Adequate nasal patency has been classically considered a crucial factor in middle ear ventilation. We valued the influence of nasosinusal polyposis on Eustachian tube (ET) function.
Material and methodsA prospective follow-up with all cases of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) assisted between January 2019 and October 2024 was carried out. Their endoscopic, radiological and clinical characteristics were noted, as well as the presence of a type 2 inflammation context (T2I) and the incidence of middle ear pathology. Polypoid involvement and tubal dysfunction were studied using several scores: Lidholdt’s scale, Lund-McKay nasal polyp grading, Lund-Kennedy endoscopic scoring system, SNOT-22 and Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire-7 (ETDQ-7) score.
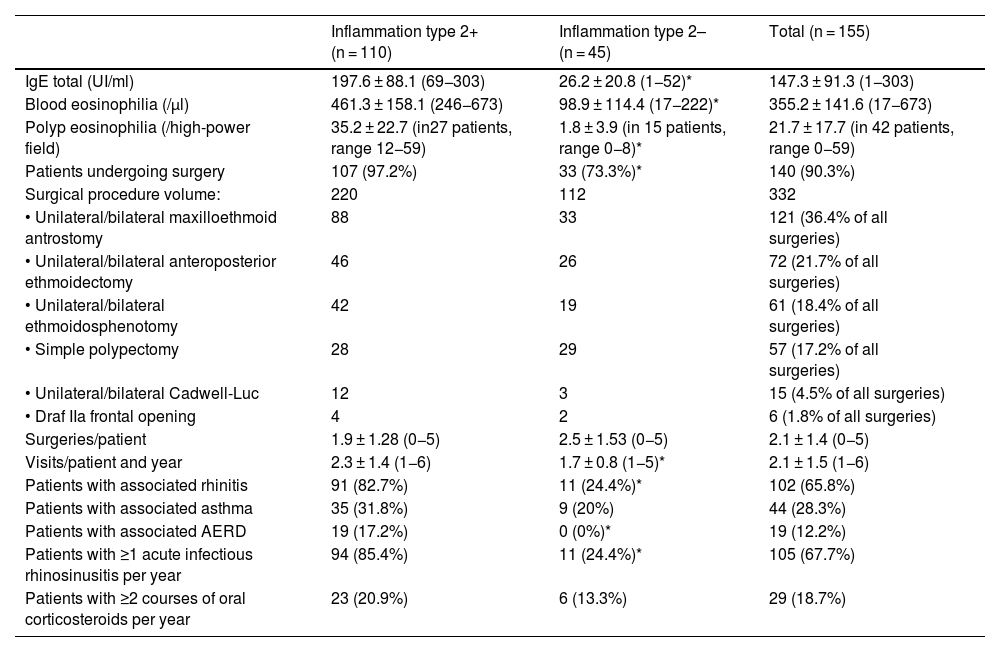
ResultsInformation was collected from 155 patients, with an incidence of 15,1 cases/100,000 inhabitants. 70,9% showed an T2I profile. This group showed a higher average of cases with acute otitis media and effusion (18,1% vs. 4,4%; P < .001), tympanometric alterations (12,7% vs. 4,4%; P < 0.01), conductive hearing loss (17,2%. vs 4,4%; P < 0.001) and needing for transtympanic drains (9,1% vs. 2,2%; P < .01) than the group without an eosinophilic profile or elevated IgE. The ETDQ-7 score correlated well with the SNOT-22 and Lund-Kennedy scales.
ConclusionsRegression analysis revealed that an T2I profile might play a more important role in tubal patency than nasal obstruction. Polyposis may alter ET function, but more likely due to its inflammatory-allergic aetiopathogenesis than to its obstructive nature.
La adecuada permeabilidad nasal ha sido clásicamente considerada factor fundamental en la ventilación del oído medio. Este estudio ha evaluado la influencia de la poliposis nasosinusal en la funcionalidad de trompa de Eustaquio (TE).
Material y metodosSe efectuó seguimiento prospectivo de todos los casos con rinosinusitis crónica con pólipos nasales (RSCcPN) atendidos entre enero de 2019 y octubre de 2024. Se anotaron sus características endoscópicas, radiológicas y clínicas, si existió un contexto de inflamación tipo 2 (IT2) y la incidencia de patología del oído medio detectada. La afectación polipoidea y la disfunción tubárica se estudiaron mediante las escalas de Lidholdt, Lund-McKay, Lund-Kennedy, SNOT-22 y Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire-7 (ETDQ-7).
ResultadosSe recogió información de 155 pacientes, con una incidencia de 15,1 casos/100.000 habitantes. El 70,9% presentó un perfil IT2. Este grupo mostró un mayor porcentaje de casos con otitis media aguda y serosa (18,1% vs. 4,4%; P < ,001), alteraciones timpanométricas (12,7% vs. 4,4%; P < ,01), hipoacusia conductiva (17,2% vs. 4,4%; P < ,001) y necesidad de drenajes transtimpánicos (9,1% vs. 2,2%; P < ,01) que el grupo sin perfil eosinofílico ni IgE elevada. La puntuación del ETDQ-7 se correlacionó bien con el SNOT-22 y la escala de Lund-Kennedy.
ConclusionesEl análisis de regresión reveló que el perfil IT2 podría desempeñar un papel más importante en la permeabilidad tubárica que la obstrucción nasal. La poliposis puede alterar la función de la TE, pero probablemente se deba más a su etiopatogenia alérgica-inflamatoria que a su naturaleza obstructiva.