Net cellular uptake of 18F-FDG is adversely affected by elevated plasma glucose levels. The purpose of our study was to investigate the influence of hyperglycemic state at the time of 18F-FDG injection on the diagnostic accuracy of 18F-FDG PET/CT.
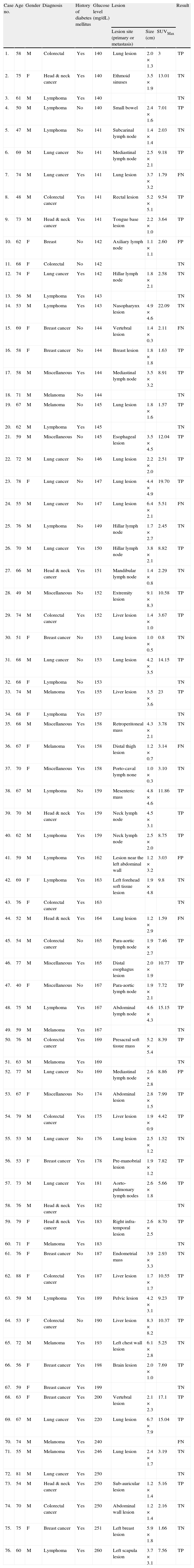
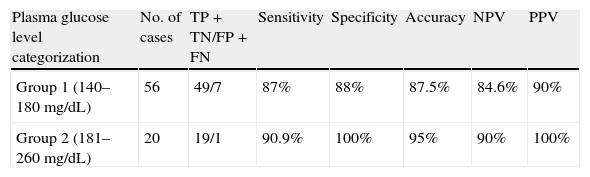
MethodPre-scan plasma glucose levels of all patients who were referred for PET/CT with an oncologic indication during the year 2005 were reviewed. All seventy-six patients (50 men, 26 women, mean age±SD: 65.5±9.7 years) with pre-scan glucose level higher than 140mg/dL (mean plasma glucose level±SD: 168.7±30.8, ranging from 140 to 260mg/dL) were enrolled into our study. The accuracy of PET/CT scans was assessed using concurrent or follow-up CT, MRI and histologic evidences as well as clinical follow-up as the reference standard.
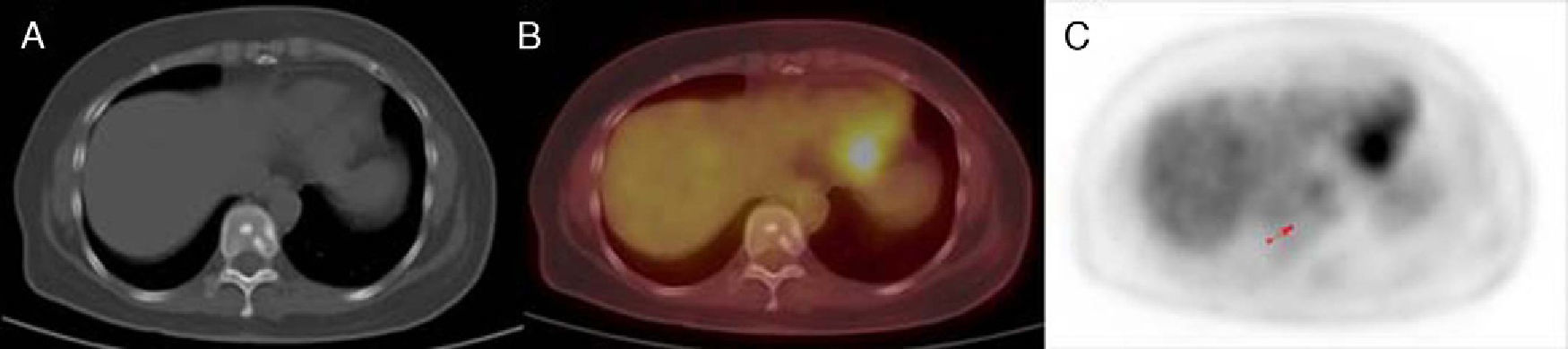
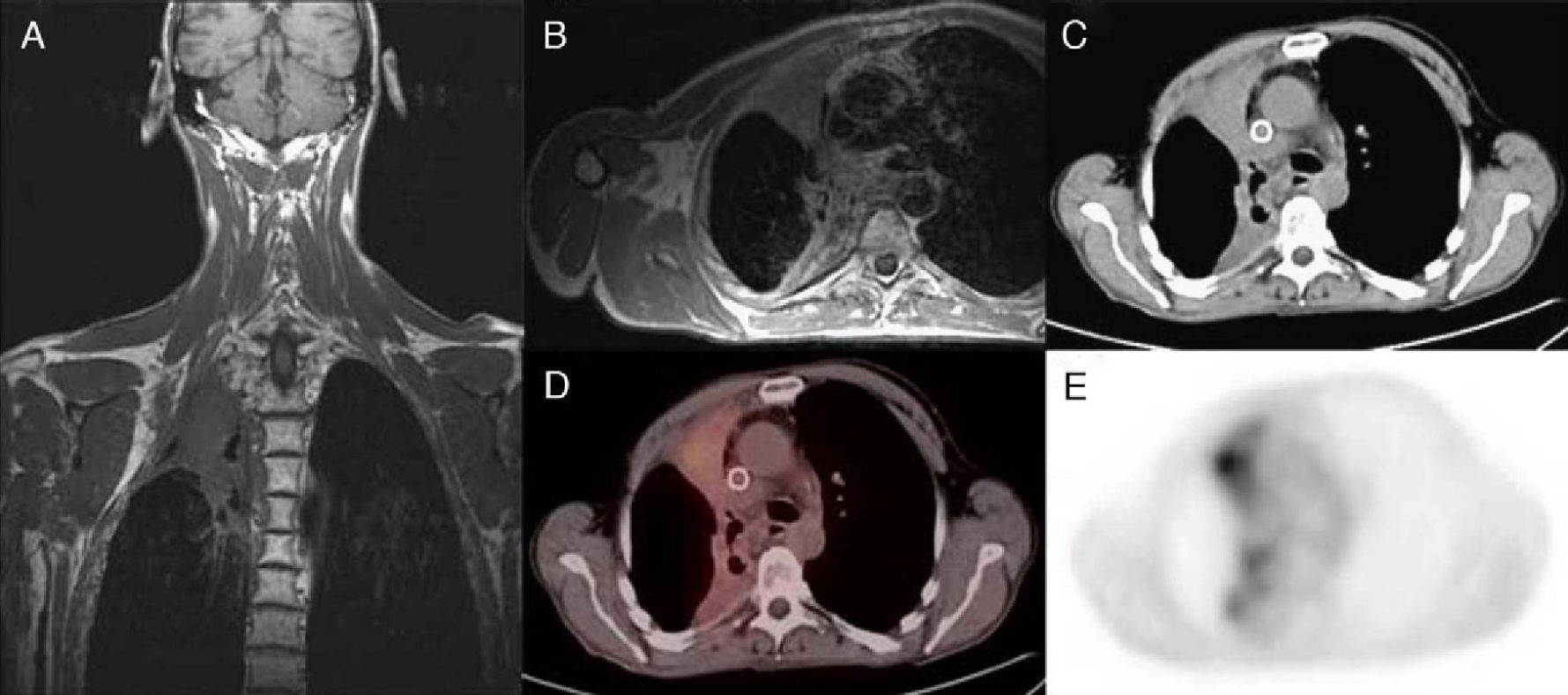
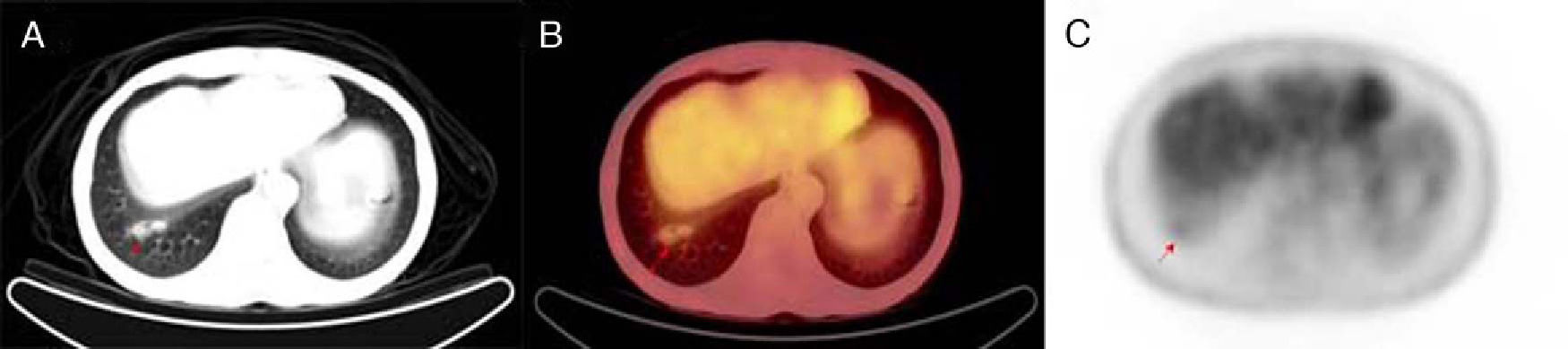
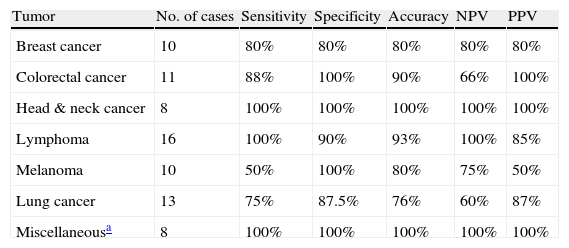
ResultsPET/CT was true positive in 37 patients, true-negative in 30 patients, false negative in 6 patients and false positive in 3 patients. Overall sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and diagnostic accuracy of 18F-FDG PET/CT on a patient basis were 86%, 90.9%, 92.5%, 83.3% and 88.1%, respectively. Diabetes mellitus was recorded in 50 patients. No significant diagnostic accuracy difference between diabetics and non-diabetics was noticed.
