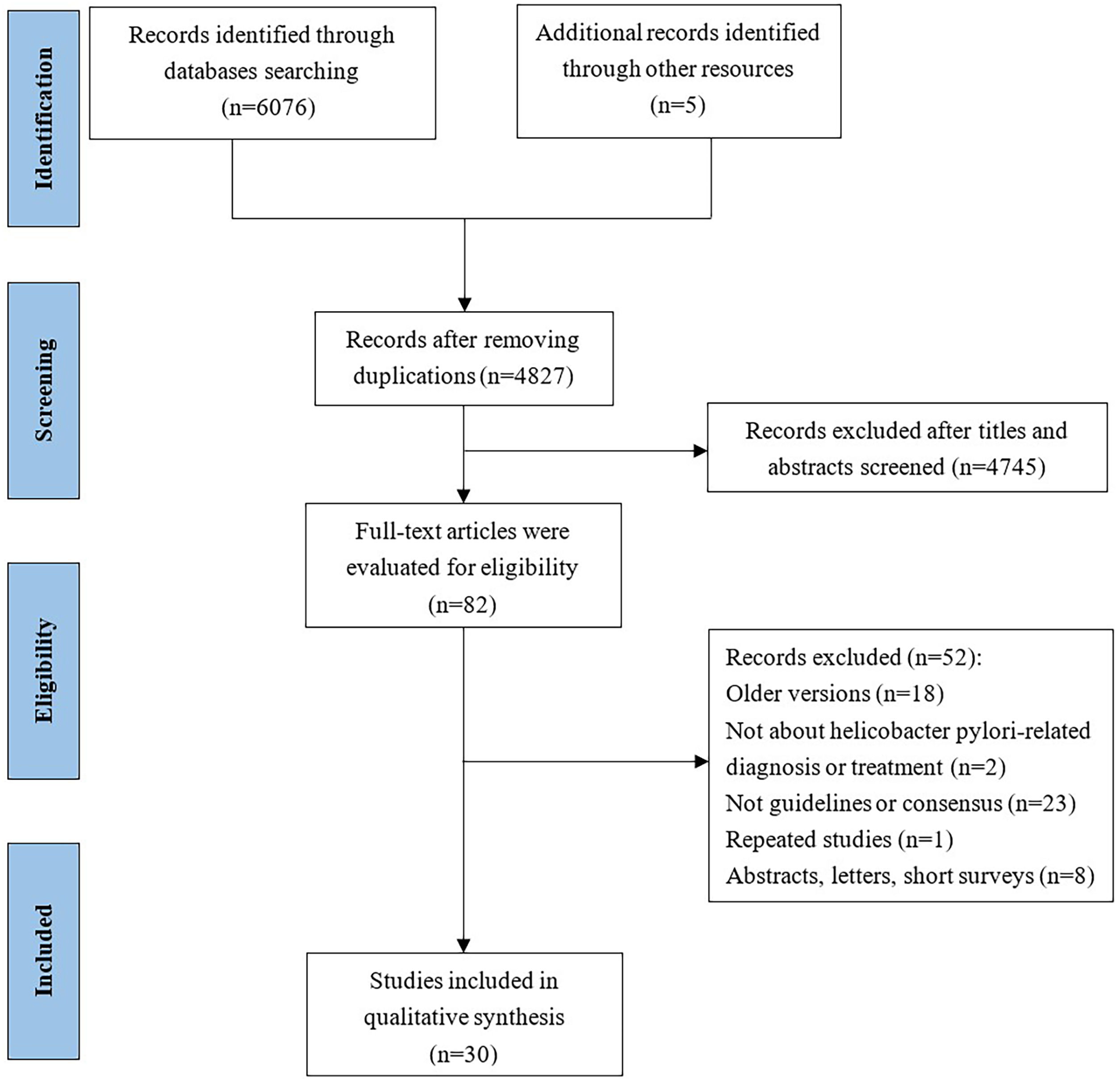
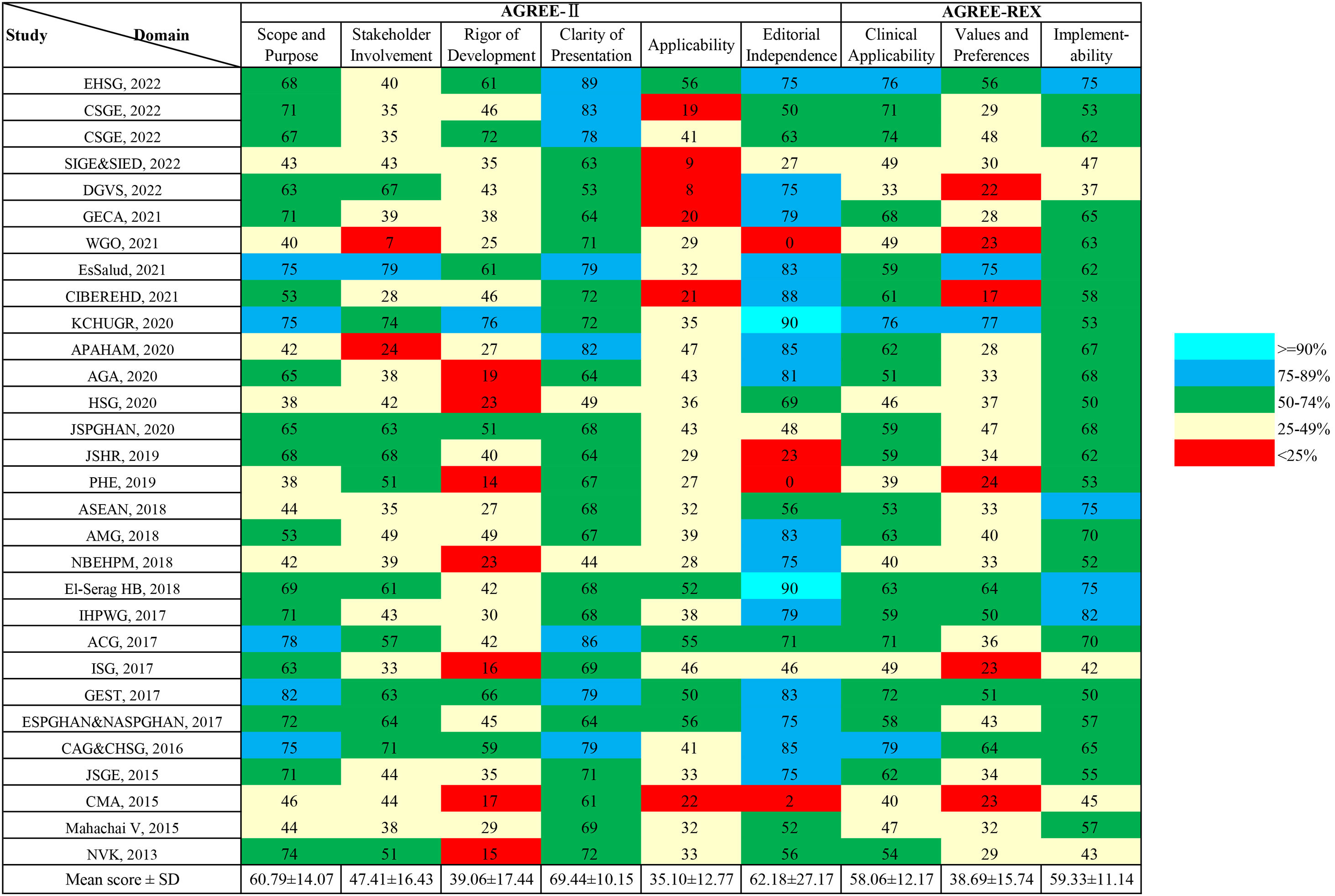
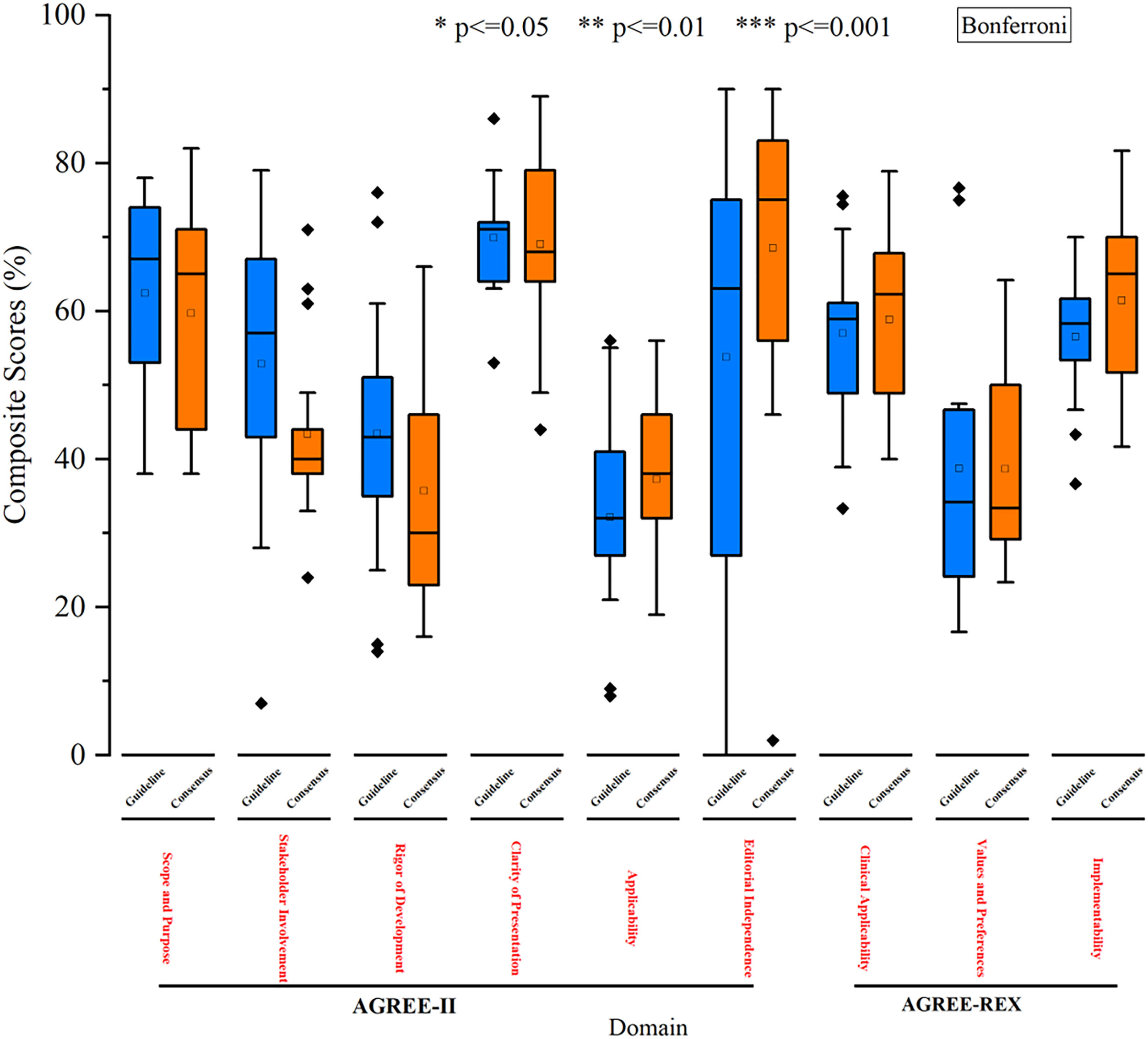
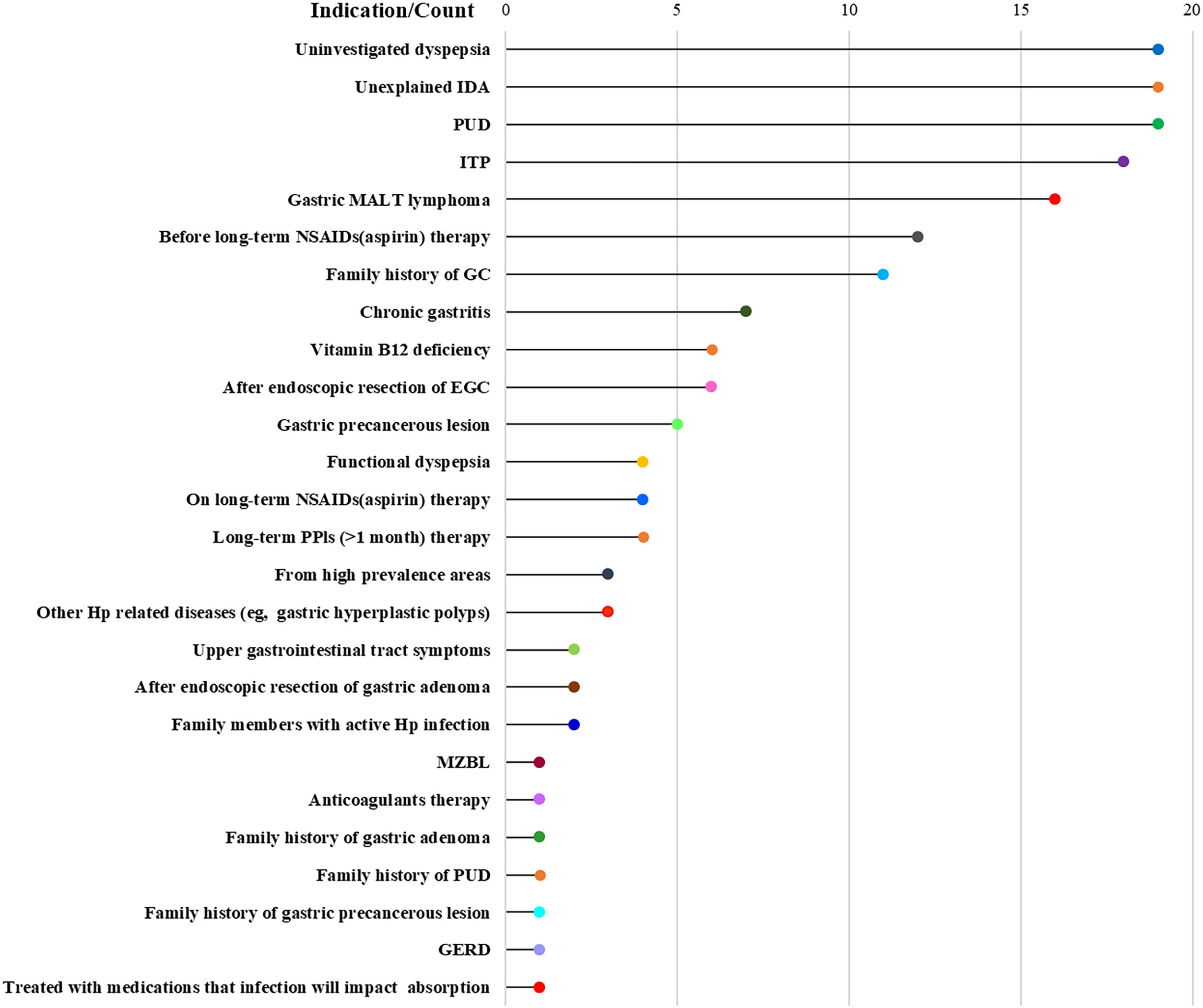
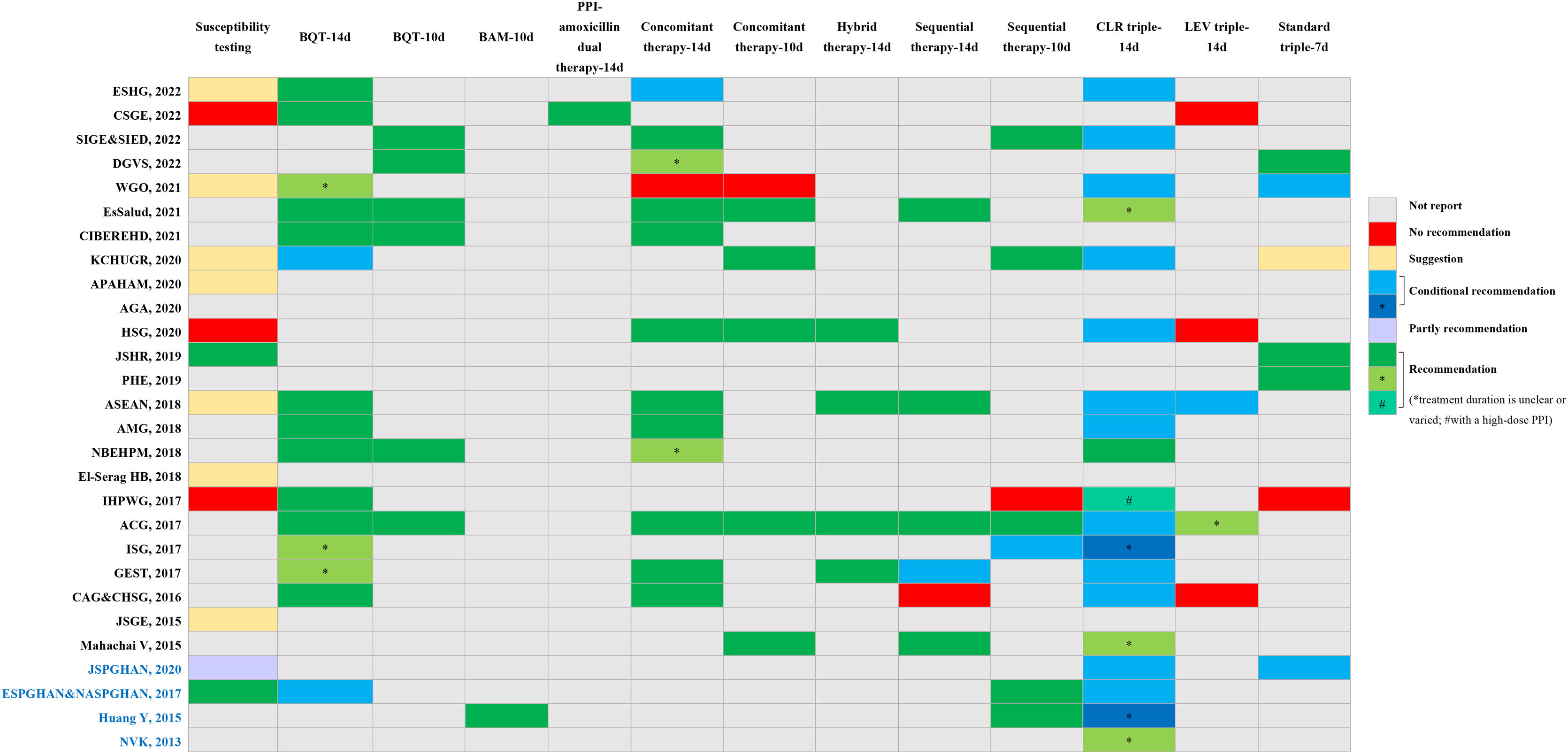
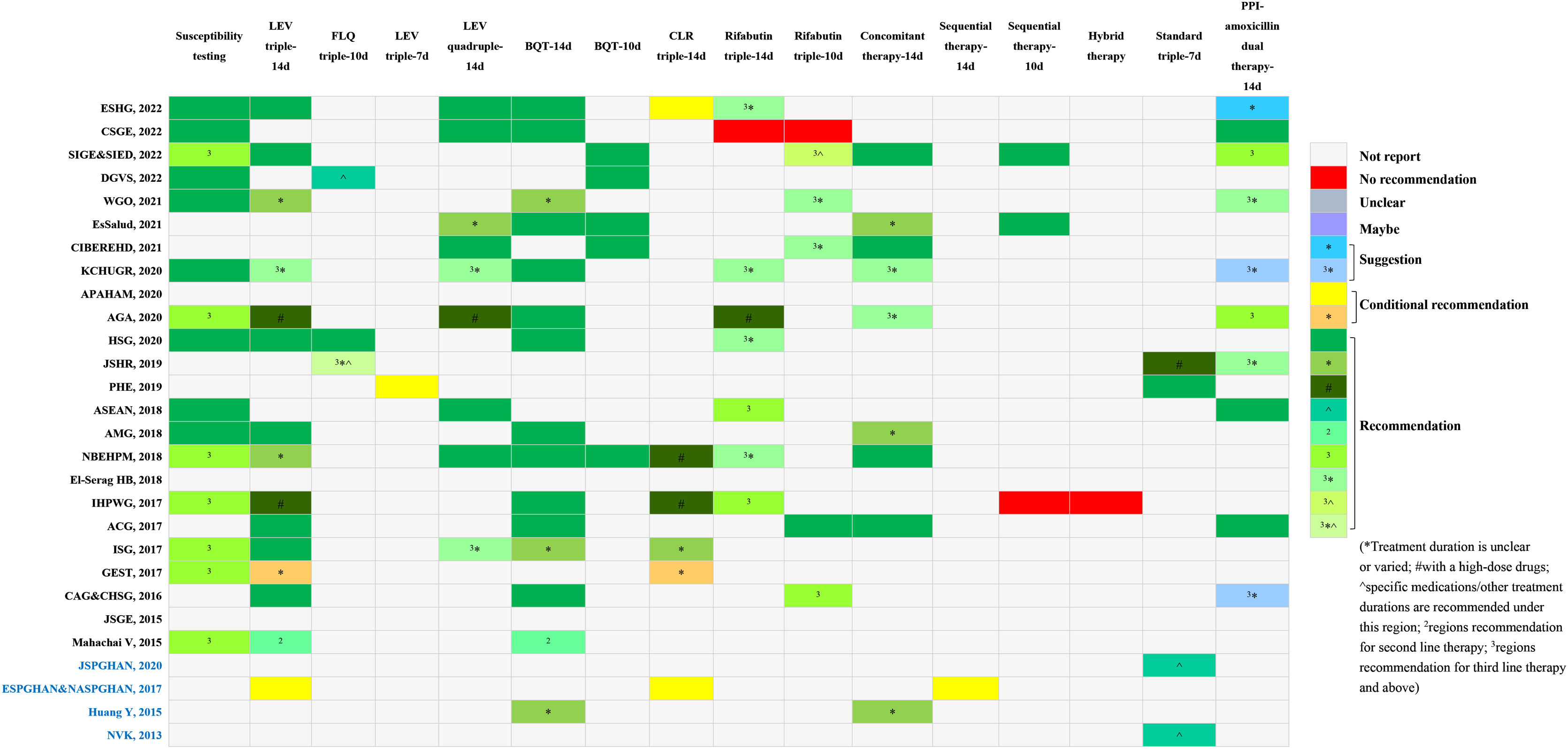
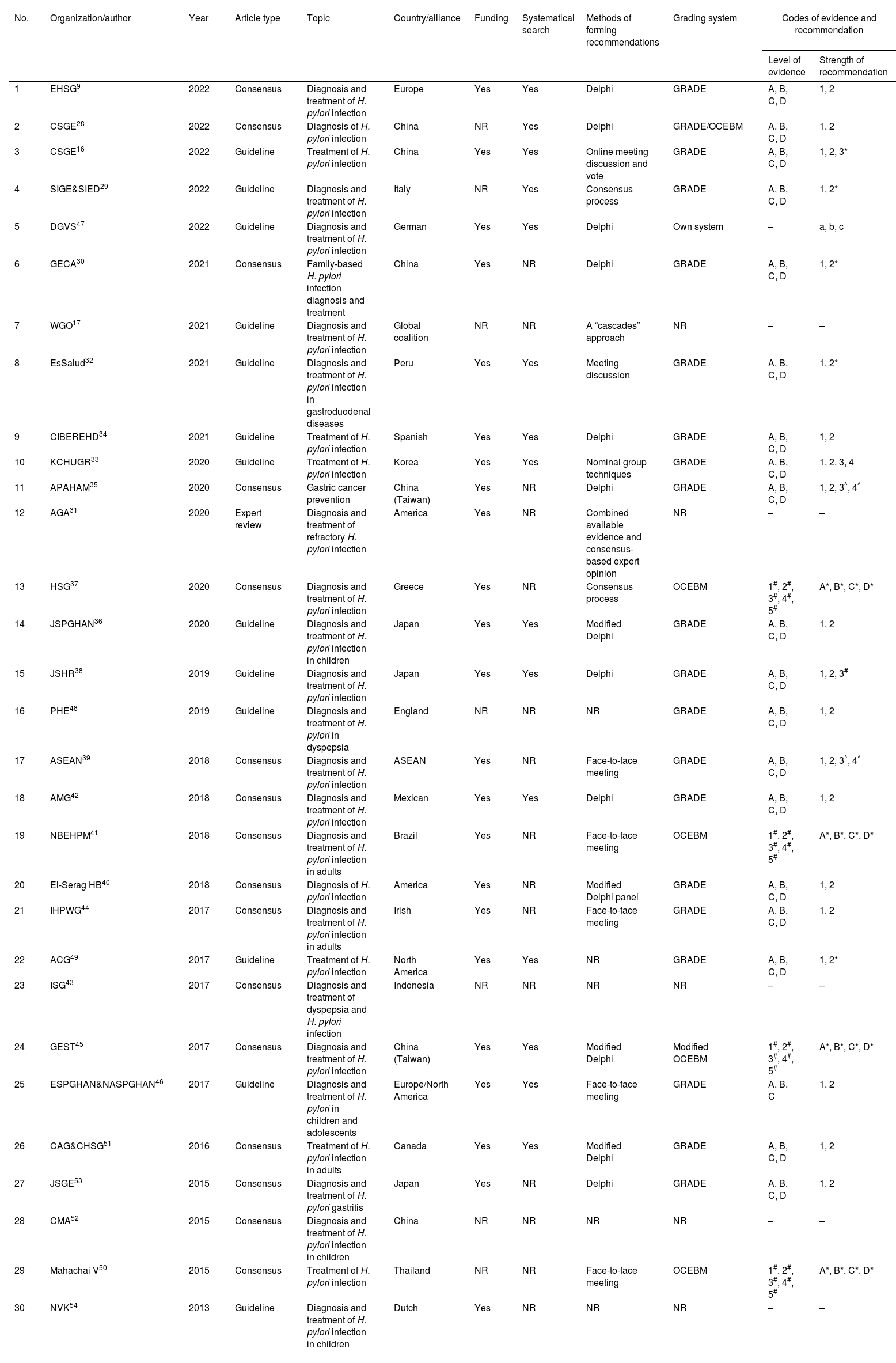
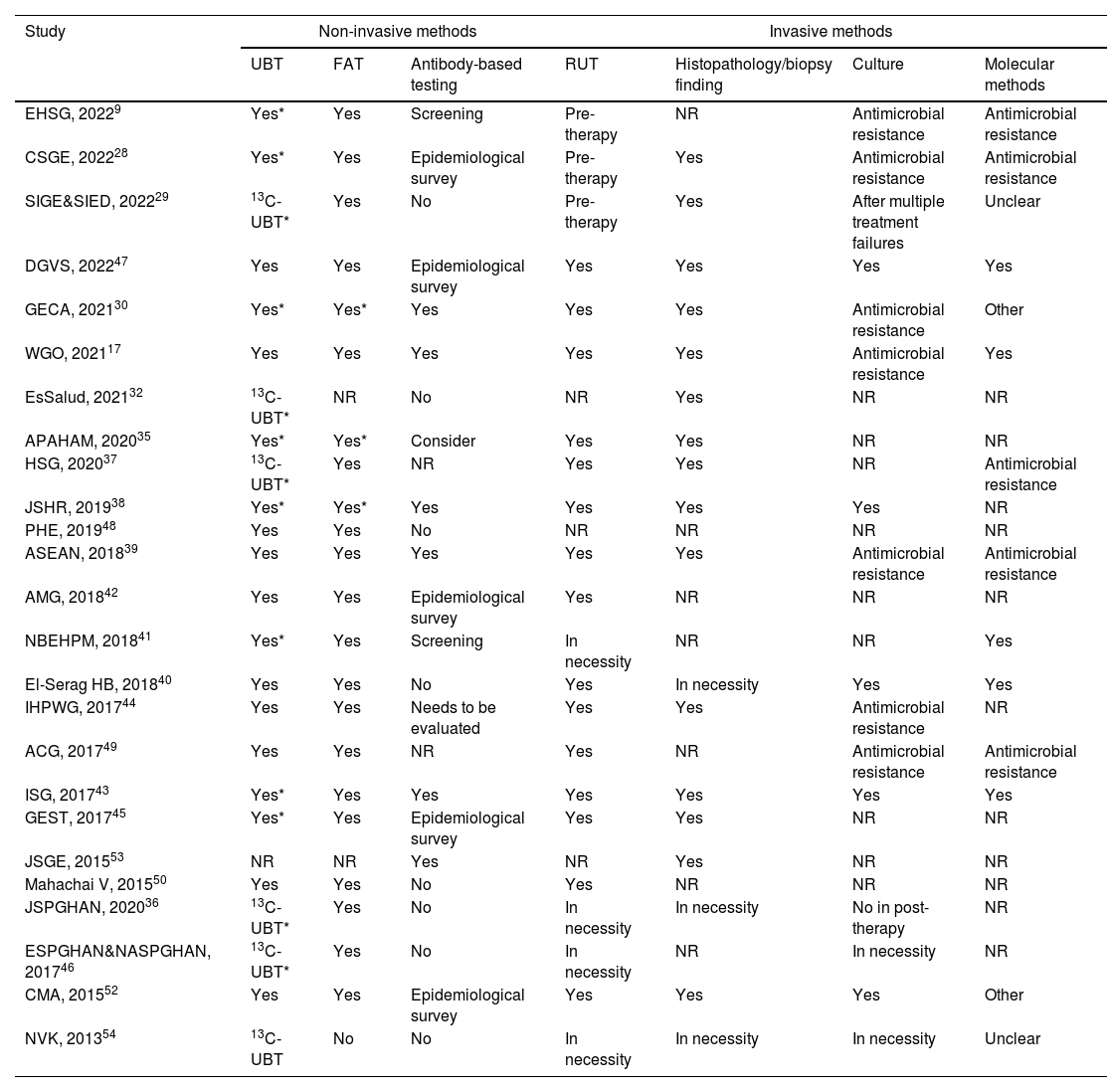
We conducted this study to systematically review and assess the current clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) related to the diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection. The aim was to evaluate the