Improvements in continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in recent years have changed the treatment of type 1 diabetes (T1D) by permitting the automation of glucose control. The Minimed 780G advanced hybrid closed-loop (ACHL) system adapts basal infusion rates and delivers auto-correction boluses in order to achieve a user-decided glucose target (100, 110 or 120mg/dL). This study set out to evaluate the effectiveness of the Medtronic 780G system in real-life conditions over 6 months.
Materials and methodsProspective study that included T1D subjects previously treated with insulin pump without CGM (pump group) or with sensor-augmented pump with predictive low-glucose suspend (SAP-PLGS group) who started with the Minimed 780G system. Sensor and pump data from baseline, and at 1, 3 and 6 months were downloaded and HbA1c was recorded at baseline and at 6 months.
ResultsFifty T1D subjects were included; 25 were previous SAP-PLGS 640G users and 25 used 640G without CGM. 66% were female, 48.6 (40–57) years of age with 20 (12–31.5) years of diabetes duration. Time in range (TIR) improved in the total cohort from baseline to 6 months (69% (57.7–76) vs. 74% (70–82); p=0.01 as did HbA1c (7.6% (7.1–7.8) vs. 7.0% (6.8–7.5); p<0.001), with improvement in times <54, >180 and >250mg/dL. Outcomes at 6 months did not differ between groups, although the SAP-PLGS subjects were prone to hypoglycaemia and the pump group mainly presented suboptimal metabolic control.
ConclusionThe AHCL Medtronic Minimed 780G system achieves and maintains good glycaemic control over 6 months in real-life conditions in different profiles of T1D subjects.
La mejoría en los sistemas de monitorización continua de glucosa (MCG) en los últimos años ha cambiado el tratamiento de la diabetes tipo 1 (DT1) permitiendo la automatización progresiva del control de la glucosa. El sistema híbrido avanzado (ACHL) Minimed 780G adapta la infusión basal y administra bolos correctores automáticos para alcanzar el objetivo glucémico deseado por el usuario (100, 110 o 120mg/dl). Este estudio evalúa la efectividad del sistema 780G en vida real durante 6 meses en personas con DT1.
Material y métodosEstudio prospectivo que incluye a individuos con DT1 tratados previamente con bomba de insulina sin MCG (grupo bomba) o con bomba y MCG con sistema de parada predictiva (grupo SAP-PLGS) que iniciaron tratamiento con sistema Minimed 780G. Se obtuvieron datos de la bomba y del sensor previo al inicio de la terapia, en el primer, el tercer y el sexto mes y datos de HbA1c al inicio y a los 6 meses de seguimiento.
ResultadosCincuenta personas con DT1 fueron incluidas: 25 usuarios previos de bomba sin MCG y 25 con sistema SAP-PLGS. El 66% fueron mujeres, con 48,6 (40-57) años de edad y 20 (12-31,5) años de duración de la diabetes. El tiempo en rango (TIR) mejoró en la cohorte total desde el momento basal a los 6 meses (69 [57,7-76] vs. 74% [70-82]; p=0,01), así como la HbA1c (7,6 [7,1-7,8] vs. 7,0 [6,8-7,5]%; p<0,001), con mejoría en los tiempos <54, >180 y >250mg/dl. Los resultados no difirieron en los 2 grupos a los 6 meses a pesar de que los pacientes en el grupo SAP-PLGS eran proclives a la hipoglucemia y los del grupo de bomba presentaban fundamentalmente mal control metabólico por HbA1c elevada.
ConclusiónEl sistema híbrido Minimed 780G consigue y mantiene un buen control metabólico durante 6 meses en vida real en diferentes perfiles de personas con DT1.
