Unilateral cochlear implantation (CI) is the recommended treatment for profound sensorineural hearing loss in older adults when hearing aids fail to provide benefit. This study aimed to determine the direct costs associated with this procedure to support health‐care provider decision-making.
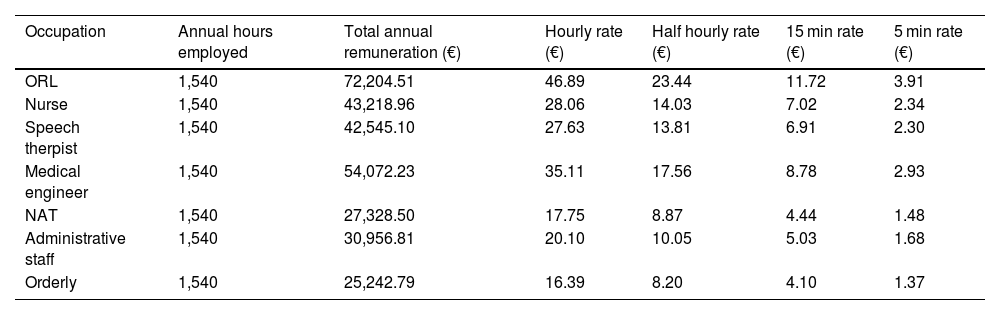
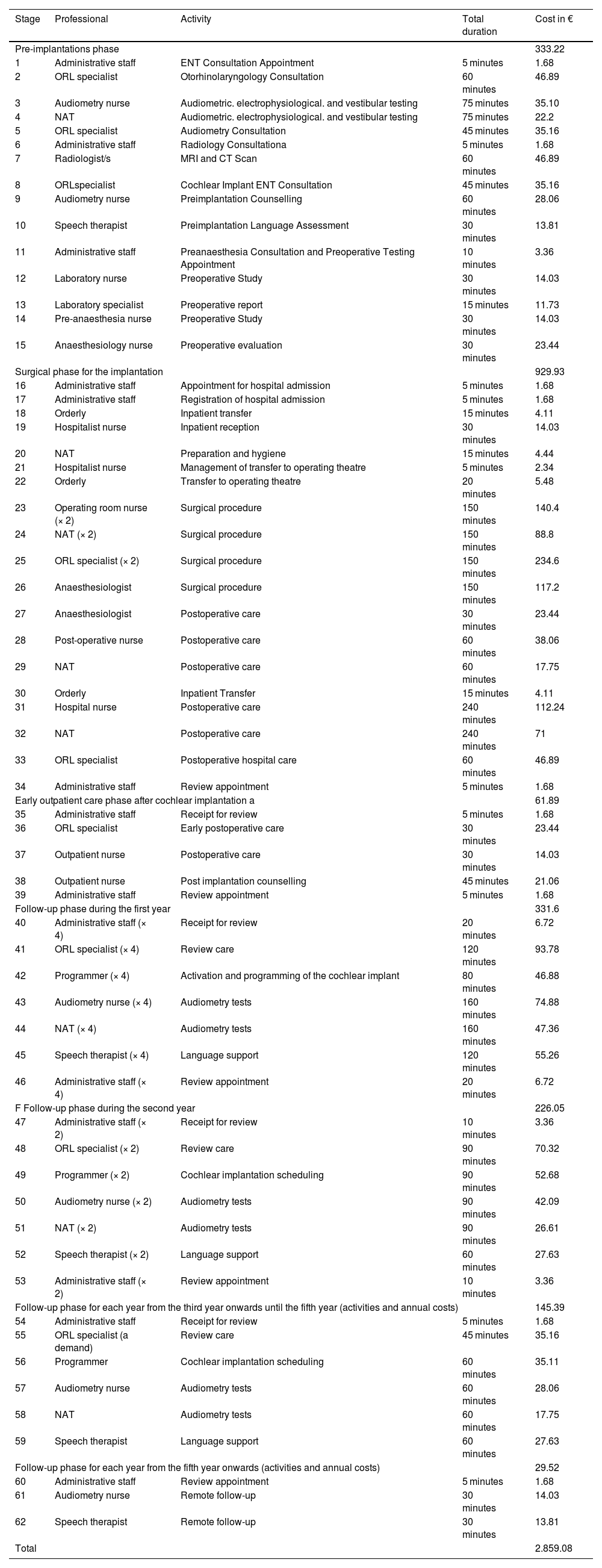
Materials and methodsA cross-sectional observational study was performed at a single-centertertiary hospital on 278 cochlear implant recipients aged 60 years or older between 2009 and 2020. A final sample of 71 subjects (37 women, 52.1%) was selected via stratified random sampling. A micro-costing (bottom-up) economic analysis was conducted. Direct costs were allocated according to the Framework Agreement and the Andalusian Health Service salary tables, including the device, allowances, personnel, surgery, hospitalisation, clinical follow‐up, complications, and technology upgrades. Costs were updated to 2024 € and calculated over a mean time horizon of 23.3 years.
