To determine if primary intravitreal injection of triamcinolone acetonide (TA) plus grid laser photocoagulation (GLP) is effective in treating cystoid diabetic macular edema (DME).
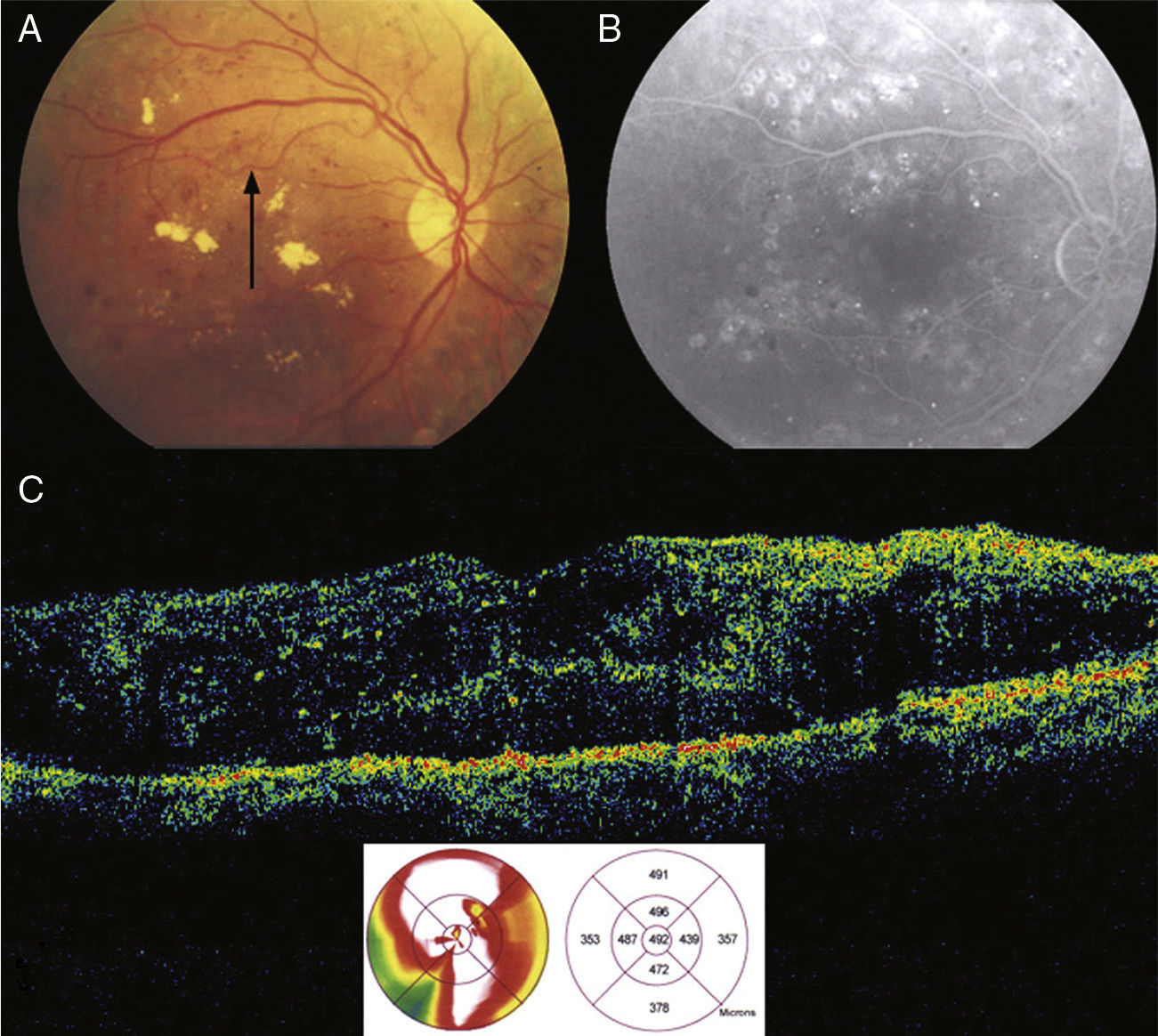
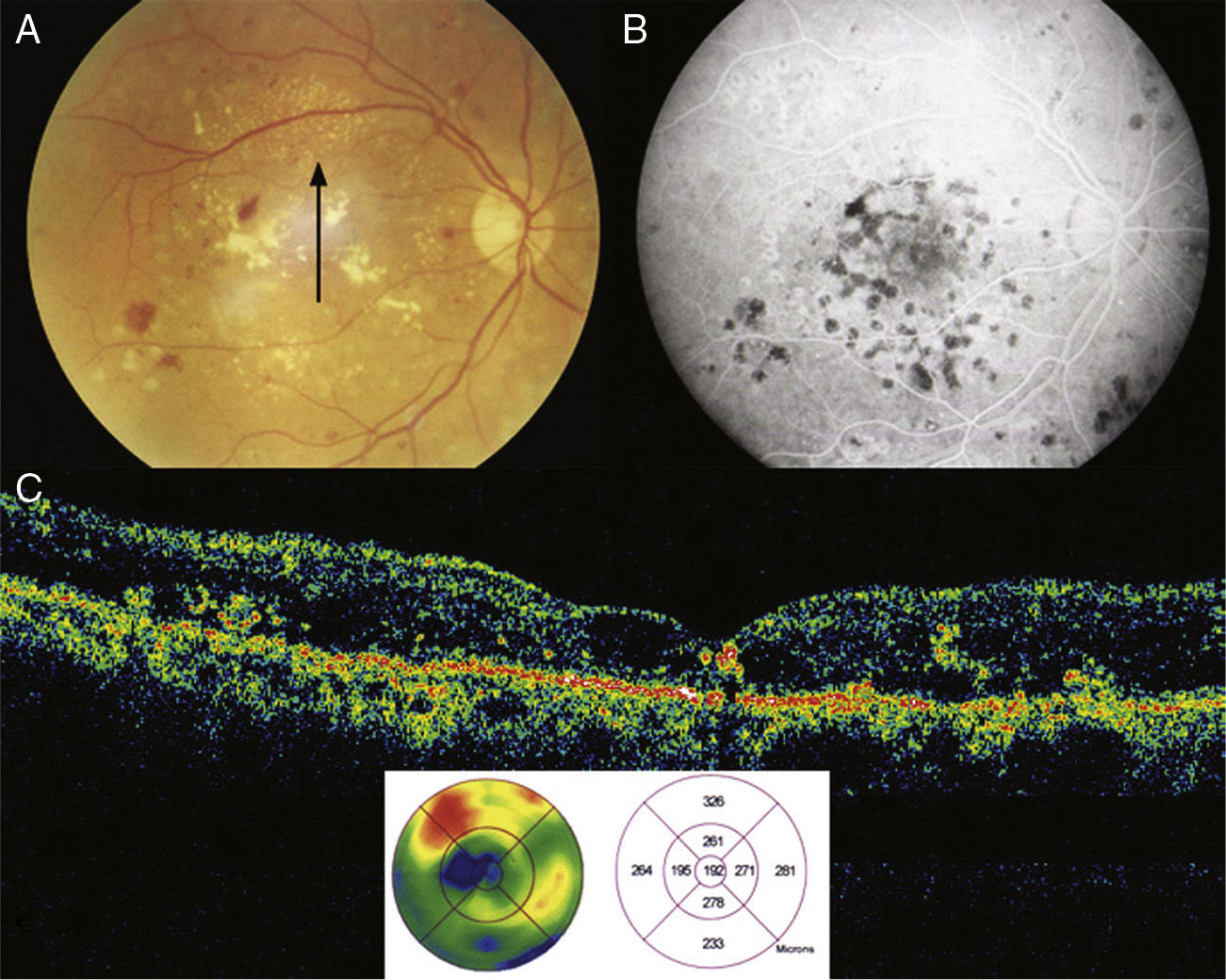
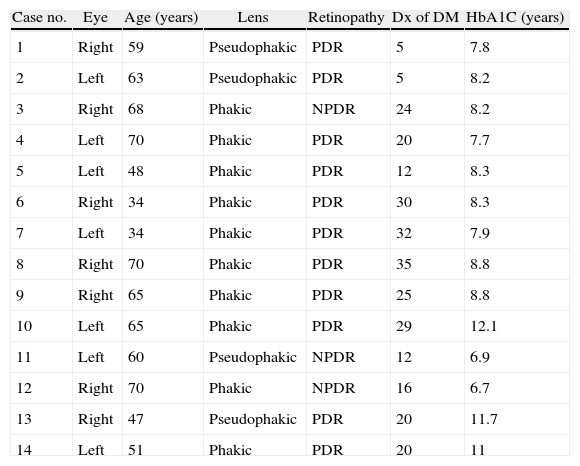
MethodsProspective comparative non-randomized clinical trial. Fourteen eyes (14 patients) diagnosed with cystoid DME were treated with GLP according to the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) guidelines, plus an intravitreal injection of 4mg of TA. A matched control group (16 eyes [16 patients]) treated with GLP was selected retrospectively from our medical records. Best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), and quantitative change in optical coherence tomography (OCT) macular thickness were assessed.