In the last two decades, improvements in real-time continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) have prompted important changes in the management of type 1 diabetes (T1D). Firstly, new therapeutic targets1 increasingly related to the development of microvascular complications2 have been obtained, complementing classical measures such as glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c). Secondly, the CGM information allows both patients and professionals to have a better understanding of glycaemic patterns and subsequently make adequate therapeutic changes to improve glycaemic control. Finally, the improvement in CGM has led to progress in the automation of glucose control. The first automatic systems available, such as the sensor-augmented pump with predictive low-glucose suspend (SAP-PLGS), stopped insulin infusion when hypoglycaemia was predicted. These systems demonstrated a reduction in hypoglycaemia both in clinical trials3 and real-world data,4,5 albeit without great improvements in HbA1c values.
The next step in automation was to create systems that administer basal insulin automatically with sensor glucose values, the so-called hybrid closed-loop (HCL) systems. These systems are intended to improve not only hypoglycaemia rates but also the time in range (TIR) and HbA1c. The Medtronic Minimed 670G was the first commercially available HCL system. This system has demonstrated superiority in TIR outcomes compared to SAP-PLGS systems in pivotal trials6–8 and in real-life data.9,10 although in most cases, the fixed glucose target at 120mg/dL, as well as certain issues with sensor management, preclude optimal satisfaction among T1D subjects.
Finally, systems that include the administration of automated correction boluses, namely advanced hybrid closed-loop (AHCL) systems, were placed on the market. Three of them are available in our country: the Medtronic Minimed 780G, the Tandem t:slim X2 with Control IQ technology and the AccuCheK Insight-DBLG1-Diabeloop system. All three have been shown to improve time in range and time in hypoglycaemia compared with sensor-augmented pump therapy.11–14
More specifically, the Medtronic Minimed 780G system makes it possible to set different glucose targets (100, 110 and 120mg/dL) and different active insulin (from 2 to 8h). Some studies have evaluated the Medtronic Minimed 780G in real life in adults, although the information about differences in outcomes depending on previous treatment is scant. With this background, this study set out to evaluate the effectiveness of the Medtronic Minimed 780G over 6 months of use in T1D adults who had previously received different insulin treatments.
Materials and methodsA longitudinal prospective protocol was designed. All the T1D patients treated in our centre with insulin pump and upgraded to the AHCL system Medtronic 780G were included.
Prior to the upgrade, the patients were treated with the Medtronic 640G pump without CGM (pump group) or the SAP-PLGS Medtronic 640G system (SAP-PLGS group).
All patients attended a structured face-to-face or virtual group (4–6 persons) education programme depending on patient characteristics. The programme consisted of 3 training sessions lasting 2–3h for patients that were not previously using CGM therapy, and 2 training group sessions lasting 2h, with a remote visit 1 week later for those who were already using CGM. The specific content of the educational programme is presented in the supplementary material. All the patients used the Guardian sensor G3. The bolus calculator settings and basal rate were programmed to be the same as the previous configuration. Glucose target and active insulin time were adjusted personally depending on patient characteristics and the auto-correction bolus function was activated in all patients.
Patient characteristics, CGM and pump settings data and blood analysis results were collected at baseline and at 6 months (the baseline CGM information in the pump group was collected from a blinded sensor – iPro2® – one week before the initiation of ACHL). Moreover, CGM and pump settings were collected at 1 and 3 months after the initiation of therapy. Time in different ranges, mean glucose, standard deviation (SD), coefficient of variation (CV) and sensor use were obtained from the CGM. Total daily insulin dose, % of basal insulin and number of SMBGs per day were assessed from the pump. Therapy-related variables, such as device use, time in Auto-Mode, percentage of insulin given as auto-correction bolus, insulin active duration and glucose target were recorded 1, 3 and 6 months after the initiation of therapy.
The data analysis was performed using the SPSS statistics software v20. The results are presented as median and interquartile range. Comparisons were performed using the Mann–Whitney U test for independent samples or the Wilcoxon test for paired samples. The Kruskall–Wallis test was used to explore correlations between categorical and continuous variables. A p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
The study protocol complied with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Hospital Universitari Mutua de Terrassa's Ethics Committee. All the participants provided their signed informed consent.
