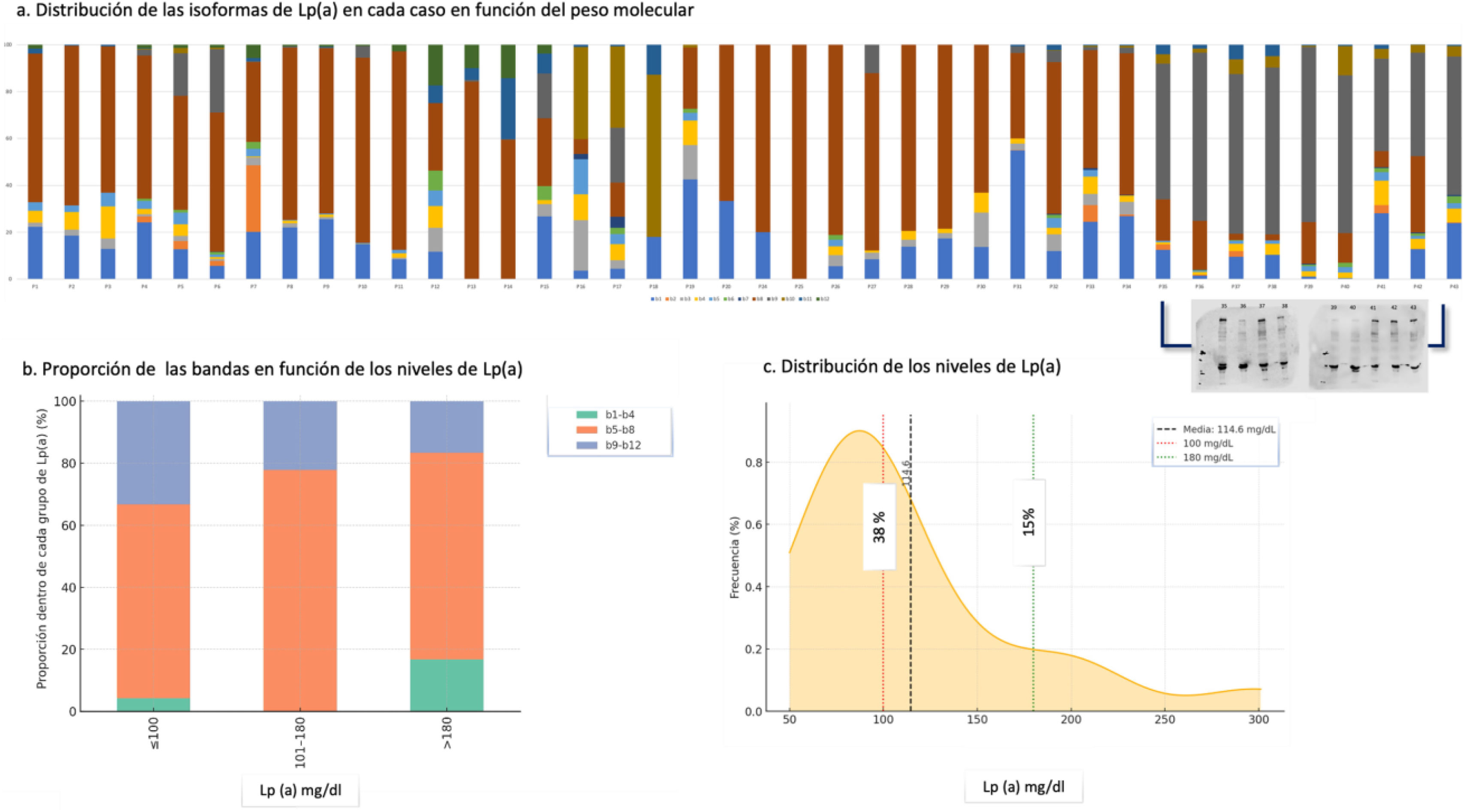
La Lp(a) es un factor de riesgo cardiovascular influido por el gen LPA y las isoformas de apo(a). Su relación no siempre es lineal, y existen fenotipos discordantes; por esta razón en nuestro trabajo evaluamos la asociación entre isoformas de apo(a) y niveles de Lp(a) en pacientes con síndrome coronario agudo (SCA). Para ello se estudiaron 43 pacientes con SCA y Lp(a) >50mg/dl. Las isoformas se caracterizaron en 12bandas mediante Western blot. Se evaluó la asociación entre bandas y concentraciones de Lp(a) mediante análisis estadístico. Se observó que las bandas de peso molecular intermedio (b5-b8) fueron las más frecuentes, predominando la banda8. No se halló asociación significativa entre el tamaño de isoformas y los niveles de Lp(a) (p>0,05). Concluimos que en esta cohorte no se observó correlación entre isoformas de apo(a) y Lp(a). Otros mecanismos genéticos o regulatorios podrían explicar la variabilidad observada, apoyando la necesidad de estudios más amplios.
Lp(a) is a cardiovascular risk factor influenced by the LPA gene and apo(a) isoforms. Their relationship is not always linear and there are discordant phenotypes, for this reason in our work we evaluated the association between apo(a) isoforms and Lp(a) levels in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS). To this end, 43 patients with ACS and Lp(a) >50mg/dL were studied. The isoforms were characterized in 12bands by Western blotting. The association between bands and Lp(a) concentrations was evaluated by statistical analysis. It was observed that the intermediate molecular weight bands (b5-b8) were the most frequent, with band 8 predominating. No significant association was found between isoform size and Lp(a) levels (P>.05). We conclude that in this cohort no correlation was observed between apo(a) and Lp(a) isoforms. Other genetic or regulatory mechanisms could explain the observed variability, supporting the need for larger studies.