Understanding the effects of chemoradiotherapy (CRT) on the swallowing and voice functions of oropharyngeal cancer patients based on their reported perceptions, and how these are related to clinical and sociodemographic variables.
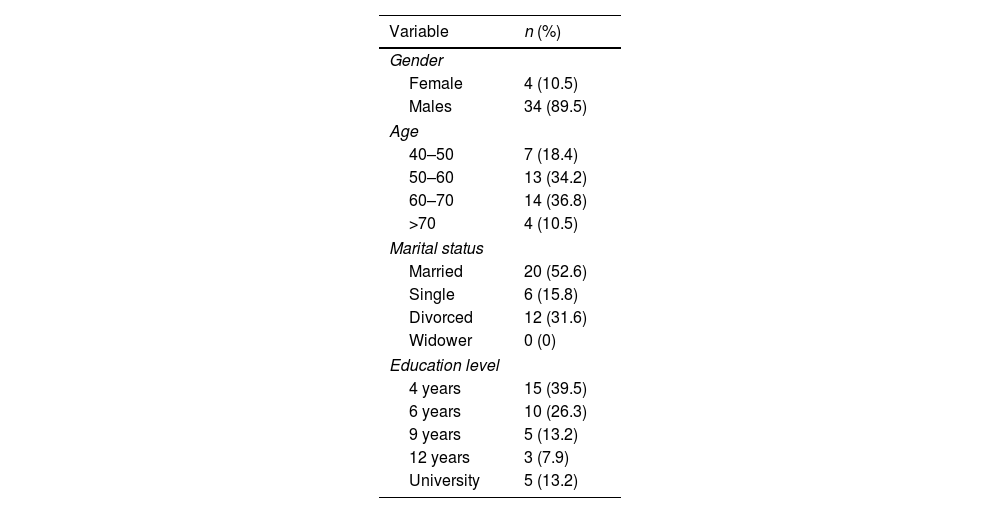
MethodsThirty-eight oropharyngeal cancer patients treated exclusively with CRT were included. Patients’ perceptions were assessed using the EORTC QLQ-C30, H&N43, VHI-9i, and SWAL-QOL questionnaires. Descriptive, correlational, and inferential analyses were performed.
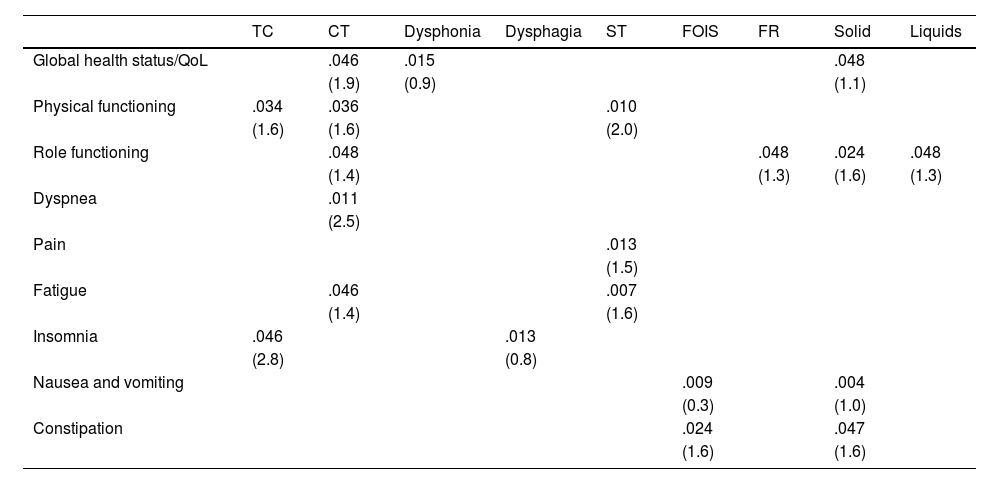
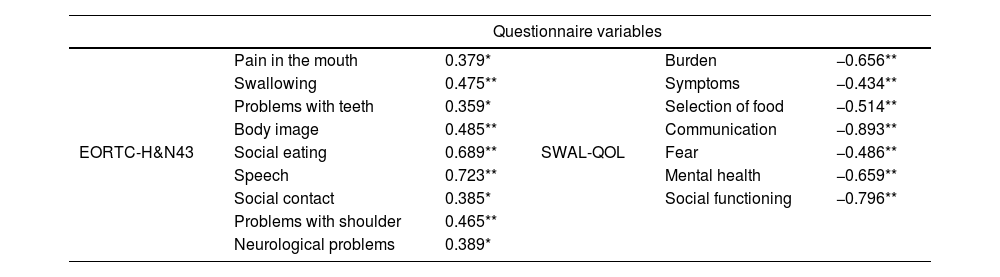
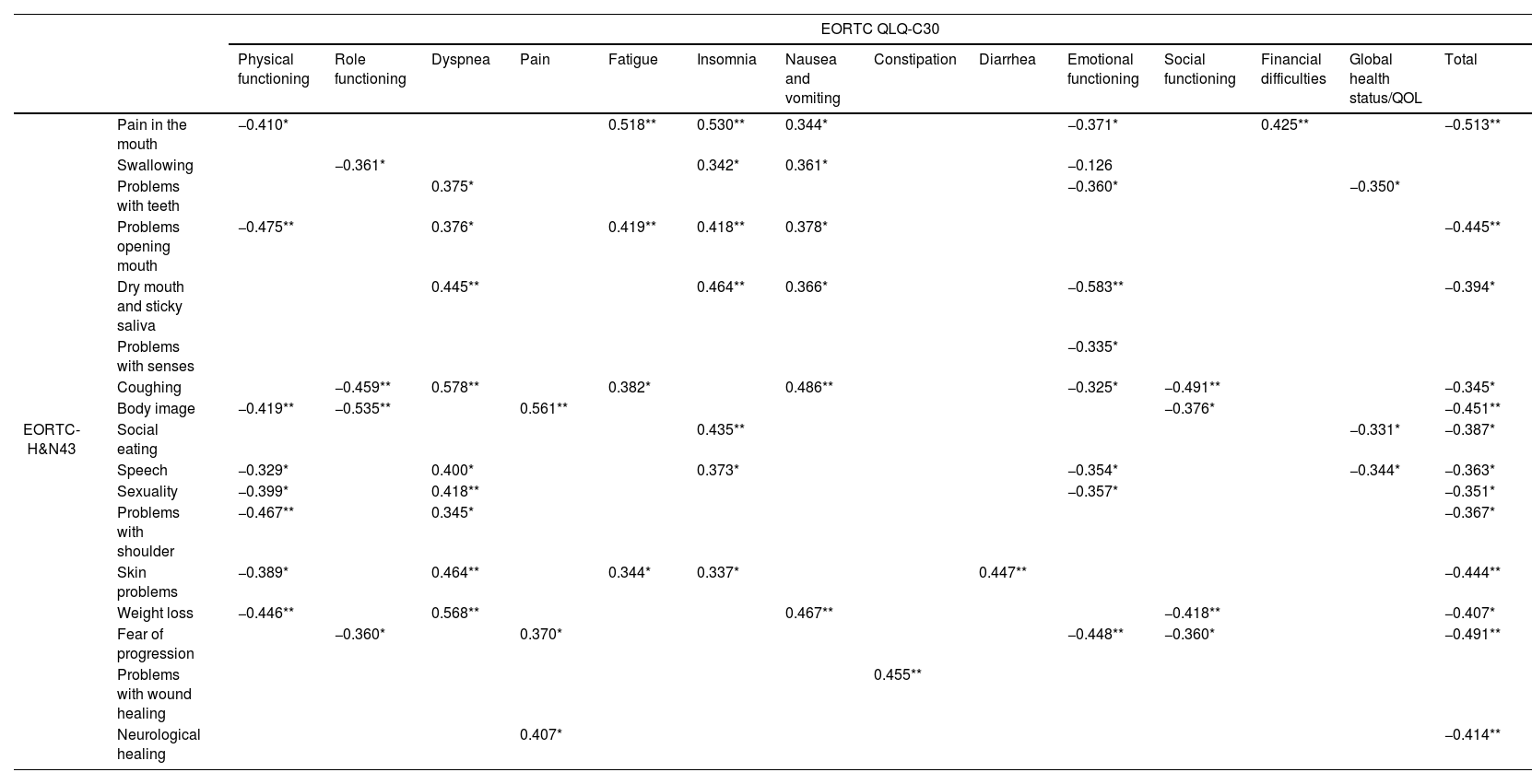
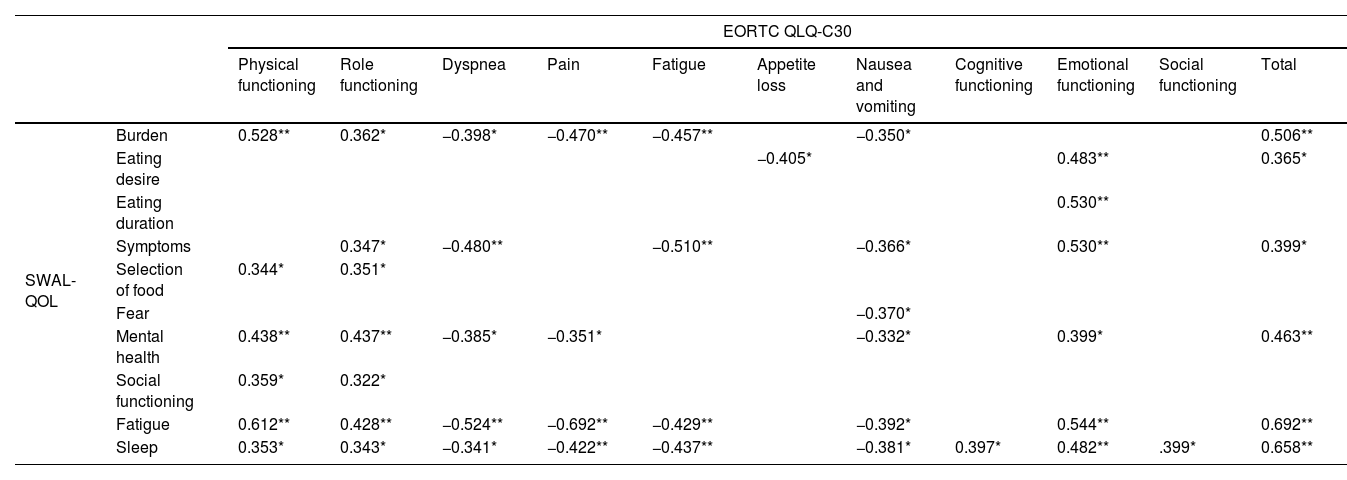
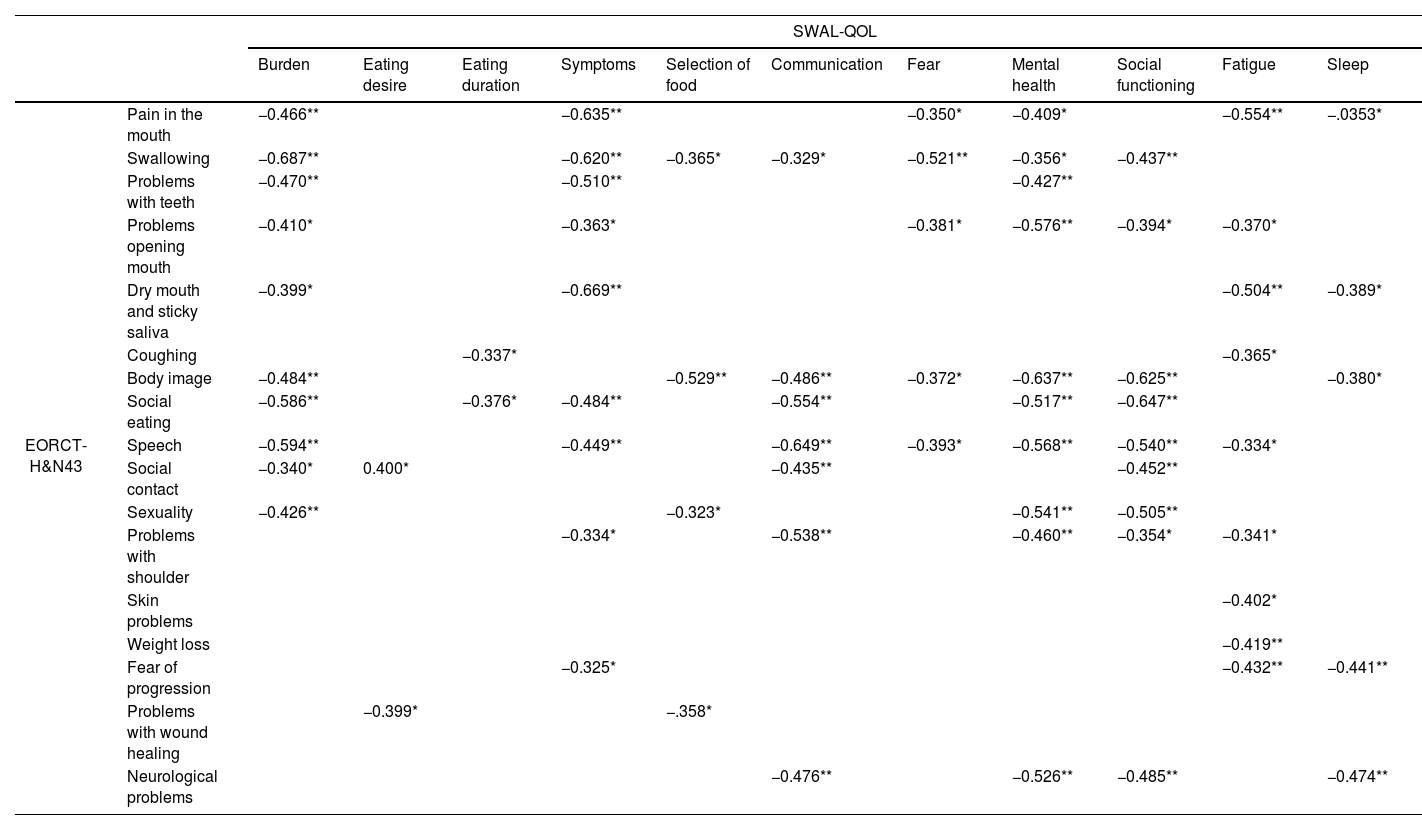
ResultsThe results from the QLQ-H&N43, SWAL-QOL, and VHI-9i revealed the existence of functional changes after CRT treatments that agreed with the results of clinical evaluations. Patients’ perceptions were associated with clinical variables such as FOIS, feeding route, solid-food consistency, and liquid