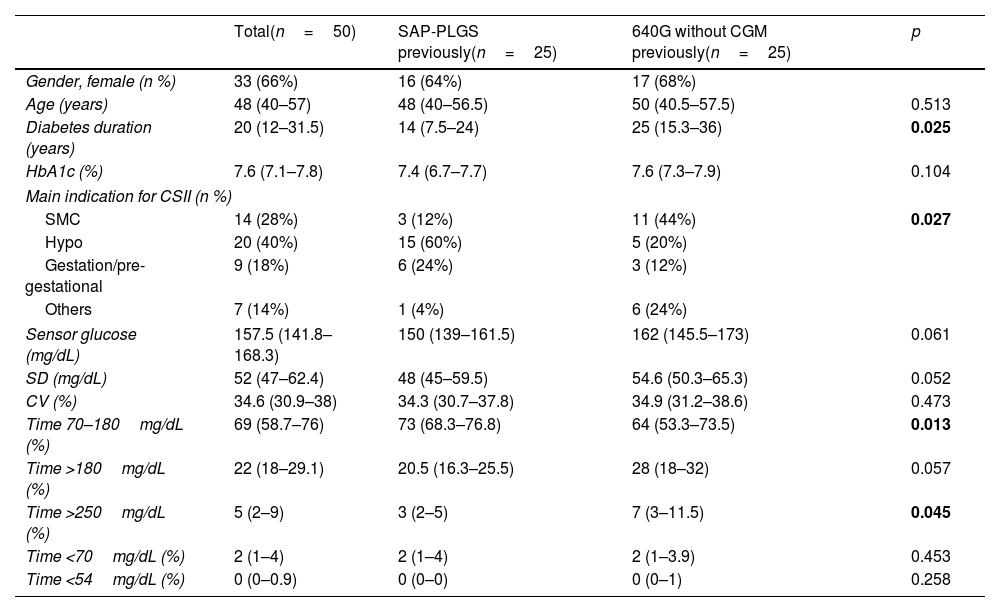
ResultsSubject characteristicsFifty T1D subjects were included, 25 were previous SAP-PLGS 640G users and 25 were using 640G without CGM. Sixty-six percent (66%) were females, with 48.6 (40–57) years of age with 20 (12–31.5) years of diabetes duration. The mean reason for starting insulin pump therapy were hypoglycaemia (40%), followed by suboptimal metabolic control (28%) and gestation or pregestational control (18%). As shown in Table 1, the patients in the SAP-PLGS group had a shorter duration of diabetes, and the main reason for starting pump therapy in the past had been the presentation of hypoglycaemic events. In contrast, the main reason for pump initiation in the pump group had been suboptimal metabolic control. In terms of glucose control, basal HbA1c was 7.6% (7.1–7.8) without differences between groups, although the TIR was greater in the SAP-PLGS group: 73% (68.3–76.8) vs. 64% (53.3–73.5); p=0.013 with less time >250mg/dL: 3 (2–5) vs. 7 (3–11.5); p=0.045.
Baseline characteristics of the patients included.
