Congenital profound bilateral hearing loss prevents the correct development of speech and voice. This study assesses certain acoustic parameters of the voice in order to determine their normality in the implanted population.
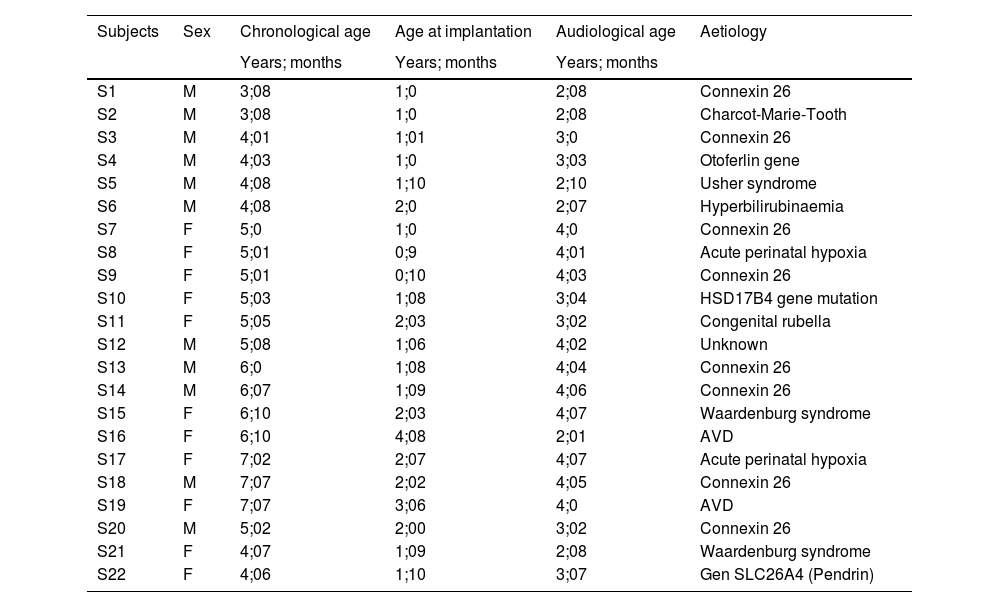
MethodTwo population groups were studied. A control group consisting of 42 healthy pediatric patients, 22 boys and 20 girls, and a group of 22 pediatric patients, 11 boys and 11 girls with congenital profound hearing loss implanted bilaterally.
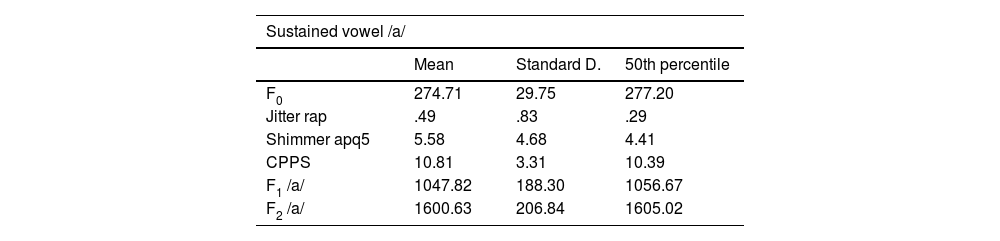
The variables median pitch, CPPS, jitter rap and shimmer apq5 were evaluated in an isolated phonation exercise and another in connected speech for the phoneme /a/ with the PRAAT program. Student's t-test and Wilcoxcon tests were applied.
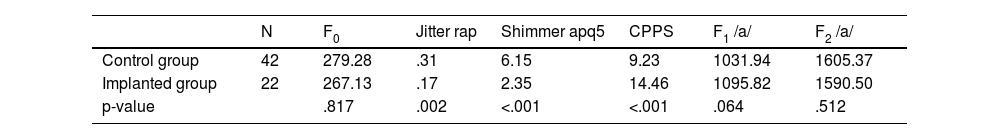
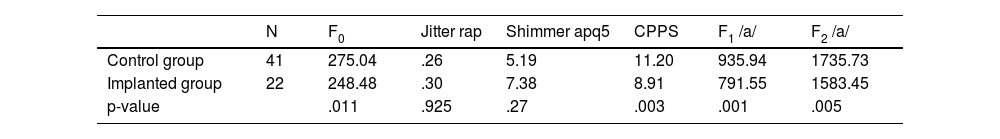
ResultsSignificant intergroup differences were obtained for all variables in the vowel extracted from connected speech, but not in the sustained vowel. The hearing-impaired population showed some significant differences in the intra-group analysis. The experimental group showed better results in the vocal quality parameters, particularly jitter, shimmer and CPPS showed statistically significant differences.
ConclusionEarly bilateral implantation allows the cochlear implant user to approximate his acoustic values to normative values in terms of pitch, stability, quality and articulatory precision.
La hipoacusia bilateral profunda cuando es congénita, impide el correcto desarrollo del habla y la voz. Este trabajo valora determinados parámetros acústicos de la voz con el fin de determinar su normalidad en la población implantada.
MétodoSe estudiaron dos grupos poblacionales. Un grupo control formado por 42 pacientes pediátricos sanos, 22 niños y 20 niñas, y un grupo de 22 pacientes pediátricos, 11 niños y 11 niñas con hipoacusia profunda congénita implantados de forma bilateral.
Las variables median pitch, CPPS, jitter rap y shimmer apq5 fueron evaluadas en un ejercicio de fonación aislada y otro de habla conectada para el fonema /a/ con el programa PRAAT. Se aplicaron los análisis de varianzas t de Student y test de Wilcoxcon.
ResultadosSe obtuvieron diferencias significativas intergrupales para todas las variables en la vocal extraída del habla conectada, no así en la vocal sostenida. La población con hipoacusia mostró algunas diferencias significativas en el análisis intra-grupo. El grupo experimental muestra mejores resultados en los parámetros de calidad vocal, particularmente, eljitter, shimmer y CPPS presentan diferencias con significación estadística.
ConclusiónLa implantación bilateral precoz permite al usuario con implante coclear aproximar sus valores acústicos a los normativos en términos de tono, estabilidad, calidad y precisión articulatoria.