ConclusionOur study suggests that 18F-FDG accumulation of malignant lesions remains sufficiently high for reliable qualitative clinical diagnosis in chronic and acute hyperglycemic states. However, regarding the discordant and inconclusive results of the available reports and the remarkable concerns with reference to the adverse effects of elevated plasma glucose levels on the diagnostic accuracy of 18F-FDG PET/CT scans, further direct clues seems to be required and should be provided by future studies.
La captación celular de 18F-FDG se afecta por los niveles elevados de glucemia. El propósito de nuestro estudio fue investigar la influencia de la hiperglucemia en el momento de la inyección de 18F-FDG sobre la exactitud diagnóstica de la 18F-FDG PET/TAC.
Material y MétodosSe revisaron los niveles de glucemia en todos los pacientes remitidos para PET/TAC con indicación oncológica durante el año 2005. En nuestro estudio se incluyeron 76 pacientes (50 hombres, 26 mujeres, edad media±DS: 65,5±9,7 años) con glucemia previa al estudio superior a 140mg/dL (glucemia media±DS: 168,7±30,8mg/dL, rango 140–260mg/dL). La sensibilidad, especificidad, valor predictivo positivo, valor predictivo negativo y exactitud diagnóstica de la PET/TAC se calcularon usando como referencia los resultados de la TAC, RM y estudio histológico así como la evolución clínica.
ResultadosLos resultados de la PET/TAC fueron verdaderos positivos en 37 pacientes, verdaderos negativos en 30, falsos negativos en 6 y falsos positivos en 3 pacientes. De forma global, la sensibilidad, especificidad, valor predictivo positivo, valor predictivo negativo y exactitud diagnóstica de la PET/TAC fueron 86%, 90,9%, 92,5%, 83,3% y 88,1%, respectivamente. Cincuenta pacientes tenían diabetes mellitus. No se observaron diferencias significativas en la exactitud diagnóstica entre los pacientes diabéticos y no diabéticos.
ConclusiónNuestro estudio sugiere que la acumulación de 18F-FDG en las lesiones malignas permanece suficientemente elevada para permitir un diagnóstico clínico fiable en las situaciones de hiperglucemia aguda y crónica. Sin embargo, en referencia a los resultados discordantes y no concluyentes de los informes disponibles y los comentarios notables en referencia a los efectos adversos de los niveles elevados de glucemia sobre la exactitud diagnóstica de los estudios con 18F-FDG PET/TAC, parece ser necesario obtener más claves directas en nuevos estudios en el futuro.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)