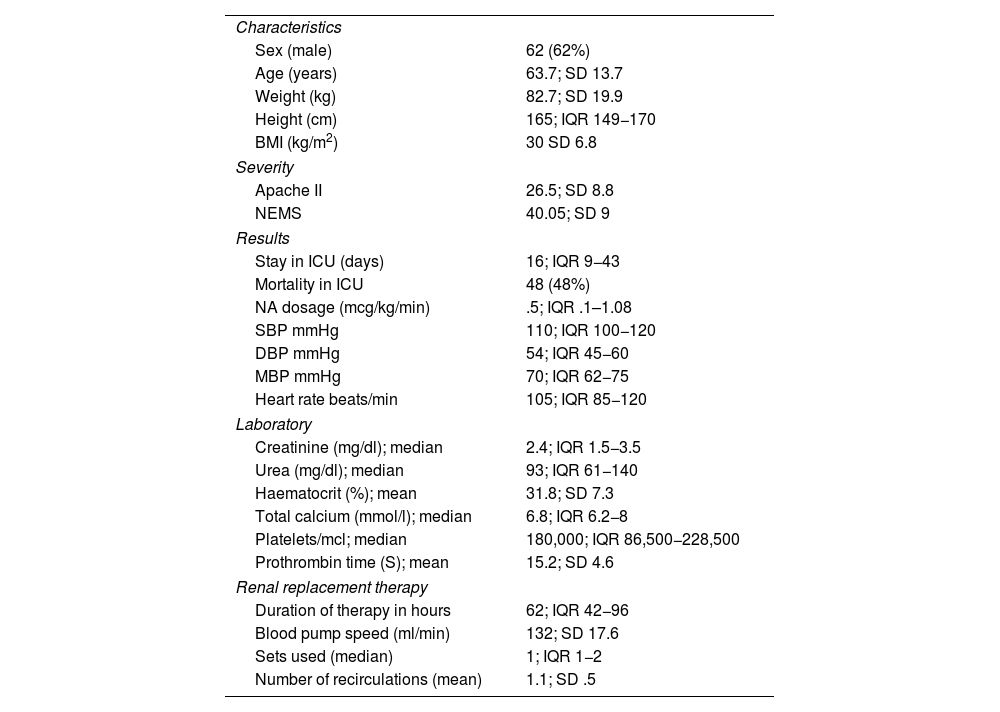
ResultsWe studied 100 patients, 62% men, with a mean age of 63 ± 14.5 years. The main causes of AKI were septic shock, hemorrhagic shock and Covid-19. The median ICU stay was 16 days (RIC 8–43), with intra-ICU mortality of 48%. Therapy lasted a median of 60.5 h (RIC 38–107). Only one patient presented bleeding, and in 26% the filter coagulated. There were no cases of citrate toxicity. Electrolyte complications included hypocalcemia (45%), hypokalemia (41%), hyponatremia (36%) and metabolic acidosis (30%).
ConclusionsMechanical and metabolic complications are common in continuous renal replacement therapies with sodium citrate. It is essential for ICU staff to be aware of their high prevalence in order to optimize clinical management.
La lesión renal aguda (LRA) es una complicación frecuente en pacientes de Unidades de Cuidados Intensivos (UCI) con alta morbimortalidad.
ObjetivoAnalizar la incidencia de eventos adversos mecánicos y metabólicos asociados con la terapia de reemplazo renal continuo usando citrato sódico como anticoagulante regional.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional, descriptivo y prospectivo realizado en una UCI polivalente durante tres años. Se incluyeron pacientes con LRA tratados con terapia de reemplazo renal y citrato sódico (Prismocitrate 18/0 mmol/L [0,5%]). Se excluyeron pacientes con insuficiencia hepática, hemorragia activa, trombocitopenia grave, estancia en UCI menor a 24 horas o tratados con otros anticoagulantes. Se registraron variables demográficas, índice de gravedad (APACHE II), uso de drogas vasoactivas, eventos adversos, y características del catéter. La eficacia de la anticoagulación se evaluó con la duración de los filtros. El análisis estadístico se realizó con SPSS v.28.0, con P < ,05 como nivel de significancia. El estudio contó con aprobación del comité ética y se obtuvo consentimiento informado de los pacientes o sus familiares.
ResultadosSe estudiaron 100 pacientes, 62% hombres, con edad media de 63 ± 14,5 años. Las principales causas de LRA fueron shock séptico, shock hemorrágico y Covid-19. La mediana de estancia en UCI fue de 16 días (RIC 8–43), con mortalidad intra-UCI del 48%. La terapia duró una mediana de 60,5 horas (RIC 38–107). Solo un paciente presentó sangrado, y en el 26% se coaguló el filtro. No hubo casos de toxicidad al citrato. Las complicaciones electrolíticas incluyeron hipocalcemia (45%), hipopotasemia (41%), hiponatremia (36%) y acidosis metabólica (30%).
ConclusionesLas complicaciones mecánicas y metabólicas son comunes en terapias de reemplazo renal continuo con citrato sódico. Es esencial que el personal de UCI esté atento a su alta prevalencia para optimizar el manejo clínico.
Article
Diríjase al área de socios de la web de la SEEIUC, (https://seeiuc.org/mi-cuenta/iniciar-sesion/) y autentifíquese.