| Total(n=50) | SAP-PLGS previously(n=25) | 640G without CGM previously(n=25) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, female (n %) | 33 (66%) | 16 (64%) | 17 (68%) | |
| Age (years) | 48 (40–57) | 48 (40–56.5) | 50 (40.5–57.5) | 0.513 |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 20 (12–31.5) | 14 (7.5–24) | 25 (15.3–36) | 0.025 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.6 (7.1–7.8) | 7.4 (6.7–7.7) | 7.6 (7.3–7.9) | 0.104 |
| Main indication for CSII (n %) | ||||
| SMC | 14 (28%) | 3 (12%) | 11 (44%) | 0.027 |
| Hypo | 20 (40%) | 15 (60%) | 5 (20%) | |
| Gestation/pre-gestational | 9 (18%) | 6 (24%) | 3 (12%) | |
| Others | 7 (14%) | 1 (4%) | 6 (24%) | |
| Sensor glucose (mg/dL) | 157.5 (141.8–168.3) | 150 (139–161.5) | 162 (145.5–173) | 0.061 |
| SD (mg/dL) | 52 (47–62.4) | 48 (45–59.5) | 54.6 (50.3–65.3) | 0.052 |
| CV (%) | 34.6 (30.9–38) | 34.3 (30.7–37.8) | 34.9 (31.2–38.6) | 0.473 |
| Time 70–180mg/dL (%) | 69 (58.7–76) | 73 (68.3–76.8) | 64 (53.3–73.5) | 0.013 |
| Time >180mg/dL (%) | 22 (18–29.1) | 20.5 (16.3–25.5) | 28 (18–32) | 0.057 |
| Time >250mg/dL (%) | 5 (2–9) | 3 (2–5) | 7 (3–11.5) | 0.045 |
| Time <70mg/dL (%) | 2 (1–4) | 2 (1–4) | 2 (1–3.9) | 0.453 |
| Time <54mg/dL (%) | 0 (0–0.9) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–1) | 0.258 |
Data are expressed as n (%) and median (interquartile range). CSII: continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion; SMC: suboptimal metabolic control; Hypo: hypoglycaemia; SD: standard deviation; CV: coefficient of variation; SAP-PLGS: sensor-augmented pump with predictive low-glucose suspend function; CGM: continuous glucose monitoring.
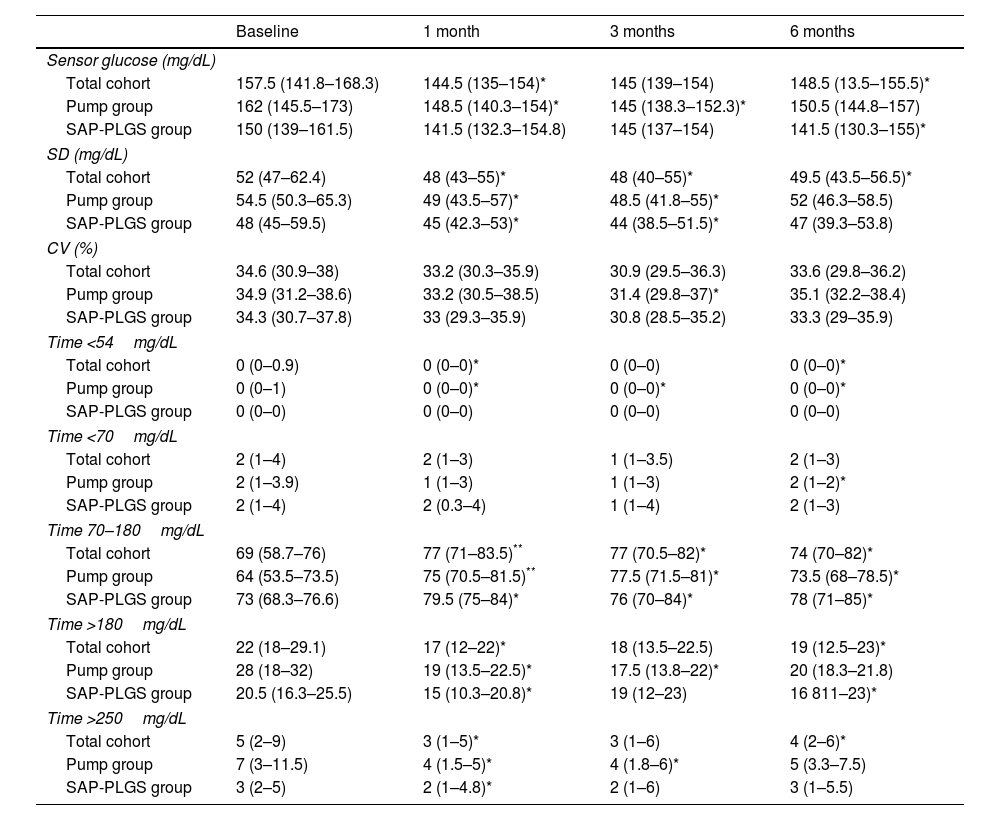
In the total cohort, the use of AHCL improved median HbA1c values at 6 months by 0.6% (7.6% (7.1–7.8) vs. 7.0% (6.8–7.5); p<0.001). As shown in Table 2, this improvement stemmed from an improvement in TIR, time <54mg/dL, and time both >180 and 250mg/dL without differences in time <70mg/dL. At 6 months, 75.7% of the patients achieved a TIR >70% and 67.6% achieved the recommended composite endpoint of TIR >70%, time <70mg/dL <4% and time <54mg/dL <1%.
