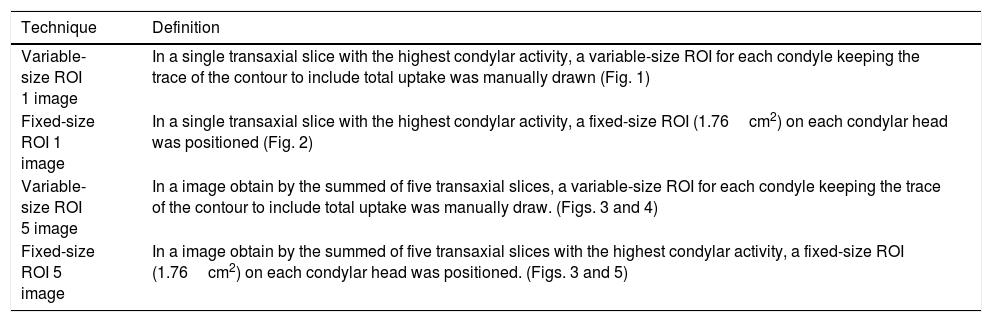
To compare variability, reproducibility and repeatability of four quantitative evaluation methods to interpret the 99mTc-MDP SPECT reports in patients with clinically suspected unilateral condylar hyperplasia (UCH).
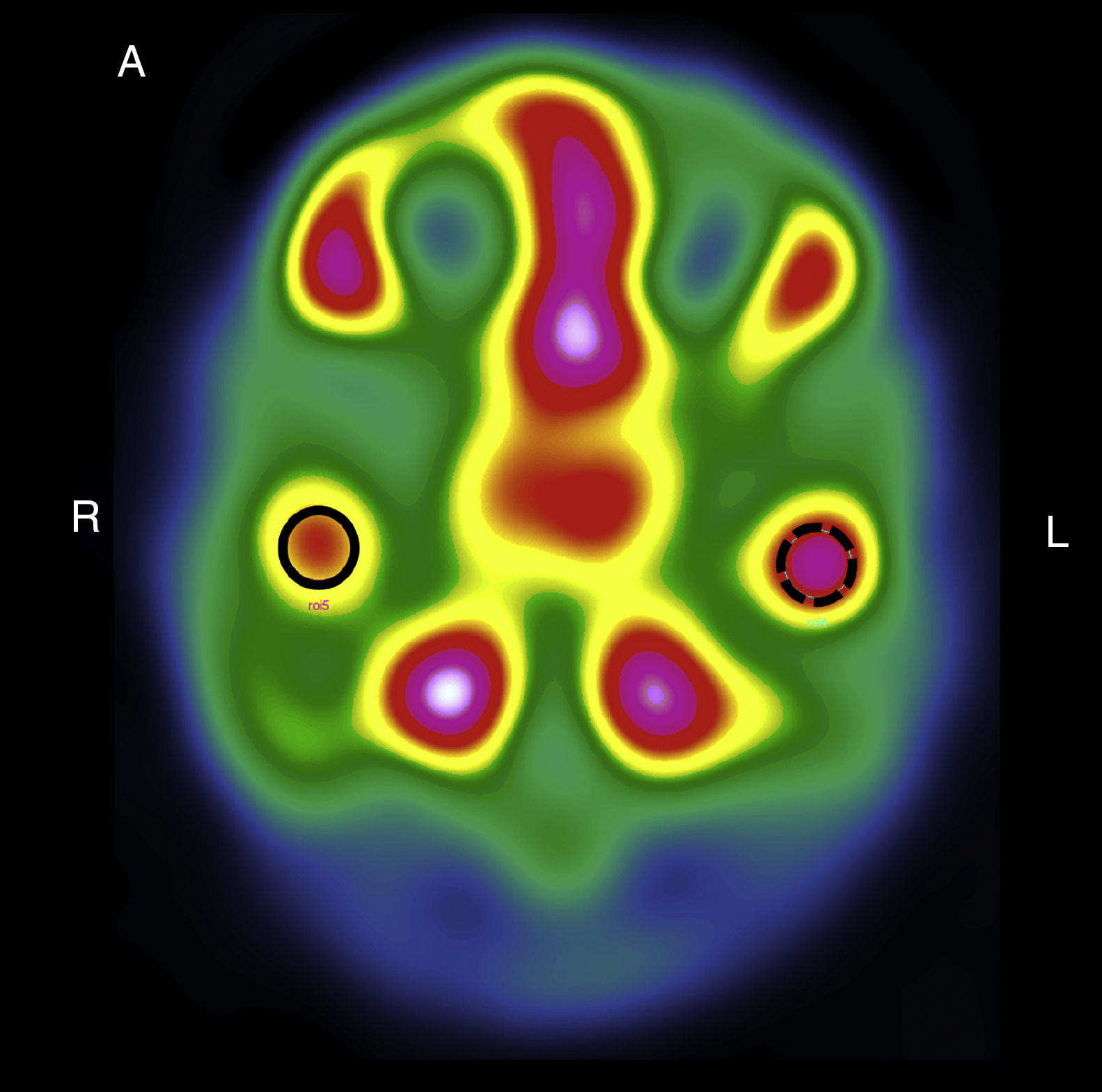
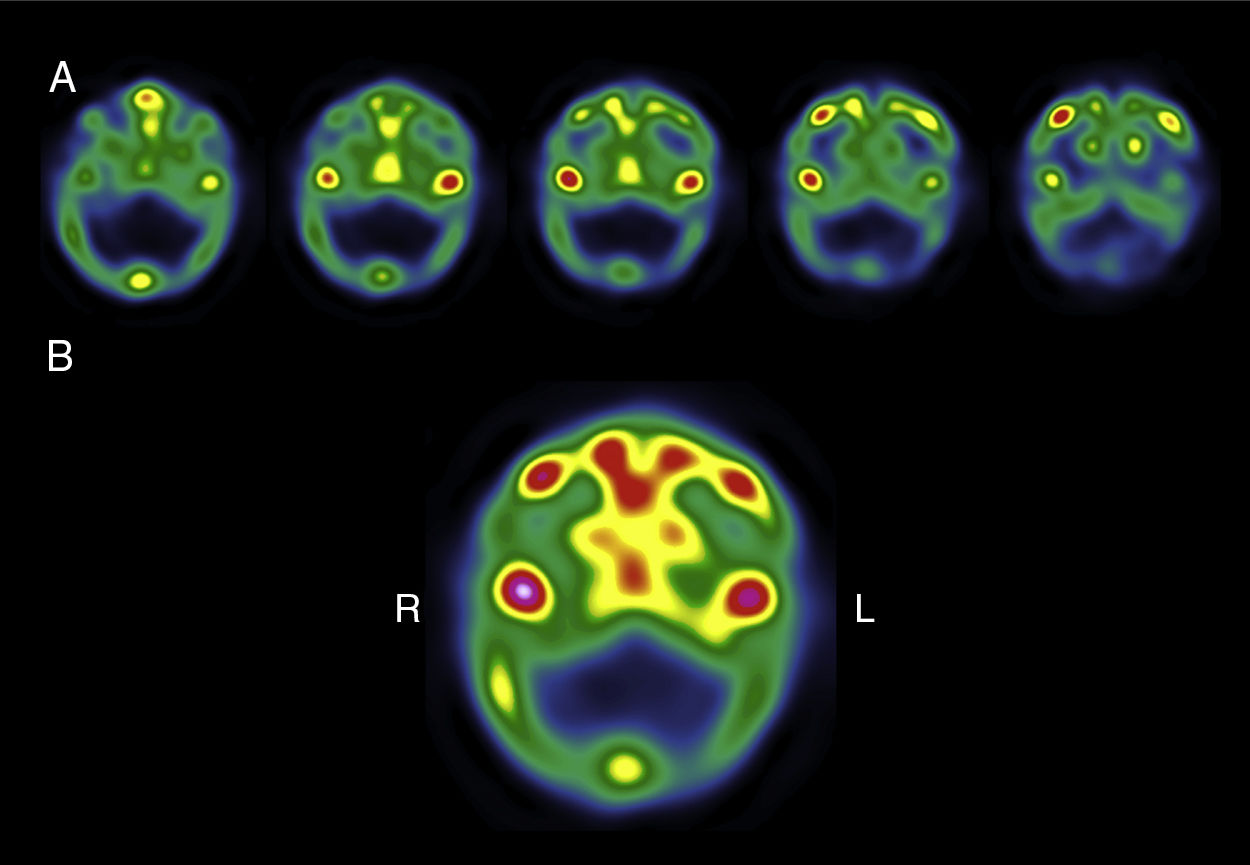