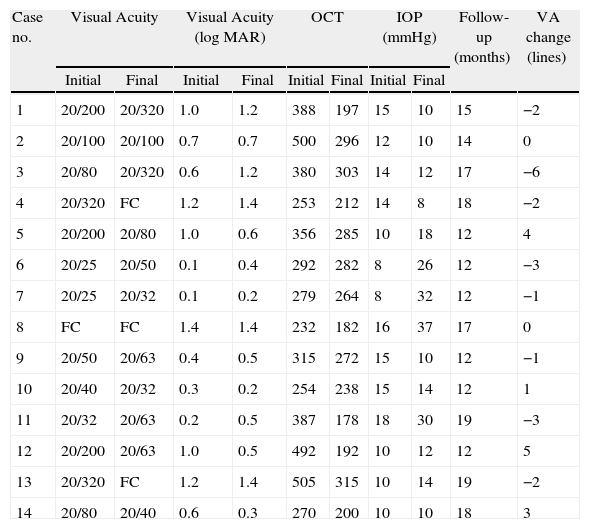
ResultsMean follow up was 14.9 months (12 to 19 months). In 3 (21.4%) eyes BCVA increased >2 ETDRS lines, in 5 (35.7%) eyes BCVA remained the same, and BCVA decreased >2 ETDRS lines in 6 (42.8%) eyes. Central macular thickness, as measured by OCT, decreased a mean of 106.2μm (30.2%). The difference with the control group was not statistically significant (p=0.2). Four (28.5%) eyes developed an increased in intraocular pressure in our study group.
ConclusionsAlthough all of our patients showed an improvement of cystoid DME by means of OCT and fluorescein angiography, 42.8% (6 eyes) lost 2 or more lines in BCVA with primary intravitreal injection of TA plus GLP. Primary intravitreal injection of TA plus GLP may not be effective for cystoid DME at 12 months.
Determinar si el tratamiento inicial de inyección intravítrea de triamcinolona (TA) asociada a la fotocoagulación con láser en rejilla (FLR) es más efectivo que el tratamiento láser aislado en el edema macular diabético (EMD) quístico.
MétodosEstudio clínico prospectivo no aleatorizado. Catorce ojos (14 pacientes) con diagnóstico de EMD quístico fueron tratados con FLR, según el protocolo del Estudio de Tratamiento Precoz de la Retinopatía Diabética (ETDRS), asociando una inyección de 4mg de TA. Se seleccionó de forma retrospectiva un grupo control (16 ojos [16 pacientes]) tratado únicamente con FLR. Las principales medidas a analizar fueron los cambios en la agudeza visual (AV) y en el grosor del edema macular medido por tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT).
ResultadosEn el grupo tratado, la media de seguimiento fue de 14,9 meses (rango 12 a 19). La AV en tres ojos (21,4%) se incrementó > 2 líneas ETDRS, en cinco ojos (35,7%) permaneció sin cambios y en 6 ojos (42,8%) disminuyó >2 líneas ETDRS. El grosor macular central disminuyó de media 106,2μm (30,2%). No hubo diferencias estadísticamente significativas con el grupo control, en los cambios de la AV ni en la disminución del espesor macular (p=0,2). En 4 ojos (28,5%) hubo incremento patológico de la presión intraocular.
ConclusionesAunque todos nuestros pacientes mejoraron anatómicamente el EMD quístico en relación con los parámetros de OCT y angiografía fluoresceínica, el 42,8% perdieron dos o más líneas de AV con el tratamiento asociado de inyección intravítrea de TA y FLR. Añadir la inyección intravítrea de TA a la FLR no resultó efectiva a los 12 meses de seguimiento para el manejo del EMD quístico.