The role of Aeromonas species in gastrointestinal disease is controversial. The aim was to analyze not only the virulence genes between different species of Aeromonas isolated from feces, but the distribution of these virulence genes between enterotoxigenic strains and co-pathogen strains.
MethodsRetrospective study of isolates of Aeromonas spp. in feces (2016–2021). The protocol included coproculture, identification by MALDI-TOF and confirmation by multiplex PCR. SPSS Statistics program was used.
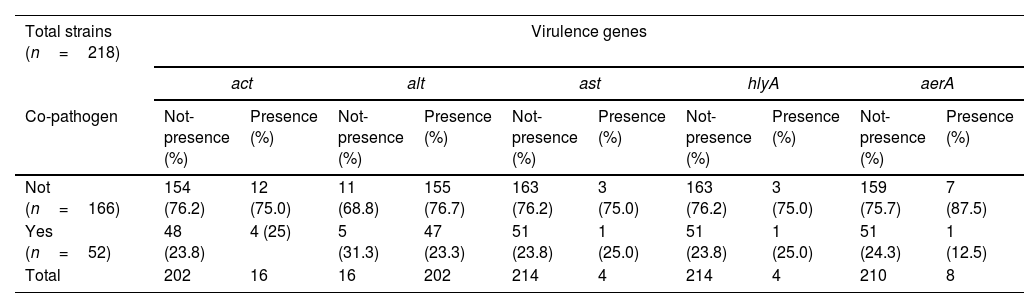
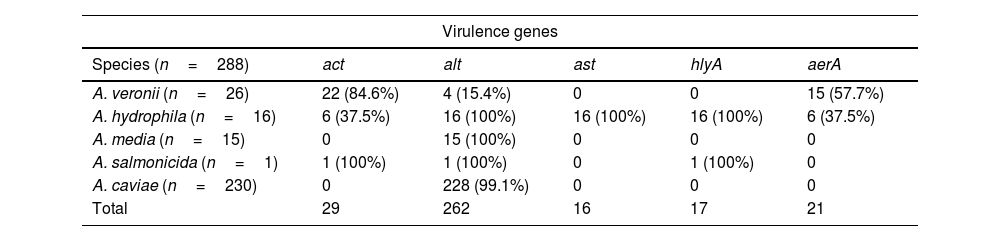
ResultsA total of 288 strains were studied for the virulence genes between different species of Aeromonas. To compare virulence genes between Aeromonas as co-pathogen and those isolated alone, 218 strains of the global set were used; 52 as co-pathogens compared with 166 Aeromonas without associated pathogen as controls.
ConclusionsWe found no significant differences in the distribution of virulence genes versus co-existence of co-pathogens or not. A. hydrophila is the potentially most virulent species of our set.
El papel de las especies de Aeromonas en las enfermedades gastrointestinales es controvertido. El objetivo fue analizar no solo los genes de virulencia entre diferentes especies de Aeromonas aisladas de heces, sino también la distribución de estos genes de virulencia entre cepas enterotoxigénicas y co-patógenas.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo de aislamientos de Aeromonas spp. en heces (2016-2021). El protocolo incluyó coprocultivo, identificación por MALDI-TOF y confirmación por PCR multiplex. Se utilizó el programa SPSS Statistics.
ResultadosSe estudiaron un total de 288 cepas para los genes de virulencia entre diferentes especies de Aeromonas. Para comparar genes de virulencia entre Aeromonas como co-patógeno y los aislados únicos, se utilizaron 218 cepas del conjunto global; 52 como co-patógenos, comparados con 166 Aeromonas sin patógeno asociado como controles.
ConclusionesNo se encontraron diferencias significativas en la distribución de los genes de virulencia versus coexistencia de co-patógenos o no. Aeromonas hydrophila es la especie potencialmente más virulenta de nuestro muestreo.
Article
Socio de la Sociedad Española de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica

Para acceder a la revista
Es necesario que lo haga desde la zona privada de la web de la SEIMC, clique aquí
Para realizar los cursos formativos
La actividad estará abierta para socios de la SEIMC. IMPORTANTE, recuerde que requiere registro previo gratuito. Empezar aquí