Glucose outcomes in the whole cohort.
| Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor glucose (mg/dL) | ||||
| Total cohort | 157.5 (141.8–168.3) | 144.5 (135–154)* | 145 (139–154) | 148.5 (13.5–155.5)* |
| Pump group | 162 (145.5–173) | 148.5 (140.3–154)* | 145 (138.3–152.3)* | 150.5 (144.8–157) |
| SAP-PLGS group | 150 (139–161.5) | 141.5 (132.3–154.8) | 145 (137–154) | 141.5 (130.3–155)* |
| SD (mg/dL) | ||||
| Total cohort | 52 (47–62.4) | 48 (43–55)* | 48 (40–55)* | 49.5 (43.5–56.5)* |
| Pump group | 54.5 (50.3–65.3) | 49 (43.5–57)* | 48.5 (41.8–55)* | 52 (46.3–58.5) |
| SAP-PLGS group | 48 (45–59.5) | 45 (42.3–53)* | 44 (38.5–51.5)* | 47 (39.3–53.8) |
| CV (%) | ||||
| Total cohort | 34.6 (30.9–38) | 33.2 (30.3–35.9) | 30.9 (29.5–36.3) | 33.6 (29.8–36.2) |
| Pump group | 34.9 (31.2–38.6) | 33.2 (30.5–38.5) | 31.4 (29.8–37)* | 35.1 (32.2–38.4) |
| SAP-PLGS group | 34.3 (30.7–37.8) | 33 (29.3–35.9) | 30.8 (28.5–35.2) | 33.3 (29–35.9) |
| Time <54mg/dL | ||||
| Total cohort | 0 (0–0.9) | 0 (0–0)* | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0)* |
| Pump group | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–0)* | 0 (0–0)* | 0 (0–0)* |
| SAP-PLGS group | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
| Time <70mg/dL | ||||
| Total cohort | 2 (1–4) | 2 (1–3) | 1 (1–3.5) | 2 (1–3) |
| Pump group | 2 (1–3.9) | 1 (1–3) | 1 (1–3) | 2 (1–2)* |
| SAP-PLGS group | 2 (1–4) | 2 (0.3–4) | 1 (1–4) | 2 (1–3) |
| Time 70–180mg/dL | ||||
| Total cohort | 69 (58.7–76) | 77 (71–83.5)** | 77 (70.5–82)* | 74 (70–82)* |
| Pump group | 64 (53.5–73.5) | 75 (70.5–81.5)** | 77.5 (71.5–81)* | 73.5 (68–78.5)* |
| SAP-PLGS group | 73 (68.3–76.6) | 79.5 (75–84)* | 76 (70–84)* | 78 (71–85)* |
| Time >180mg/dL | ||||
| Total cohort | 22 (18–29.1) | 17 (12–22)* | 18 (13.5–22.5) | 19 (12.5–23)* |
| Pump group | 28 (18–32) | 19 (13.5–22.5)* | 17.5 (13.8–22)* | 20 (18.3–21.8) |
| SAP-PLGS group | 20.5 (16.3–25.5) | 15 (10.3–20.8)* | 19 (12–23) | 16 811–23)* |
| Time >250mg/dL | ||||
| Total cohort | 5 (2–9) | 3 (1–5)* | 3 (1–6) | 4 (2–6)* |
| Pump group | 7 (3–11.5) | 4 (1.5–5)* | 4 (1.8–6)* | 5 (3.3–7.5) |
| SAP-PLGS group | 3 (2–5) | 2 (1–4.8)* | 2 (1–6) | 3 (1–5.5) |
Data are expressed as n (%) and median (interquartile range). SD: standard deviation; CV: coefficient of variation.
