Describir la progresión fenotípica en los pacientes con enfermedad de Stargardt por mutación del gen ABCA4 e informar sobre las variantes alélicas mutadas.
MétodoEstudio observacional, ambispectivo y descriptivo. Se incluyeron pacientes con enfermedad de Stargardt por mutación del gen ABCA4, se utilizó el informe genético y los exámenes basales del historial clínico. Para evaluar la variación fenotípica se realizó una nueva evaluación oftalmológica mediante OCT macular, retinografía, autofluorescencia y electrorretinograma.
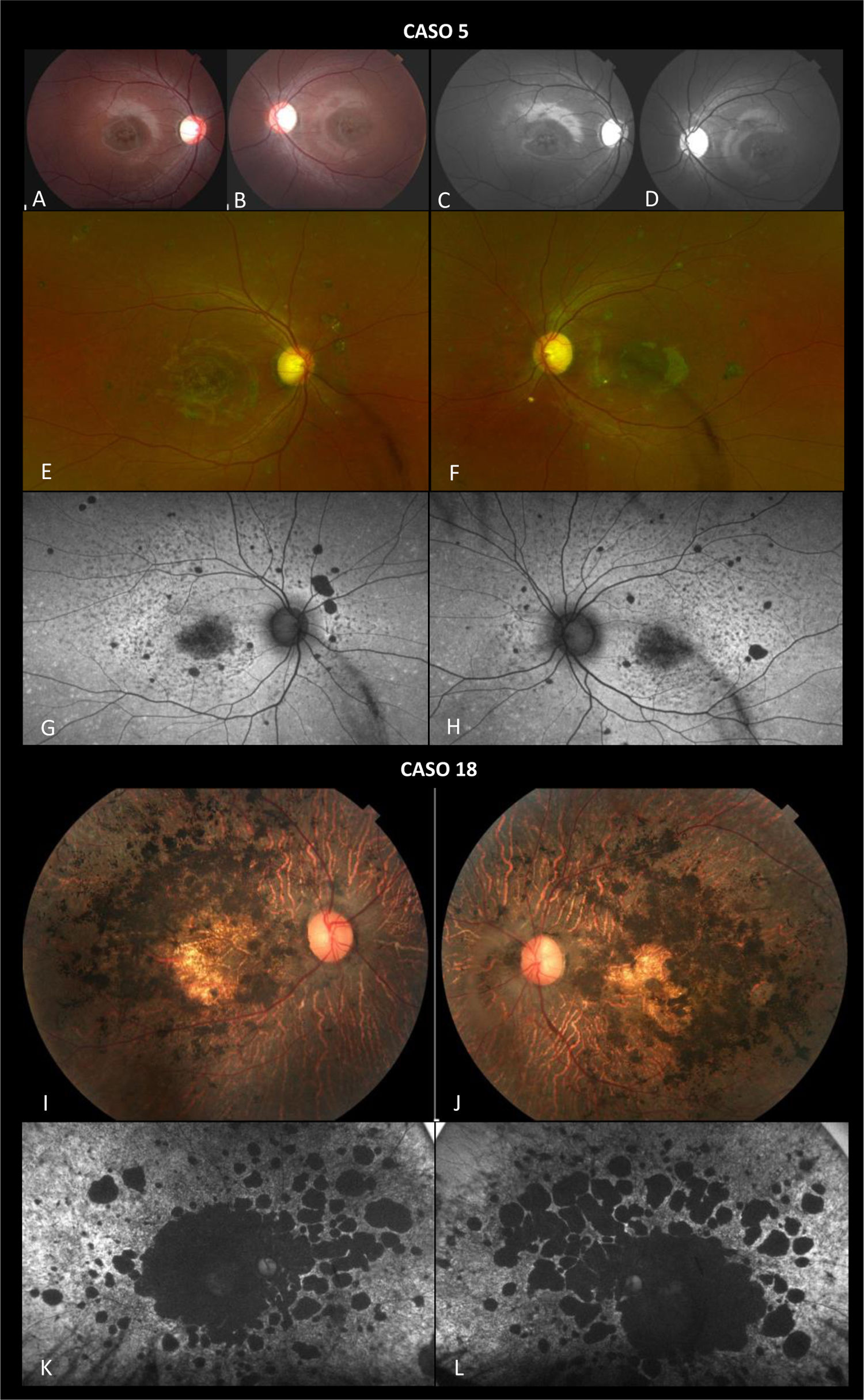
ResultadosSe identificaron 32 casos con seguimiento promedio de 6 años. La edad media de aparición fue de 16 años. La AV promedio inicial y final fue de 0,79 y 0,95 logMAR, respectivamente. El GMC medio inicial y final fue de 142,5 y 135μm, respectivamente. El grado de afectación del fondo de ojo y patrón de autofluorescencia predominante al inicio y al final fue atrofia macular con flecks y baja señal de autofluorescencia macular rodeada de un fondo heterogéneo, respectivamente. La electrorretinografía inicial mostró predominantemente función conservada de conos y bastones, mientras que al final la mayoría de los casos presentaban disfunción del sistema de conos y bastones. Nueve casos eran homocigotos y se identificaron 31 variantes alélicas mutantes diferentes. La variante más frecuente fue p.Trp1618Cys, seguida de p.Ala1773Val. También se descubrieron 2 nuevas variantes alélicas, p.Leu634Pro y p.Tyr665Serfs*5.
ConclusionesEl estudio encontró que los pacientes experimentaron deterioro estructural y funcional durante el período de seguimiento. El estudio también identificó 2 variantes predominantes y 2 variantes nuevas. Los homocigotos tuvieron un inicio más temprano de la enfermedad.
This study aims to describe the phenotypic progression of patients with Stargardt disease caused by mutations in the ABCA4 gene and reports on the mutated allelic variants.
MethodWe conducted an observational, ambispective, and descriptive study. Patients who had Stargardt disease by the ABCA4 gene mutation were included. The study used the genetic report and the baseline examinations appearing on health records. To evaluate the phenotypic variation, a new ophthalmological evaluation was conducted using macular OCT, retinography, autofluorescence, and electroretinogram.
ResultsThe study identified a total of 32 cases with a mean follow-up of 6 years. The mean age of onset was 16 years. The mean initial and final VA were 0.79 and 0.95 logMAR, respectively. The mean initial and final CMT were 142.5 and 135 microns, respectively. The predominant degree of fundus involvement and autofluorescence pattern at the beginning and end was macular atrophy with flecks and the low signal of macular autofluorescence surrounded by a heterogeneous background, respectively. Initial electroretinography showed predominantly preserved function of rods and cones, while in the end most cases presented rod and cone system dysfunction. A total of 9 cases were homozygous, and 31 different mutant allelic variants were identified. The most common variant was p.Trp1618Cys, followed by p.Ala1773Val. Two new allelic variants, p.Leu634Pro, and p.Tyr665Serfs*5, were also discovered.
ConclusionsThe study found that patients experienced structural and functional deterioration at the follow-up. The study also identified 2 predominant variants and 2 new variants. Homozygotes had an earlier onset of the disease.