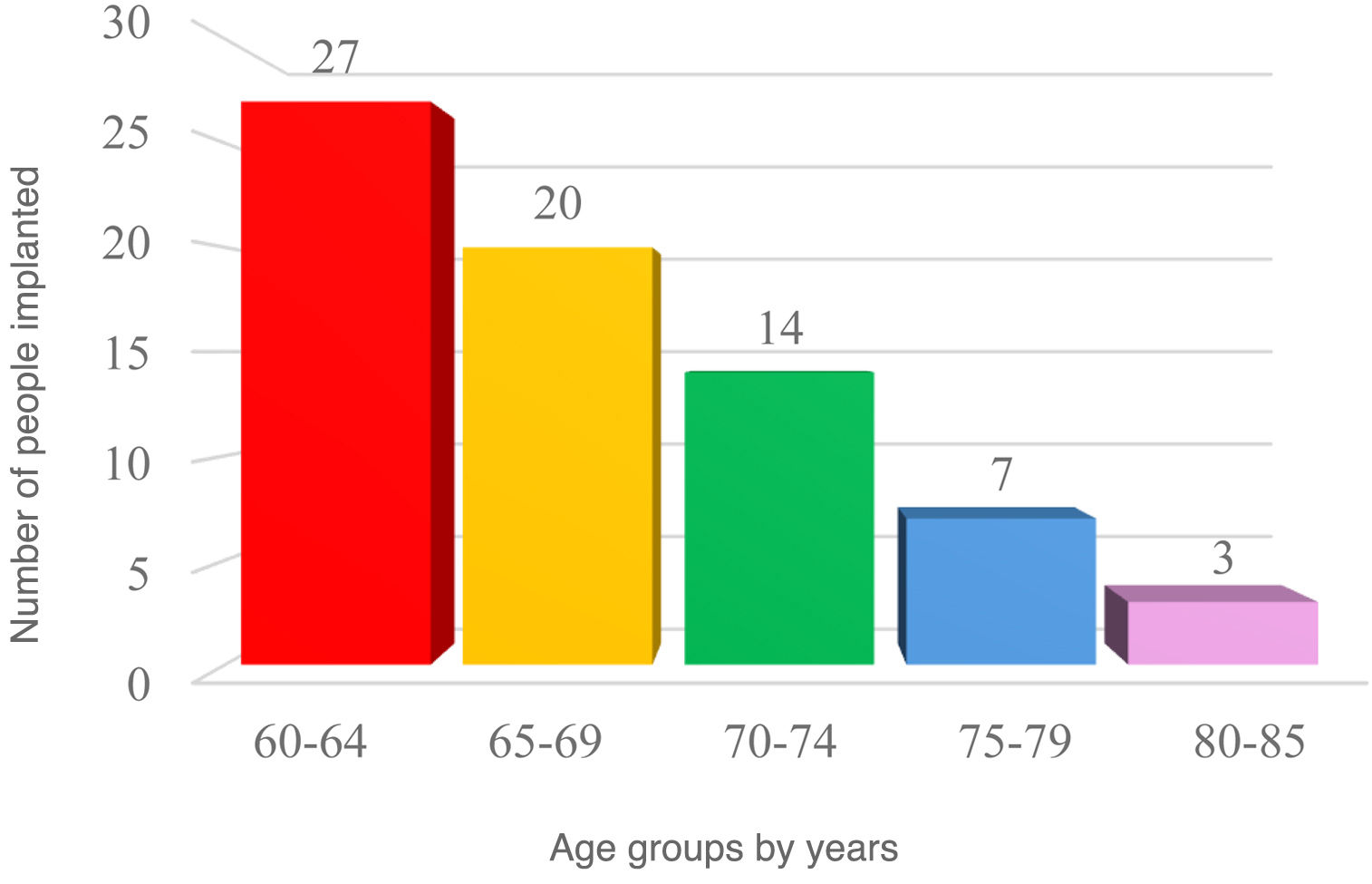
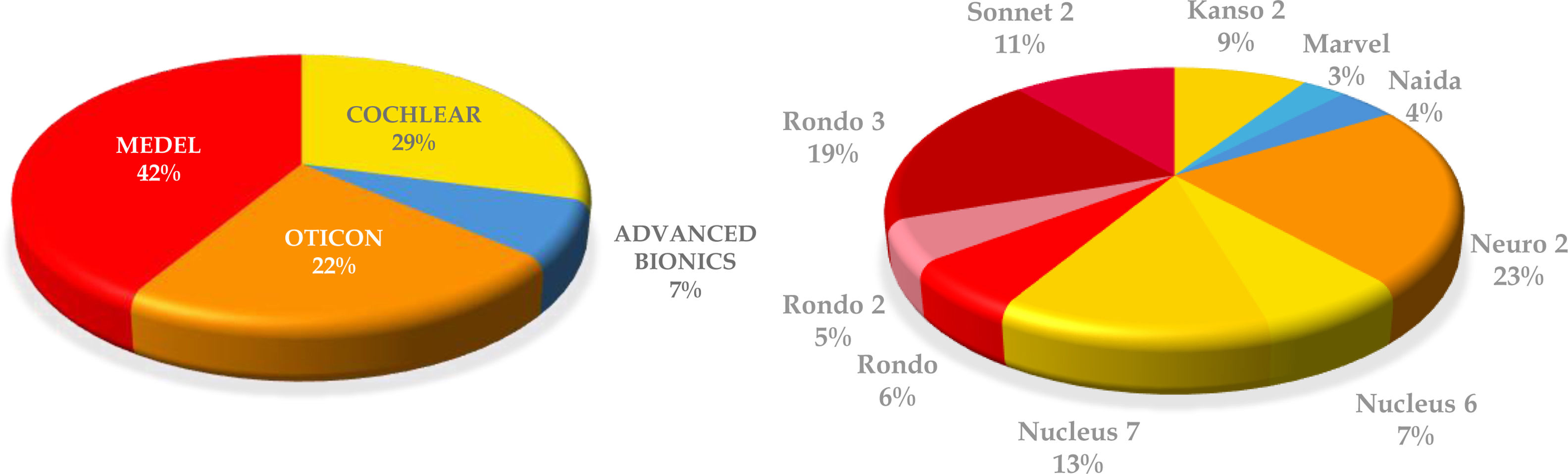
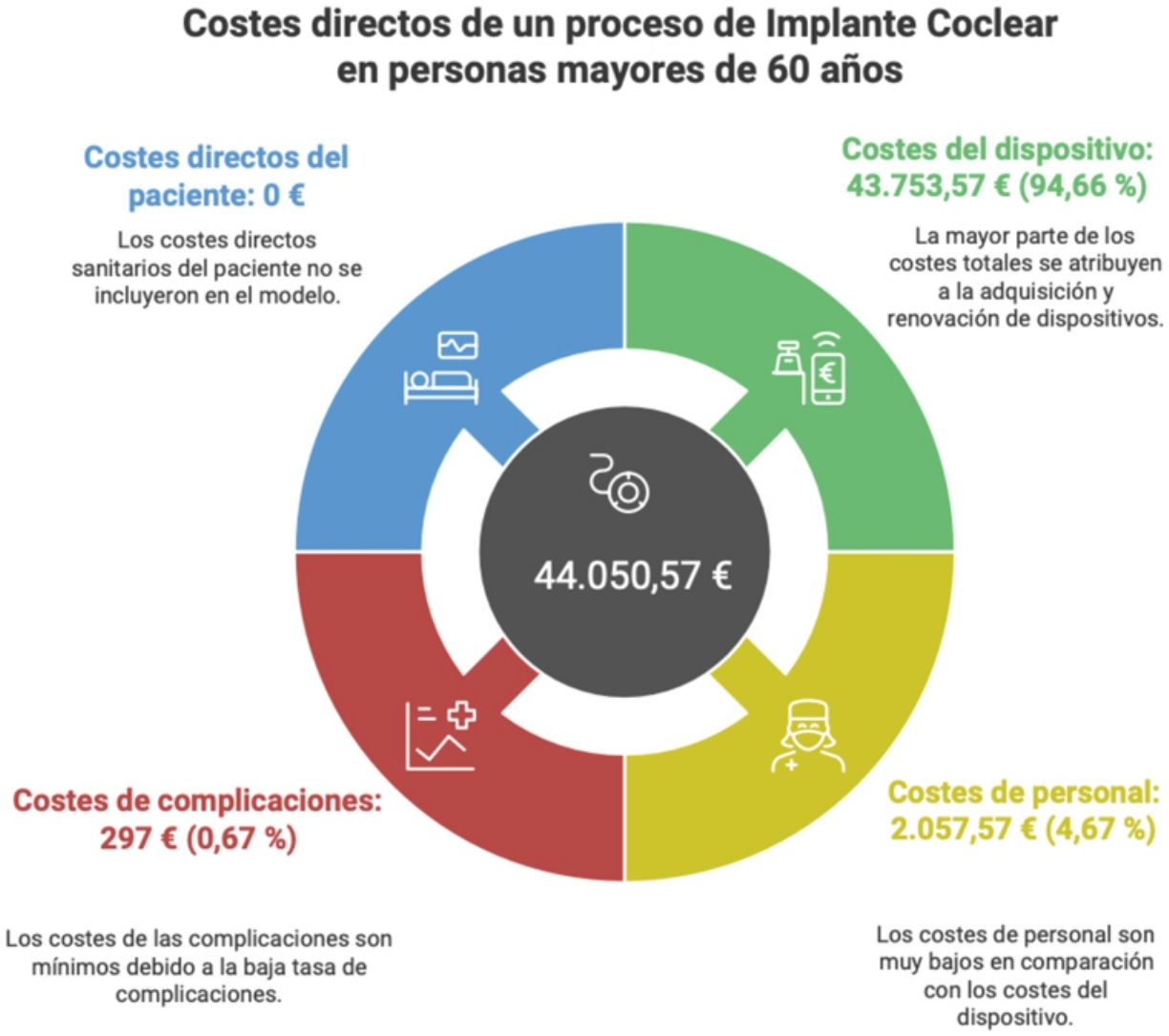
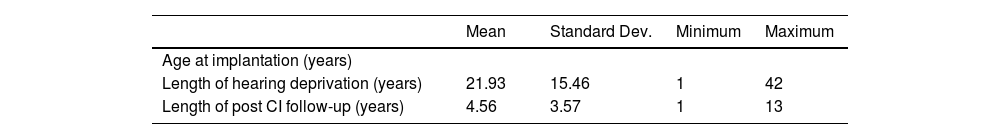
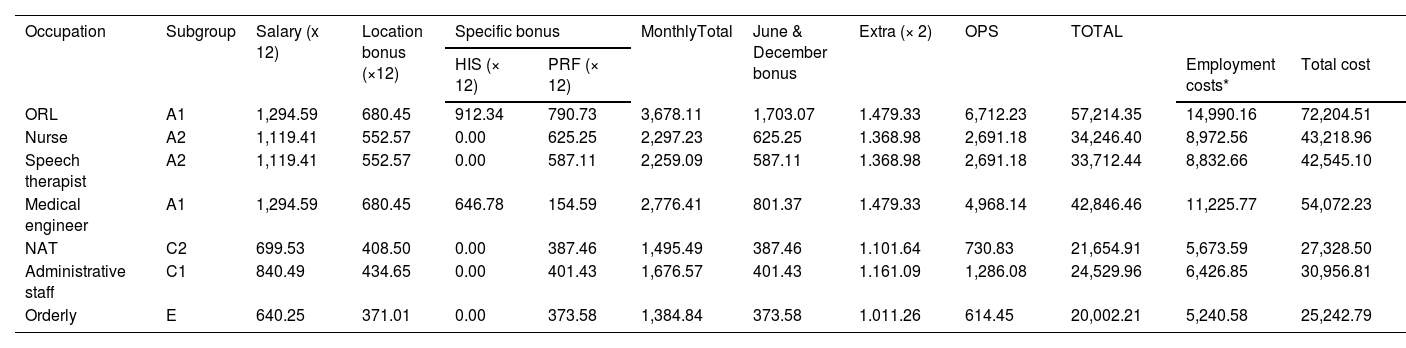
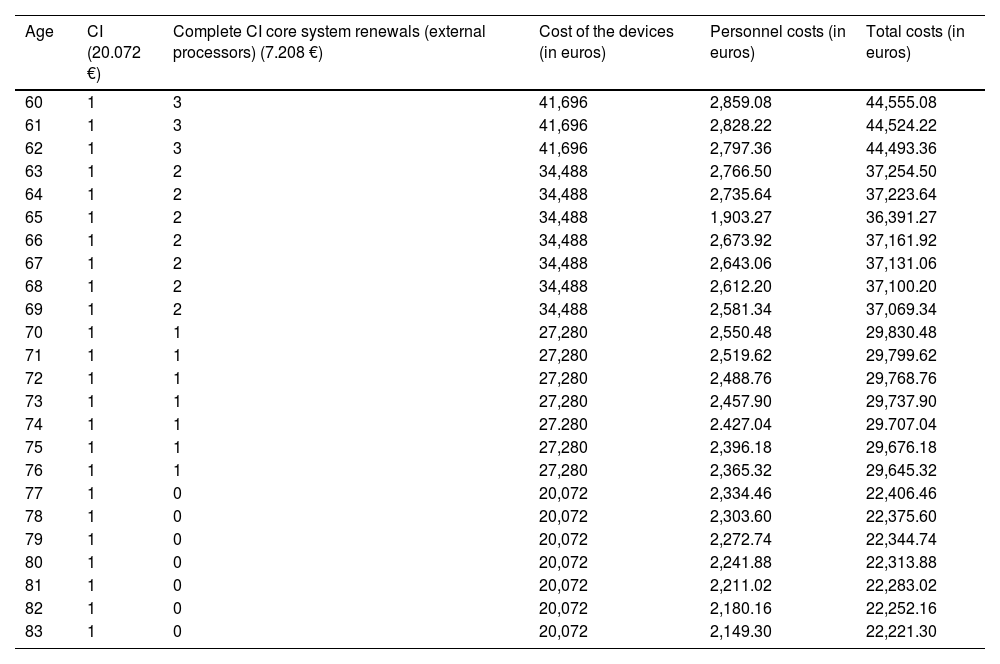
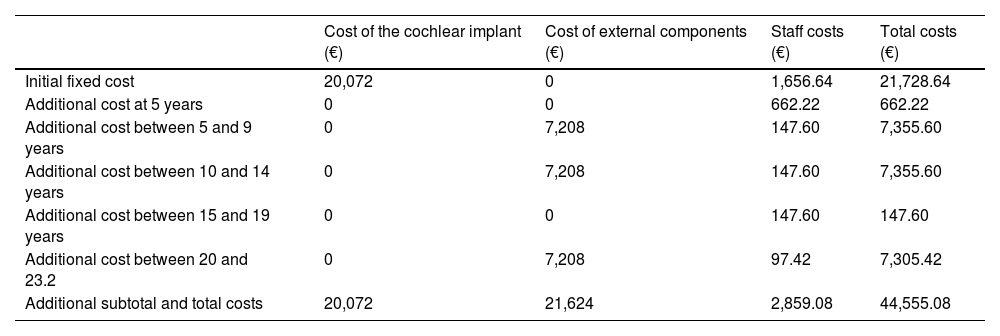
ResultsThe mean age at CI was 67.7 ± 5.8 years. Complications occurred in 8.4% of patients, incorporating the costs of one explantation/reimplantation. The mean total cost per patient was € 44,555.08. Device acquisition and processor upgrades represented the largest share (93.58%, € 41,696), while personnel accounted for 6.41% (€ 2,859.08) and complications for 0.67% (€ 297).