When glycaemic outcomes were evaluated according to the baseline system, HbA1c values did not differ between the pump and the SAP-PLGS group (7.0% (6.8–7) vs. 7% (6.8–7.5), respectively) at 6 months after the AHCL had been started. Nevertheless, the improvement in HbA1c during the study was greater in the pump group (ΔHbA1c −0.8 (−1.1 – 0.6) vs. −0.2 (−0.5 – 0.05); p=0.03). CGM metrics did not differ either between groups, with no statistically differences observed in improvement in TIR (ΔTIR in total cohort 7.15 (−1 – 12.6); ΔTIR pump group 9.9 (−0.8 – 17.5) vs. 5.5 (−1 – 9.8) in the SAP-PLGS group; p=0.295).
Adverse eventsThe year before the initiation of AHCL, one patient in the pump group presented two episodes of severe hypoglycaemia and one patient in the SAP-PLGS group presented one episode of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). No DKA or severe hypoglycaemia events occurred during the first 6 months of AHCL therapy.
Use of the systemFinally, use of AHCL was found to be high at 6 months of use (92%; 90.5–95), with a large reduction in the number of SMBG per day (5 vs. 2.8; p<0.001), and with the system operating in Auto-Mode 100% (98–100) for a long time. The total amount of insulin per day did not differ from baseline to 6 months (34.7 (26.7–47.8) vs. 36 (28.4–50.6)units/day; p=0.154). No differences in the percentage of insulin administered as basal insulin were observed (46% (36.5–58.5) vs. 46% (40–53); p=0.734). Active insulin time was set at 3.5 (3–4)h at baseline and 3.5 (3–3.8)h at 6 months (p=0.04) and the glucose target was 110 (100–110)mg/dL at baseline and 110 (100–110)mg/dL at 6 months (p=0.046). No statistically significant differences were observed between groups. There was a tendency towards a negative correlation between TIR and glucose target at 6 months (Chi-square 3.8; p=0.144) and between TIR and active insulin duration (Chi-square 2.8; p=0.243).
DiscussionIn this prospective study, we observed that the implementation of AHCL in a real-world setting led to sustained improvement in glycaemic control from the first month up to 6 months, even in CGM-naïve subjects. Overall, this was achieved with a reduction in the percentage of time <54mg/dl. To date, only one study has evaluated the results of AHCL initiation in patients with different baseline treatments.15
Clinical trials have shown that the Medtronic Minimed 780G AHCL system produces major improvements in metabolic control in subjects with T1D in terms of HbA1c and TIR,13,14 reporting TIRs of 70.4% and 74.5%. Nevertheless, real-world studies provide some insight into whether or not the results of highly-structured clinical trials with strict inclusion criteria can be mainstreamed.16 To date, several real-world studies have evaluated new ACHL systems, most of which yielded similar or even better TIR outcomes than clinical trials, albeit in the short term. A multicentre observational study including 4120 Minimed 780G users reported a TIR of 76.2% in a mean of 54 days of treatment.17 Beato et al. reported a TIR of 81.9%, 79.6$ and 80.1% at 2 weeks and 1 and 3 months of therapy, respectively,18,19 demonstrating that excellent glycaemic outcomes can be achieved with this system from the initial days of the use of this technology. However, technologic treatments can sometimes present a great impact in the early weeks of use, and this improvement may subsequently be lost when patient motivation diminishes. Our study shows that the effect of the Minimed 780G was maintained after 6 months of use (TIR 1 vs. 6 months 77% vs. 74%; p>0.05). Similar results have been observed in children and adolescents.20 In adults, Lepore et al.15 obtained exactly the same TIR (74%) at 6 months in a cohort of patients previously treated with multiples doses of insulin (MDI), insulin pump, SAP-PLGS or the Medtronic 670G hybrid system. In this case, TIR two months after the initiation of ACHL was slightly lower than our data (72% as opposed to 77%), mainly due to a lower TIR in patients in MDI at 2 months, indicating that a little more time is probably needed to observe the benefits of the ACHL therapy in these patients. Matejko et al.21 evaluated the transitioning of patients from MDI to the Medtronic 780G, obtaining a very high TIR at 3 months (85%), although no information of glycaemic outcomes before 3 months was assessed. In this case, baseline HbA1c was significantly better than in Lepore et al. (7.4% vs. 8.0%), indicating that patients are probably not comparable.
