Recent studies have found increased markers of endothelial activation in men with chronic spinal cord injury. This study was conducted to determine the effects of arm-cranking exercise on endothelial dysfunction in male adults with chronic SCI.
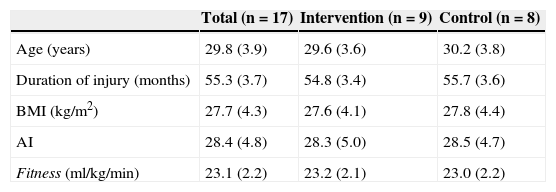
MethodA prospective randomised study of 17 sedentary adult males with chronic SCI at or under T5 level. Nine performed a supervised exercise programme at a moderate intensity (arm-cranking: 12 weeks, 3 sessions/week). Plasma levels of endothelin-1, soluble intercellular adhesion molecule type 1 (sICAM-1), and soluble vascular adhesion molecule type 1 (sVCAM-1) were assessed by ELISA. Outcome measurements also included physical fitness and total body fat mass percentage.
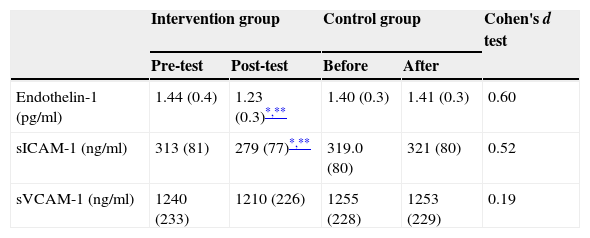
ResultsWe observed both in the randomised and in the before–after studies a significant reduction of the levels of endothelin-1 and sICAM-1. Furthermore, significant improvements of both physical fitness and body composition were also found.
ConclusionArm-cranking exercise improved endothelial dysfunction in adult males with chronic SCI. Long-term studies are still required to determine whether the correction of endothelial dysfunction improves the clinical outcomes of adults with chronic SCI.
La morbimortalidad cardiovascular se ha incrementado entre las personas con lesión medular crónica (LMC). Se planteó como objetivo determinar el efecto del ejercicio sobre marcadores de disfunción endotelial en adultos sedentarios con LMC.
MétodoEstudio prospectivo aleatorizado en 17 adultos varones con LMC a nivel o debajo de T5. Nueve de ellos realizaron un programa supervisado de ejercicios en ergómetro de manivela a intensidad moderada (12 semanas, 3 sesiones/semana). Se determinaron mediante enzimoinmunoanálisis los valores plasmáticos de endotelina-1, fracción soluble de la molécula de adhesión celular vascular tipo-1, y fracción soluble de la molécula de adhesión intercelular tipo-1 (sICAM-1), antes y después del programa de ejercicio. La capacidad aeróbica y el porcentaje de masa grasa también fueron evaluados.
ResultadosTras completar el programa de entrenamiento, tanto en el estudio comparativo como en el estudio antes-después, se observó una disminución significativa de los valores de endotelina-1 y fracción soluble de la molécula de adhesión intercelular tipo-1. Asimismo, se observó una mejora estadísticamente significativa de la capacidad aeróbica y la composición corporal.
ConclusiónEl ejercicio mejoró la disfunción endotelial en varones adultos con LMC.