To evaluate the correlations between PADUA and RENAL scores, WIT and postoperative complications in a cohort of patients who underwent elective open or minimally invasive nephron sparing surgery for renal cell carcinoma.
Materials and methodsWe analyzed 96 consecutive patients who underwent partial nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma between 2004 and 2013 at our Institution. The Spearman test was used to compare categorical variables. For all statistical analyses, a two-sided p<.05 was considered statistically significant.
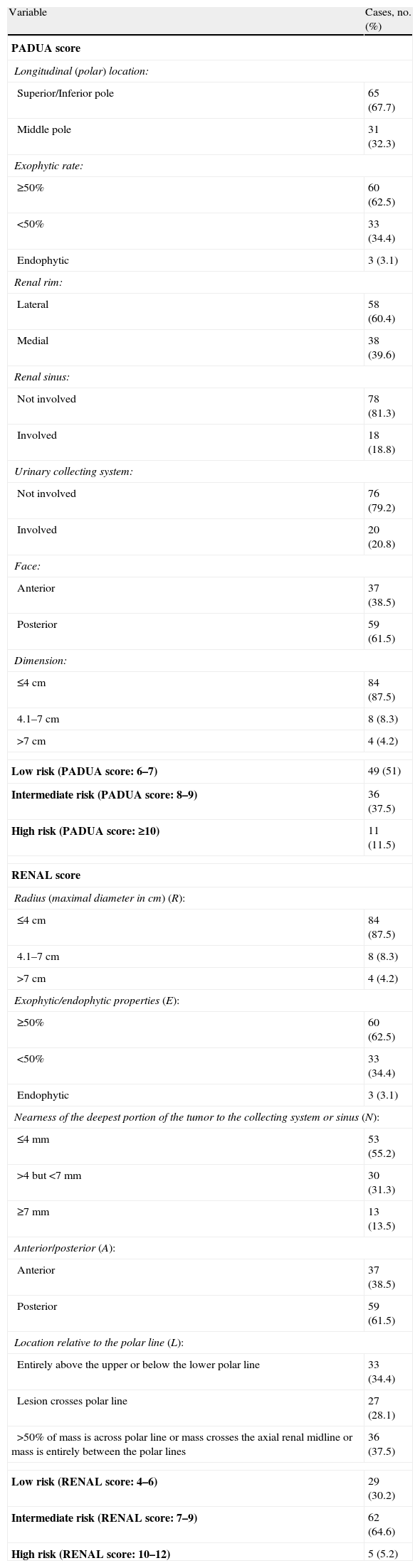
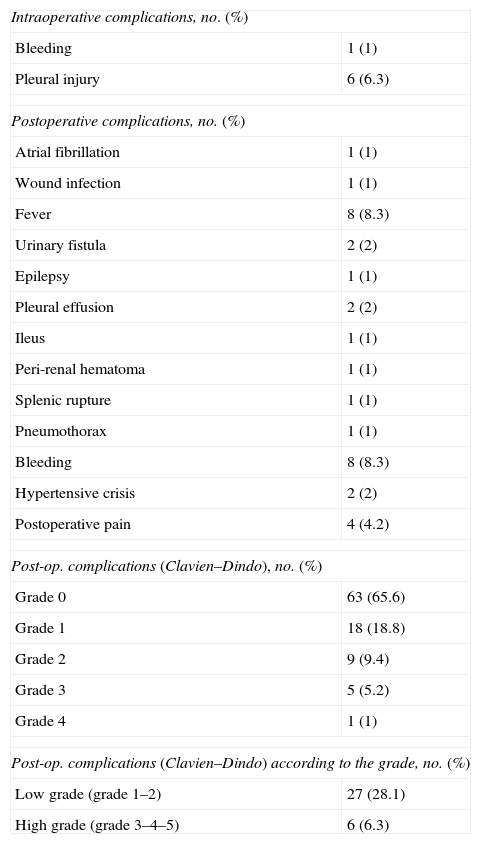
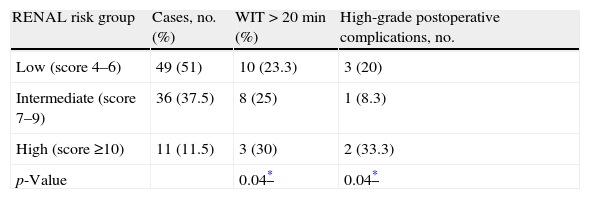
ResultsThe median (IQR) PADUA score was 7 (7–8) and the median (IQR) RENAL score was 7 (6–8). The median (IQR) warm ischemia time was 14min (8–20). Low grade and high grade postoperative complications were found in 27 (28.1%) and 6 (6.3%) patients, respectively. PADUA risk group categories significantly correlated with WIT>20min and high grade postoperative complications, respectively (p=.04), regardless of the surgical approach. RENAL risk group categories significantly predicted longer hilar clamping time in our cohort (p=.04), but no statistically significant correlations with high grade postoperative complications were found.
ConclusionsIn our retrospective series nephrometric scores demonstrated to significantly predict longer warm ischemia time and higher postoperative complications, especially in those patients with more challenging and complex renal tumors. Therefore, when planning to perform partial nephrectomy, urologists should widely use these comprehensive tools.
Evaluar las correlaciones entre puntuaciones PADUA y RENAL, TIC y complicaciones postoperatorias en una cohorte de pacientes que se sometieron a cirugía de conservación de nefronas por elección abierta o mínimamente invasiva para el carcinoma de células renales.
Material y métodosAnalizamos 96 pacientes consecutivos que fueron sometidos a nefrectomía parcial por carcinoma de células renales entre 2004 y 2013 en nuestra institución. La prueba de Spearman se utilizó para comparar variables categóricas. Para todos los análisis estadísticos un valor de p<0,05 de 2 caras se consideró estadísticamente significativo.
ResultadosLa mediana de puntuación PADUA (RI) fue de 7 (7–8) y la puntuación RENAL mediana (RI) fue de 7 (6–8). La mediana de tiempo de isquemia caliente (RI) fue de 14min (8–20). Se encontraron complicaciones postoperatorias de grado bajo y alto en 27 (28,1%) y 6 (6,3%) pacientes, respectivamente. Las categorías de grupos de riesgo de PADUA se correlacionaron significativamente con TIC>20min y las complicaciones postoperatorias de alto grado, respectivamente (p=0,04), independientemente del abordaje quirúrgico. Las categorías de grupos de riesgo RENAL predijeron significativamente más tiempo de pinzamiento hiliar en nuestra cohorte (p=0,04), pero no se encontraron correlaciones estadísticamente significativas con las complicaciones postoperatorias de alto grado.
ConclusionesEn nuestra serie retrospectiva las puntuaciones nefrométricas demostraron predecir significativamente mayor tiempo de isquemia caliente y mayores complicaciones postoperatorias, especialmente en aquellos pacientes con tumores renales más difíciles y complejos. Por lo tanto, al planificar realizar la nefrectomía parcial los urólogos deberían utilizar ampliamente estas herramientas completas.