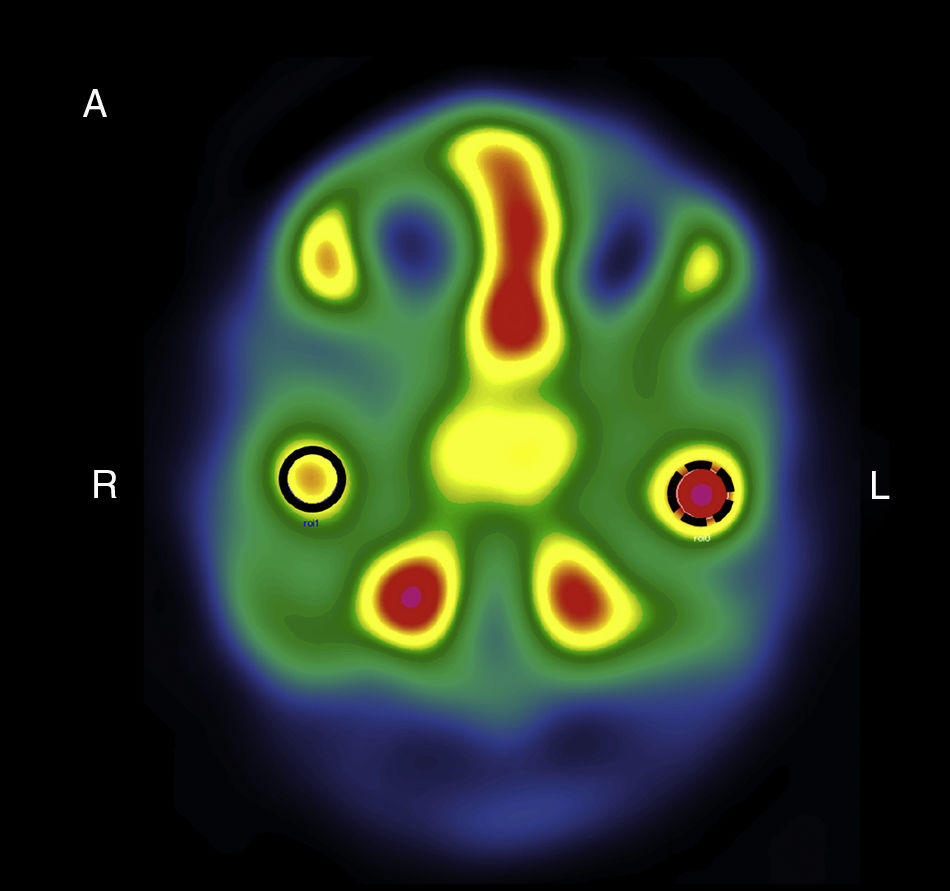
MethodThis was a descriptive observational study carried out with SPECT images of 38 patients with clinical and radiographic signs of UCH, and interpreted using four quantitative methods: (1) one image, variable-size region of interest (ROI); (2) one image, fixed-size ROI (1.76cm2), (3) five image variable-size ROI; (4) five image, fixed-size ROI (1.76cm2). Each of the images were report simultaneously but in an independent way by the two nuclear medicine experts in both total radioactive counts as well as normalized counts to quantify the reproducibility (inter-operator variability) and the repeatability (intra-operator variability).