The rapid improvement achieved and maintained over time with this therapy could be mainly related to the simplicity of the system and the scant need for user intervention. In our study, time in Auto-Mode was 100% (98–100) and it should be noted that in this mode patients need only enter their carbohydrate intake and use temporal objectives when exercising, since the basal rate and auto-correction boluses are administered automatically by the system.
Our data provide evidence that the Medtronic 780G AHCL can achieve similar glycaemic outcomes in different patient profiles, such as CGM-naive CSII users. In the clinical trials evaluating the efficacy of the Medtronic 780G AHCL, the number of CGM-naïve subjects was very low.13,14 Until the last quarter of 2020, our health care system only funded the use of real-time CGM in patients with hypoglycaemic issues and those with difficult metabolic control could only be offered CSII. For this reason, in our cohort, patients that started 780G from the SAP-PGLS system were patients who in the past, with insulin pump treatment without CGM, had presented high rates of hypoglycaemia (9.2% of time below 70mg/dL (TB 70) and 2.6% of time below 54mg/dL (TB 54)) (data not published). However, in our cohort, the pump group were subjects with suboptimal metabolic control (baseline TIR 64%) with a low frequency of hypoglycaemia (TB 70 2% and TB 54 0%). Although these patients were trained in the use of the pump, they were not accustomed to using the CGM system. Despite this, the Medtronic 780G system achieved similar benefits in this population as in clinical trials in which most of the subjects were SAP or SAP-PLGS users13,14 (TIR 74%, 67.6% of patients achieving combined outcomes of TIR >70%, TB 70 <4% and TB 54 0%). In addition, these positive results were possible with only one extra hour of diabetes education. Overall, these results reinforce the fact that these systems are simple to use and can be widely offered to all subjects with T1D.
Finally, some information is now available regarding which system settings provide better outcomes. A pivotal study of the 780G system14 showed that a glycaemic target of 100mg/dL achieves a better TIR than a target of 120mg/dL (69% vs. 75% of patients achieving TIR >70%, respectively). Moreover, adding an active insulin time of 2h to the glycaemic target of 100mg/dL achieves an even better TIR without increasing hypoglycaemia.22 Since this information was not available at the time of our study, we individualised the system settings depending on the characteristics of the patients (mainly risk of hypoglycaemia), generally with conservative settings (median active insulin time 3.5h, median glucose target 110mg/dL). Perhaps the better glycaemic outcomes achieved by Beato et al.18,19 could be explained by these differences in the initial system settings (although different populations are analysed).
We acknowledge several limitations of our study. It was a single-centre study with a limited number of participants and no comparison group. However, the data were prospectively collected, thereby avoiding memory bias. On the other hand, the study has several strengths. Firstly, it was an observational study in real-life clinical practice, including different patient profiles and providing information about system performance in different T1D populations. Although clinical trials provide high-quality evidence, studies are needed to confirm the results observed in real-world situations. Finally, this study has a longer follow-up than previous studies published with this technology in adults, confirming that the effectiveness of ACHL is not transient.
In conclusion, the AHCL Medtronic Minimed 780G achieves and maintains good glycaemic control over 6 months in real-life conditions in different profiles of T1D subjects.
FundingNo funding was received for this research.
Conflicts of interestThe authors report no potential conflicts of interest.