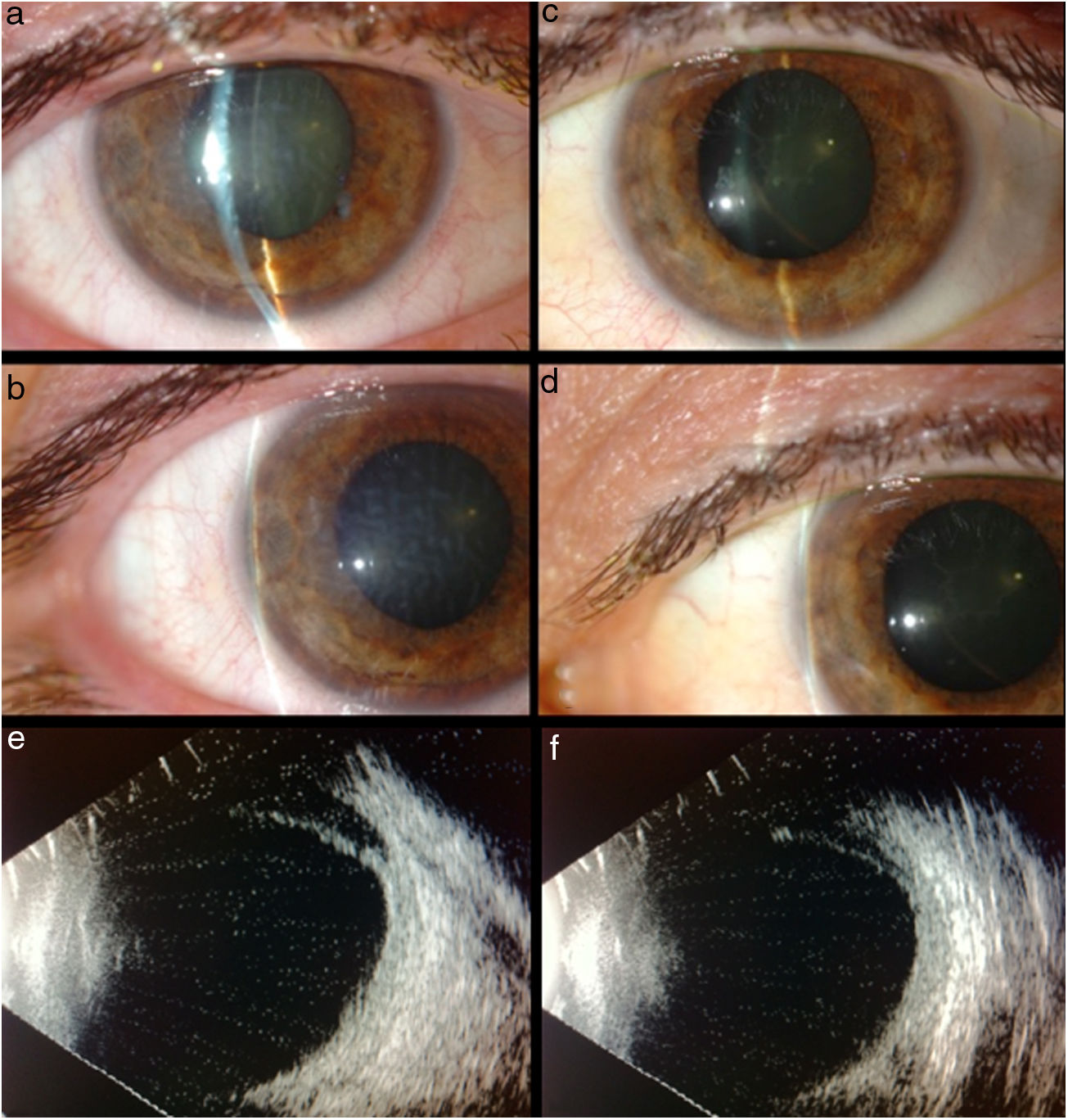
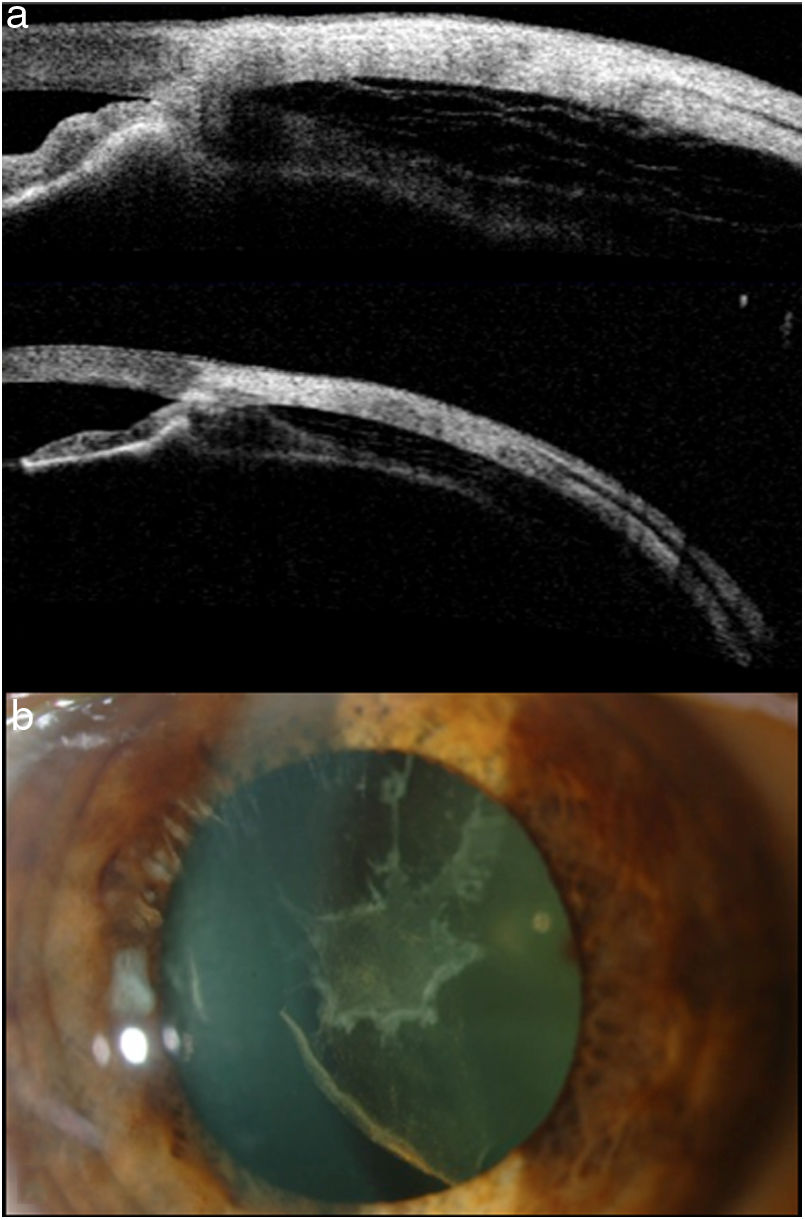
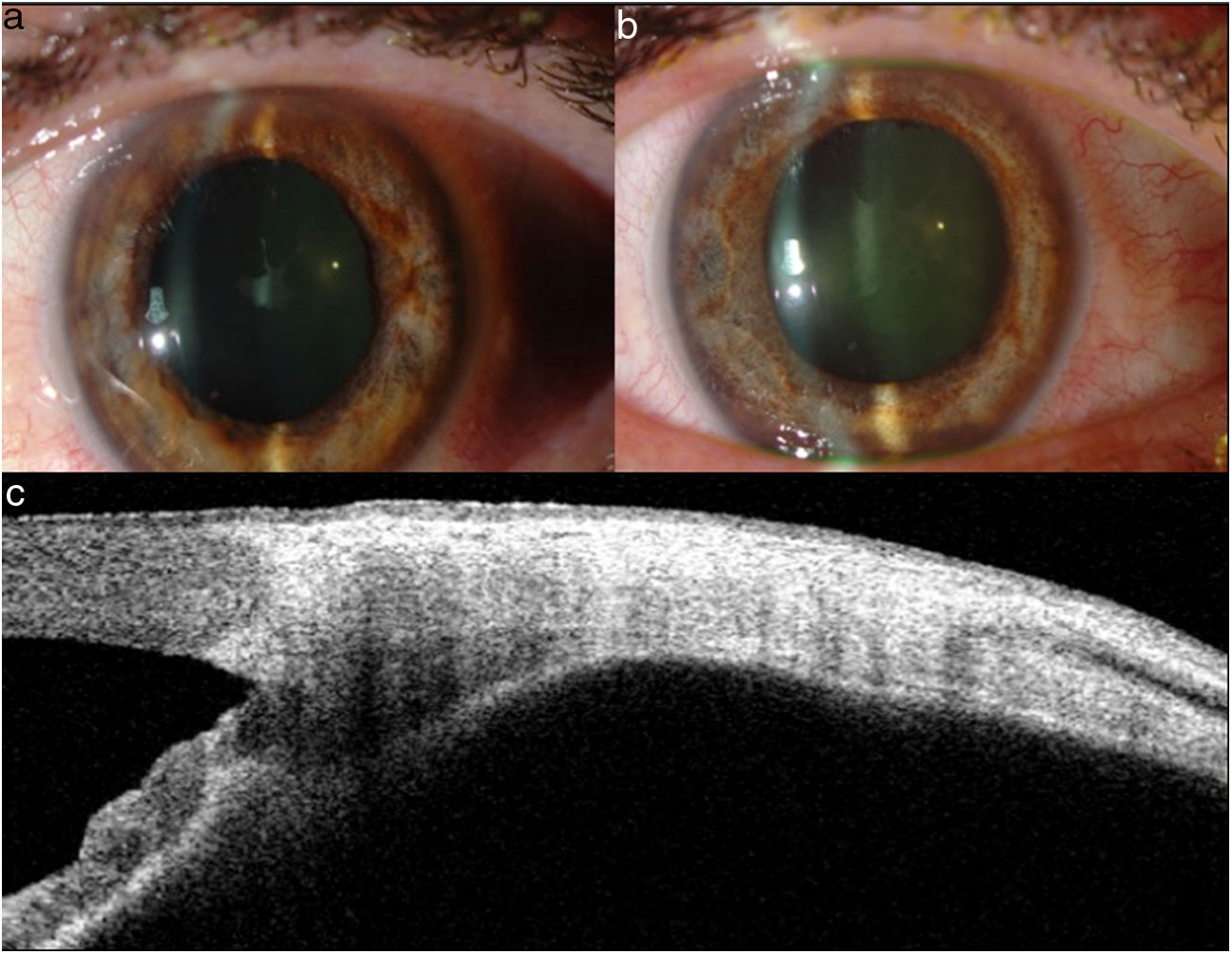
Se trata de un hombre de 45 años con cierre angular y miopía aguda bilateral tras inicio de tratamiento con topiramato por dependencia al alcohol y la heroína. La tomografía de coherencia óptica Visante® y la ecografía ocular muestran efusión ciliocoroidea bilateral como mecanismo fisiopatológico. El tratamiento consistió en la retirada del topiramato, y la utilización de hipotensores oculares, ciclopléjico y corticoides tópicos, con lo cual se resolvió el síndrome de efusión ciliocoroidea.
La tomografía de coherencia óptica Visante® y la ecografía ocular son herramientas útiles en el diagnóstico y seguimiento de los pacientes con cierre angular y miopía en el contexto del síndrome de efusión ciliocoroidea secundario a topiramato. Debido al amplio espectro de indicaciones de esta medicación, tanto el personal sanitario que lo indica como los oftalmólogos, deben conocer las posibles manifestaciones oculares atribuidas a este medicamento.
A 45 year-old man with bilateral acute angle-closure and myopia after starting treatment with topiramate, secondary to alcohol and heroin dependence. Using Visante® OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) and B-scan Ultrasound he was diagnosed with bilateral ciliochoroidal effusion as the pathophysiological mechanism. Topiramate was stopped and ocular hypotensive therapy with a topical cycloplegic and corticosteroids were started, resolving ciliochoroidal effusion syndrome.
Visante® OCT and B-scan Ultrasound are useful tools for the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with acute angle-closure and myopia due to topiramate. As a result of broad spectrum of indications for topiramate, physicians and ophthalmologists should be aware of the possible ophthalmological manifestations attributable to this drug.