Evaluar la seguridad y eficacia de la quimioembolización transarterial con microesferas radiopacas cargadas con doxorrubicina (rDEB-TACE) en pacientes con carcinoma hepatocelular (CHC).
Materiales y métodosEste estudio observacional retrospectivo de un solo centro incluyó a todos los pacientes mayores de 18 años diagnosticados con CHC y tratados con rDEB-TACE entre 2017 y 2020 en nuestra institución. La eficacia de rDEB-TACE se evaluó mediante la respuesta al tratamiento a los 1, 3 y 6 meses, el tiempo hasta la progresión (TTP) y la supervivencia global (OS). La seguridad se evaluó según la ocurrencia de eventos adversos (EA). La distribución de rDEB se clasificó en distribución general: tipo 1 (intratumoral), tipo 2 (intratumoral-arteria nutricia) y tipo 3 (arteria nutricia); y por distribución intratumoral (0-50% y 50-100%).
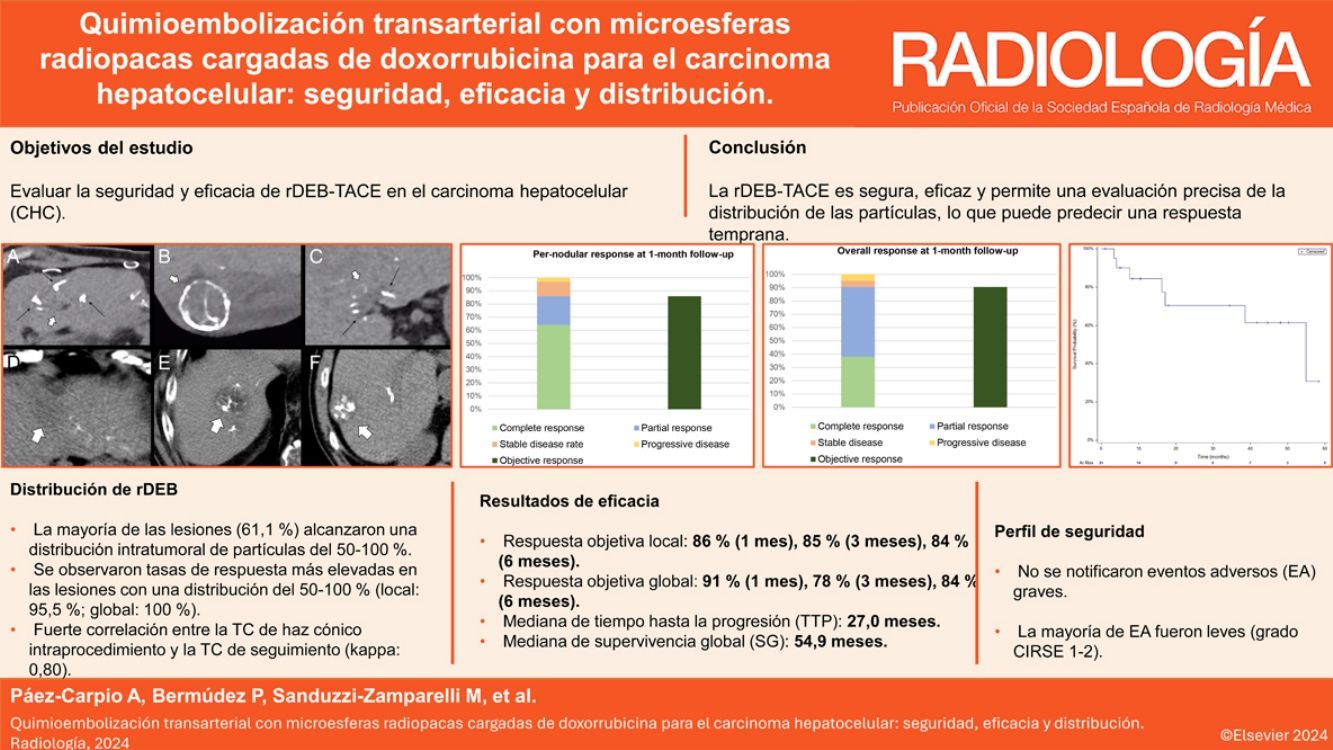
ResultadosSe incluyeron 21 pacientes con 36 lesiones tratadas con rDEB-TACE. El tiempo medio de seguimiento fue de 17 meses (RQI: 6,0-45,5). La respuesta objetiva local y global a los 1, 3 y 6 meses fue del 86%, 85%, 84%, y 91%, 78% y 84%, respectivamente. La mediana de TTP fue de 27,0 meses (IC 95%: 8,9-28,1) y la mediana de OS fue de 54,9 meses (IC 95%: 16,3-no estimable). No se reportaron eventos adversos mayores. El tipo de distribución de partículas más común fue el tipo 2 (69,4%). La concordancia entre la distribución de partículas en el cone beam TC intraprocedimiento y el TC de seguimiento fue alta (kappa=0,80). La mayoría de las lesiones tratadas mostraron una distribución intratumoral de partículas del 50-100%, con una mayor tasa de respuesta objetiva local (95,5% vs. 71,4%) y global (100% vs. 71,4%) en este grupo en comparación con el grupo de 0-50%.
ConclusiónLa rDEB-TACE es un tratamiento seguro y eficaz para el CHC. La distribución de rDEB puede evaluarse con precisión y predecir la respuesta radiológica temprana.
To evaluate the safety and efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization with radiopaque doxorubicin-loaded microspheres (rDEB-TACE) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Materials and MethodsThis single-center, retrospective, observational study included all patients 18 years and older diagnosed with HCC and treated with rDEB-TACE from 2017 to 2020 at our institution. rDEB-TACE efficacy was evaluated by type of response after treatment at 1-, 3- and 6-month, time to progression (TTP), and overall survival (OS). Safety of the technique was assessed based on the occurrence of adverse events (AEs). rDEB distribution was classified by overall distribution as type 1: intratumoral, type 2: intratumoral-feeding artery, and type 3: feeding artery and by intratumoral distribution in 0-50% and 50-100%.
ResultsTwenty-one patients with 36 lesions treated with rDEB-TACE were included. Median follow-up time was 17 months (IQR: 6.0-45.5). Local and overall objective response at 1, 3 and 6 months was 86%, 85%, 84% and 91%, 78% and 84%, respectively. Median TTP was 27.0 months (95%CI: 8.9-28.1) and median OS was 54.9 months (95%CI: 16.3-NE). No major AEs were reported. The most common particle distribution was type 2 (69.4%). Concordance of particle distribution between intraprocedural cone beam CT and follow-up CT was high (kappa=0.80). Most lesions treated showed a 50-100% intratumoral particle distribution, with higher rates of local (95.5% vs 71.4%) and overall objective response in this group (100% vs 71.4%) compared with the 0-50% group.
ConclusionrDEB-TACE is a safe and effective treatment for patients with HCC. Distribution of rDEB can be accurately assessed during and after the procedure and may predict early response.
.