To study the biometric modifications of the eyeball during suction in Laser assisted in Situ Keratomileusis (LASIK).
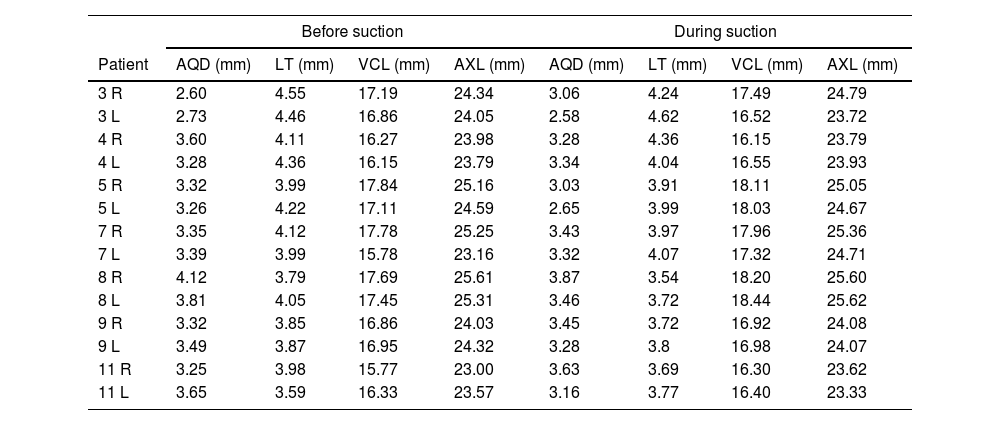
MethodsObservational and cross-sectional study. We studied 43 patients who underwent surgery for myopia and myopic astigmatism. Mean age was 38.3 ± 11.5 years, and 19 were female (44.2%). Conventional LASIK surgery with a manual microkeratome was performed. Before and during the suction maneuvre the following parameters were measured using an 11 Mhz biometric probe: aqueous depth (AQD), lens thickness (LT), vitreous cavity length (VCL) and axial length (AXL). Paired t-test was used to compare the biometric measurements before and during suction.
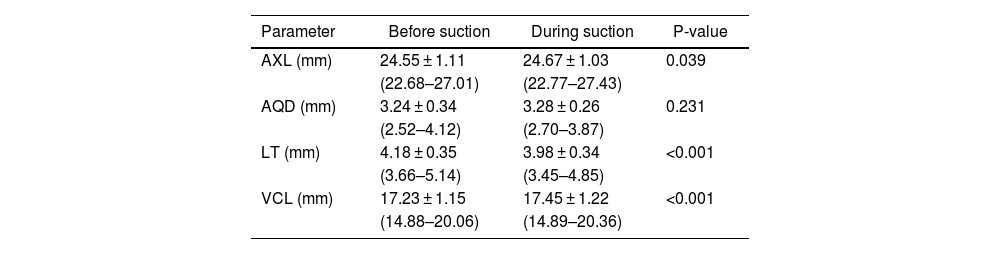
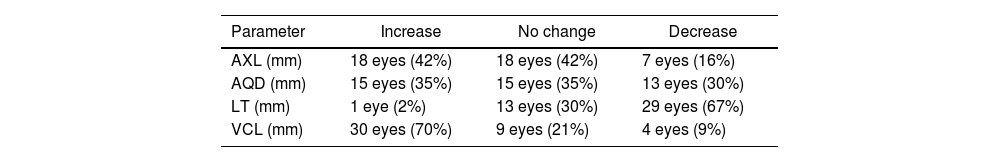
ResultsThe mean spherical equivalent refractive error was −4.5 ± 2.3 diopters. During suction, the AQD did not change significantly (p = 0.231). However, AXL and VCL increased by 0.12 mm and 0.22 mm respectively (p = 0.039 and <0.01) and LT decreased by 0.20 mm (p < 0.01). AXL increased in 42% of the eyes and decreased in 16%, VCL increased in 70% of the eyes and decreased in 9%, and the LT was reduced in 67% of the eyes.
ConclusionsSuction maneuvres during LASIK surgery produce changes of little magnitude in the eye globe, mainly a decrease in LT and an increase in VCL and AXL. Therefore, these modifications are expected to produce minimal anatomic alterations.
Estudiar las modificaciones biométricas del globo ocular durante la succión en la cirugía de Keratomileusis In Situ asistida por Láser (LASIK).
MétodosEstudio observacional transversal. Se estudiaron 43 pacientes intervenidos de miopía y astigmatismo miópico. La edad media fue de 38,3 ± 11,5 años, 19 eran mujeres (44,2%). Se realizó una cirugía LASIK convencional con microqueratomo manual. Antes y durante la maniobra de succión se midieron los siguientes parámetros mediante una sonda biométrica de 11 Mhz: profundidad acuosa (AQD), espesor del cristalino (LT), longitud de la cavidad vítrea (VCL) y longitud axial (AXL). Se utilizó la prueba t pareada para comparar las medidas biométricas antes y durante la succión.
ResultadosEl equivalente esférico medio fue de -4,5 ± 2,3 dioptrías. Durante la succión, la AQD no aumentó significativamente (p = 0,231). Sin embargo, la AXL y VCL aumentaron en 0,12 mm y 0,2 mm respectivamente (p = 0,039 y <0,01) y LT disminuyó en 0,20 mm (p < 0,01). La AXL aumentó en el 42% de los ojos y disminuyó en el 16%, mientras que la VCL aumentó en el 70% de los ojos y disminuyó en el 9%, y el LT se redujo en el 67% de los ojos.
ConclusionesLas maniobras de succión durante la cirugía LASIK producen cambios de poca magnitud en el globo ocular, principalmente disminución de LT y aumento de VCL y AXL. Por lo tanto, es esperable que estas modificaciones produzcan alteraciones anatómicas mínimas.