consistency. Having undergone tracheostomy or having dysphagia or dysphonia was associated with poorer QLQ-C30, QLQ-H&N43, SWAL-QOL, and VHI-9i scores. In contrast, having undergone speech therapy was associated with having a better QoL as assessed by the QLQ-C30, QLQ-H&N43, and SWAL-QOL. Statistical analysis revealed correlations between scores from the QLQ-H&N43, SWAL-QOL, and VHI-9i, and scores from the QLQ-C30 with QLQ-H&N43 and SWAL-QOL. Statistically significant associations were found between the questionnaires scores and some sociodemographic variables (age, sex, and educational level).
ConclusionScores from generic QoL and specific symptom questionnaires were correlated with swallowing and voice function in oropharyngeal cancer patients. In cases with unfavourable scores, patients could benefit from early referral for the assessment of swallowing and voice functions to improve their QoL. The results of this study further indicate that there are certain clinical characteristics that, when present, should initiate this same course of action.
Comprender los efectos de la quimiorradioterapia (QRT) en las funciones de la deglución y la voz de los pacientes con cáncer de orofaringe en función de sus autopercepciones y cómo estas se relacionan con variables clínicas y sociodemográficas.
MétodosSe han incluido 38 pacientes con cáncer de orofaringe tratados exclusivamente con QRT. Las percepciones de los pacientes se evaluaron mediante los cuestionarios EORTC QLQ-C30, H&N43, VHI-9i y SWAL-QOL. Se realizaron análisis descriptivos, de correlación e inferenciales.
ResultadosLos resultados del QLQ-H&N43, SWAL-QOL y VHI-9i revelaron la existencia de cambios funcionales tras los tratamientos con QRT, que coincidían con los resultados de las evaluaciones clínicas. Las percepciones de los pacientes se asociaron con variables clínicas, como el FOIS, la ruta de alimentación, la consistencia de los alimentos sólidos y la consistencia líquida. Tener una traqueostomía, o tener disfagia o disfonía se asoció con peores puntuaciones en QLQ-C30, QLQ-H&N43, SWAL-QOL y VHI-9i. Por el contrario, haber recibido logopedia se asoció con una mejor calidad de vida según lo evaluado por QLQ-C30, QLQ-H&N43 y SWAL-QOL. El análisis estadístico reveló correlaciones entre las puntuaciones de QLQ-H&N43, SWAL-QOL y VHI-9i, y las puntuaciones de QLQ-C30 con QLQ-H&N43 y SWAL-QOL. Se encontraron asociaciones estadísticamente significativas entre las puntuaciones de los cuestionarios y algunas variables sociodemográficas (edad, sexo y nivel educativo).
ConclusiónLas puntuaciones de los cuestionarios genéricos de calidad de vida y de síntomas específicos se correlacionaron con las funciones de la deglución y de la voz en los pacientes con cáncer de orofaringe. En los casos con puntuaciones desfavorables, los pacientes podrían beneficiarse de una derivación temprana para la evaluación de las funciones de la deglución y de la voz para mejorar su calidad de vida. Los resultados de este estudio indican, además, que existen ciertas características clínicas que, cuando están presentes, deberían iniciar este mismo curso de acción.