quality of these included CPGs and provide clinicians with a convenient and comprehensive reference for updating their own CPGs. We searched four databases to identify eligible CPGs focusing on H. pylori diagnosis and treatment recommendations. The results were presented using evidence mappings. Quality and clinical applicability were assessed comprehensively using AGREE-II and AGREE-REX. Statistical tests, specifically Bonferroni tests, were employed to compare the quality between evidence-based guidelines and consensus. A total of 30 eligible CPGs were included, comprising 17 consensuses and 13 guidelines. The quality showed no statistical significance between consensuses and guidelines, mainly within the moderate to low range. Notably, recommendations across CPGs exhibited inconsistency. Nevertheless, concerning diagnosis, the urea breath test emerged as the most frequently recommended method for testing H. pylori. Regarding treatment, bismuth quadruple therapy stood out as the predominantly recommended eradication strategy, with high-dose dual therapy being a newly recommended option. Our findings suggest the need for specific organizations to update their CPGs on H. pylori or refer to recently published CPGs. Specifically, CPGs for pediatric cases require improvement and updating, while a notable absence of CPGs for the elderly was observed. Furthermore, there is a pressing need to improve the overall quality of CPGs related to H. pylori. Regarding recommendations, additional evidence is essential to elucidate the relationship between H. pylori infection and other diseases and refine test indications. Clinicians are encouraged to consider bismuth quadruple or high-dose