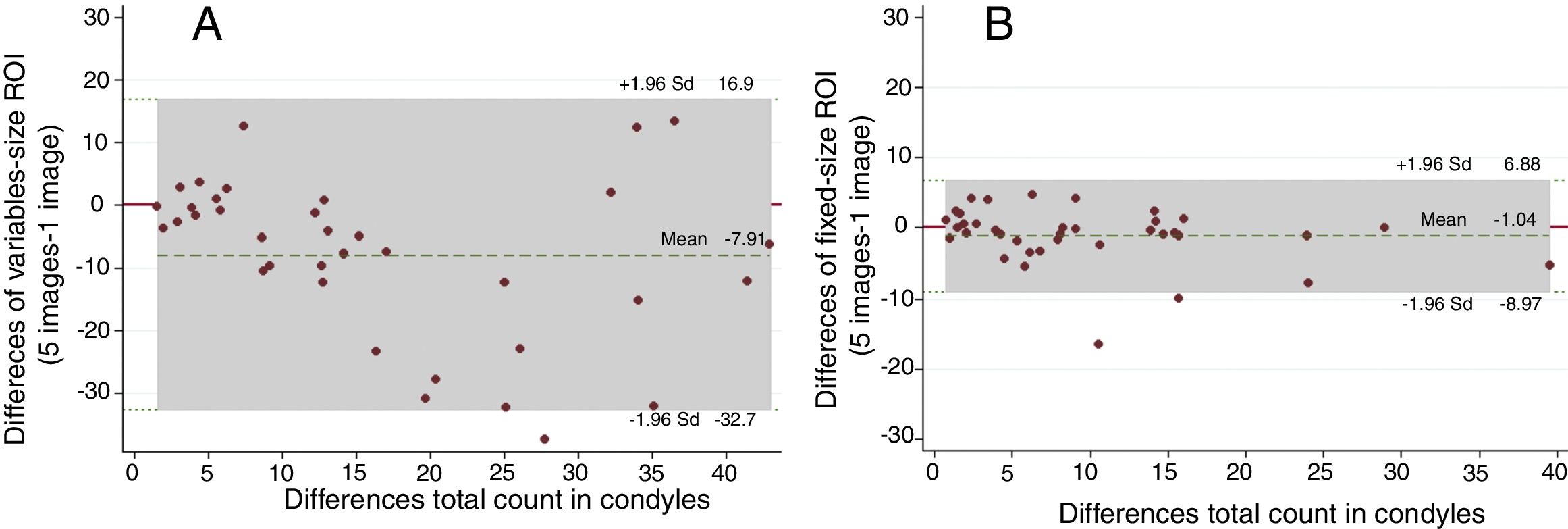
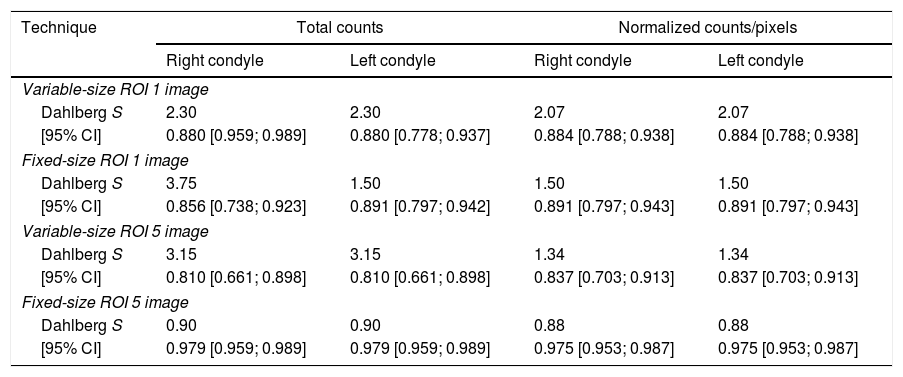
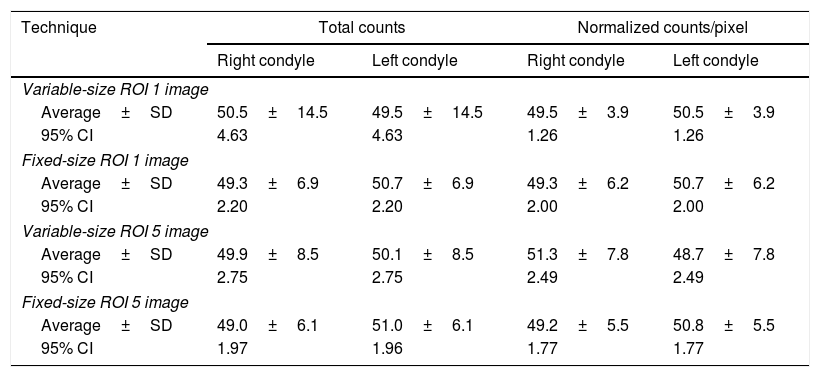
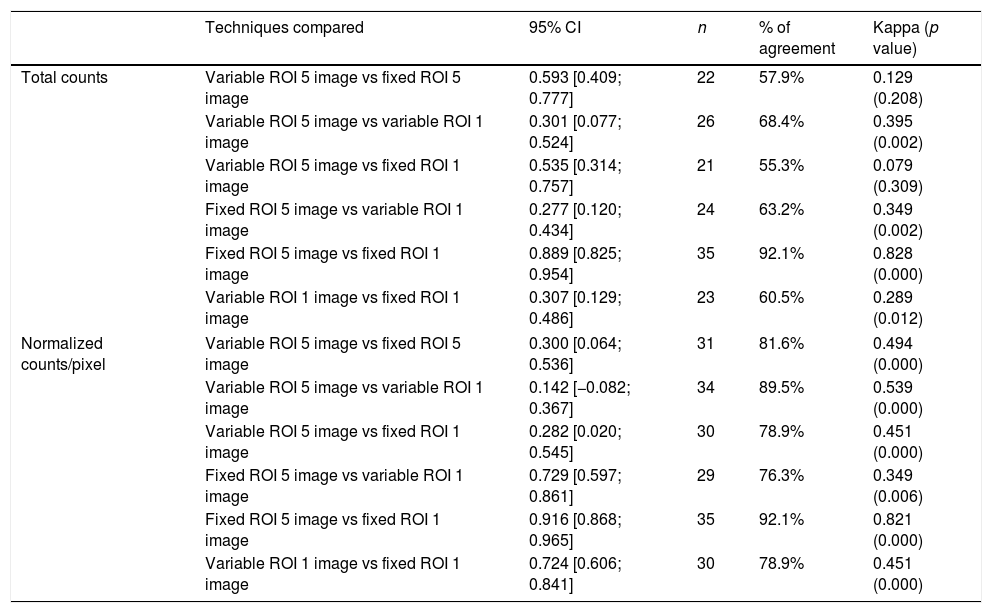
ResultsHigher reproducibility and repeatability were obtained in 5-image fixed-size ROI method (intra-class correlation coefficient: 0.979 [0.959; 0.989]). A high grade of diagnostic agreement (97.4%) was also attained in fixed methods (Kappa 0.940, p value: 0.000) from either total or normalized counts. There was no difference between fixed-size 1 vs 5 image methods. The methods based on variable-size ROI had a low grade of agreement (Kappa<0.20). More positive cases were identified using one image, ROI variable total counts (27 cases), but when the counts were normalized, they presented a lower number (5 cases).
ConclusionFive-image fixed-size ROI provides the best intra-operator and inter-operator reliability for the diagnosis of unilateral condylar hyperplasia. In the four methods using normalized counts fewer positive cases were detected (≥10%), unlike with total counts when more positive cases were found.
Comparar la variabilidad, reproducibilidad y repetitividad de cuatro métodos de evaluación cuantitativa del SPECT con 99mTc-MDP en pacientes con sospecha clínica de hiperplasia condilar unilateral (HCU).
MétodosEstudio observacional descriptivo, realizado en 38 imágenes SPECT de pacientes con signos clínicos y radiográficos de HCU. Estos fueron interpretados utilizando cuatro métodos cuantitativos de la prueba SPECT: (1) Región objeto de interés (ROI) variable de 1 imagen, (2) ROI fija de 1,76cm2 en 1 imagen, (3) ROI variable de 5 imágenes y (4) ROI fija de 1,76cm2 en 5 imágenes. Cada una de las imágenes fue leída simultáneamente de forma independiente por dos médicos nucleares tanto en sus cuentas totales como en las cuentas normalizadas para cuantificar la reproducibilidad (variabilidad inter-observador) de los métodos y la repetitividad (variabilidad intra-observador).
ResultadosMayor reproducibilidad y repetitividad fue obtenida con el método de ROI fija de 1.76cm2 en 5 imágenes (coeficiente de correlación intra-clase de 0,979 [0,959; 0,989]). De igual forma se obtuvo un mayor grado de correspondencia diagnóstica (97,4%) en los métodos fijos (Kappa 0,940, valor p: 0.000) tanto en cuentas totales como normalizadas. No se encontraron diferencias entre ellos. Los métodos basados en el análisis de ROIs variables presentaron un menor grado de correspondencia (Kappa<0,20). El mayor número de casos positivos fue identificado utilizando una ROI variable de 1 imagen en cuentas totales (27 casos), pero al normalizar las cuentas presentaron el menor número (5 casos).
ConclusionesDe acuerdo a la variación intra e interoperadores, la técnica de mejor repetitividad y reproducibilidad para el diagnóstico de la hiperplasia condilar unilateral fue la ROI fija de 5 imágenes. En los cuatro métodos, al usar cuentas normalizadas, se detectaron menos casos positivos (≥10%) y con cuentas totales mas casos positivos.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)