ConclusionsThe direct costs of a unilateral CI procedure in individuals over 60 amount to an investment of € 44,555.08, driven primarily by device and processor upgrade expenses. Personnel costs are low but involve substantial multiprofessional organisational complexity. Deriving direct costs from primary sources tied to a specific clinical pathway provides a more realistic estimate than probabilistic modelling and can aid health‐care administrations in decision-making.
El implante coclear (IC) unilateral es el tratamiento recomendado para la sordera neurosensorial profunda en adultos mayores cuando los audífonos no dan respuesta. Se planteó el objetivo de conocer los costes directos asociados a este procedimiento para facilitar la toma de decisiones por el proveedor sanitario.
Material y métodosSe llevó a cabo un estudio unicéntricotransversal observacional en un hospital terciario. Se realizó un análisis económico por microcosteo (bottom-up). Se imputaron los costes directossegún el Acuerdo Marco y las tablas salariales del Servicio Andaluz de Salud: dispositivo, complementos, personal, cirugía, hospitalización, seguimiento clínico, complicaciones y renovaciones tecnológicas. Se calculó el coste acumulado actualizado a euros de 2024 con un horizonte temporal medio de 23,3 años.
ResultadosSobre 278 personas implantadas cocleares con 60 años o más entre 2009–2020, se incluyó finalmente una muestra de 71 individuos (37 mujeres, 52,1%) tras un muestreo aleatorio estratificado. La edad media al IC fue 67,7 ± 5,8 años. El 8,4% de los pacientes presentó complicaciones, asumiéndose los costes de 1 explantación/reimplantación. El coste total medio por paciente ascendió a 44.555,08€. La adquisición del dispositivo y renovación de procesadores representaron la mayor proporción (93,58%,41.696€), mientras que el personal supuso el 6,41% (2.859,08 €) y las complicaciones el 0,67% (297 €).
ConclusionesLos costes directos de un proceso de IC unilateral en personas mayores de 60 años suponen una inversión de 44.555,08€, destacando principalmente los costes del dispositivo y la renovación de procesadores. El coste de personal es muy bajo, aunque implica una gran complejidad organizativa multiprofesional. La determinación de costes directos a partir de fuentes primarias asociados a una vía clínica específica es más representativa de la realidad que las estimaciones probabilísticas, y pueden facilitar a la administración sanitaria la toma de decisiones.