dual therapy, incorporating locally sensitive antibiotics, as empirical radical therapy.
.
Hemos realizado este estudio para revisar y evaluar sistemáticamente las guías de práctica clínica (GPC) actuales sobre las recomendaciones de diagnóstico y tratamiento de la infección por Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), así como valorar la calidad de las GPC incluidas. Esperamos que esto facilite a los clínicos el diagnóstico al igual que el tratamiento y proporcione una referencia para la actualización de las GPC. Se realizaron búsquedas en cuatro bases de datos para encontrar GPC elegibles sobre recomendaciones de diagnóstico y tratamiento de H. pylori y los resultados se presentaron en mapeos de evidencia. Se emplearon la Appraisal of Guidelines, Research and Evaluation Colaboration (AGREE) II y la AGREE-Recommendation EXcellence (REX) para evaluar rotundamente la índole y la aplicabilidad clínica. La calidad entre las guías basadas en la evidencia y los consensos se comparó mediante pruebas estadísticas de Bonferroni. Se incluyeron 30 GPC elegibles, de las cuales 17 eran consensos y 13 guías. La calidad no tuvo significación estadística entre consensos y guías, siendo en su mayoría moderada o incluso baja. Las recomendaciones de las GPC presentaban incoherencias. Sin embargo, en cuanto al diagnóstico, la prueba del aliento con urea fue el método más recomendado para detectar H. pylori. Y en cuanto al tratamiento, la terapia cuádruple con bismuto fue la estrategia de erradicación más utilizada, mientras el método dual a dosis altas es la recomendada recientemente. Nuestros hallazgos sugieren la necesidad de que organizaciones específicas actualicen sus GPC sobre H. pylori o se remitan las publicadas recientemente. Las GPC para niños deberían mejorarse y actualizarse, y faltan también las de ancianos. Además, es necesario mejorar la calidad de las GPC sobre H. pylori. En cuanto a las recomendaciones, se necesitan más pruebas que ilustren la relación entre la infección por H. pylori y otras enfermedades para perfeccionar las indicaciones de las pruebas, y los clínicos podrían elegir la terapia cuádruple con bismuto o la dual a dosis altas con antibióticos localmente sensibles como tratamiento radical empírico.