A simple and reliable method for diagnosing COVID 19 infections is the needed. The role of saliva in the transmission of the infection has already been established.
MethodSaliva and nasopharyngeal swabs from patients suspected to have COVID 19 infections were taken simultaneously, and the results of the RT-PCR were compared.
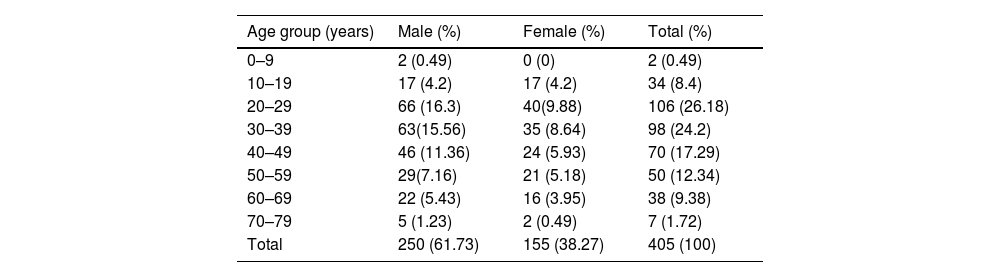
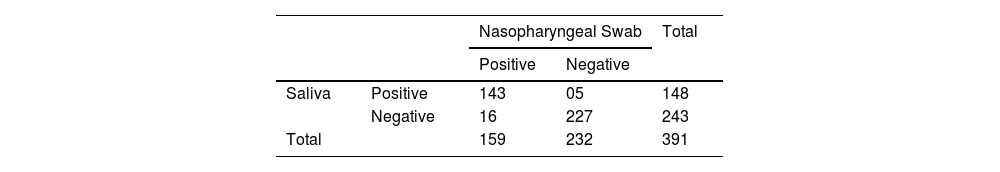
ResultTotal 405 samples were collected, of which 250 males and 155 females. In the 391 samples included for analysis, 370 (94.63%) samples were found to have concordance results, and 21 (5.37%) samples had discordant results.
ConclusionThe use of saliva to diagnose COVID 19 infection is reliable, and its use can be recommended.
Un método simple y confiable para diagnosticar infecciones por COVID 19 es necesario. Ya se ha establecido el papel de la saliva en la transmisión de la infección.
MétodoSe tomaron simultáneamente hisopos de saliva y nasofaríngeos de pacientes con sospecha de infección por COVID 19 y se compararon los resultados de la RT-PCR.
ResultadoSe recogieron 405 muestras, de las cuales 250 hombres y 155 mujeres. En las 391 muestras incluidas para el análisis, se encontró que 370 (94,63%) muestras tenían resultados de concordancia y 21 (5,37%) muestras tenían resultados discordantes.
ConclusiónEl uso de la saliva para diagnosticar la infección por COVID 19 es confiable y se puede recomendar su uso.