In this research, we evaluated the association of genetic variants rs1800629 in TNF and rs2228145 in IL6R with production of neutralising antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and the frequency of adverse effects following immunisation (AEFIs) in adult population from Western of Mexico that received AZD1222 vaccination.
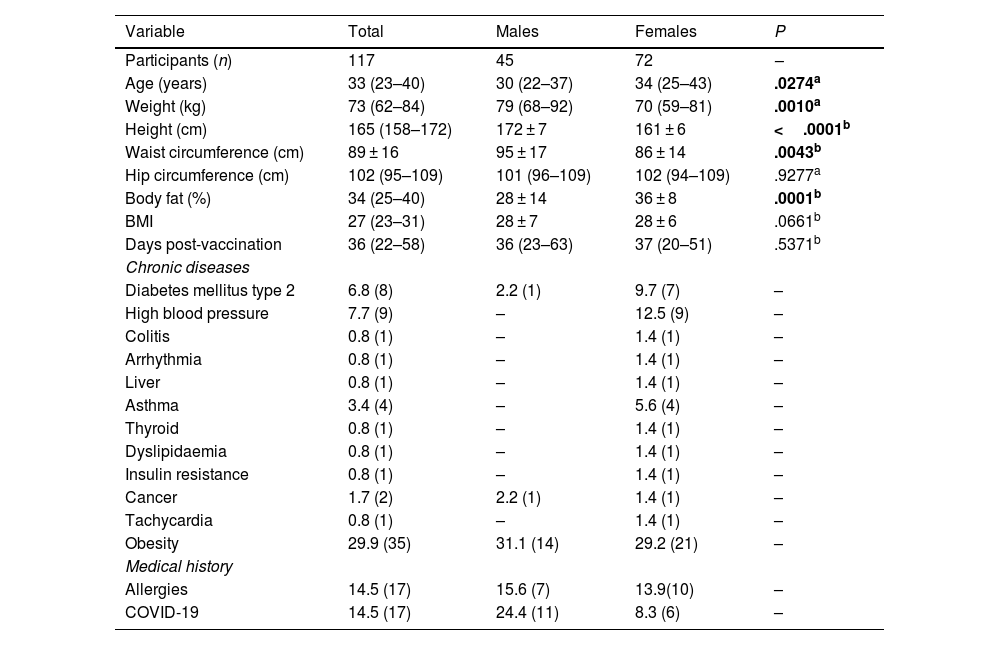
Methods117 adults were evaluated [33 years (23–40), 65% women]. The self-reported frequency of AEFIs was recorded and the percentage of post-vaccination neutralising antibodies was quantified. The identification of rs1800629 variant in TNF and rs2228145 in IL6R was performed by qPCR.
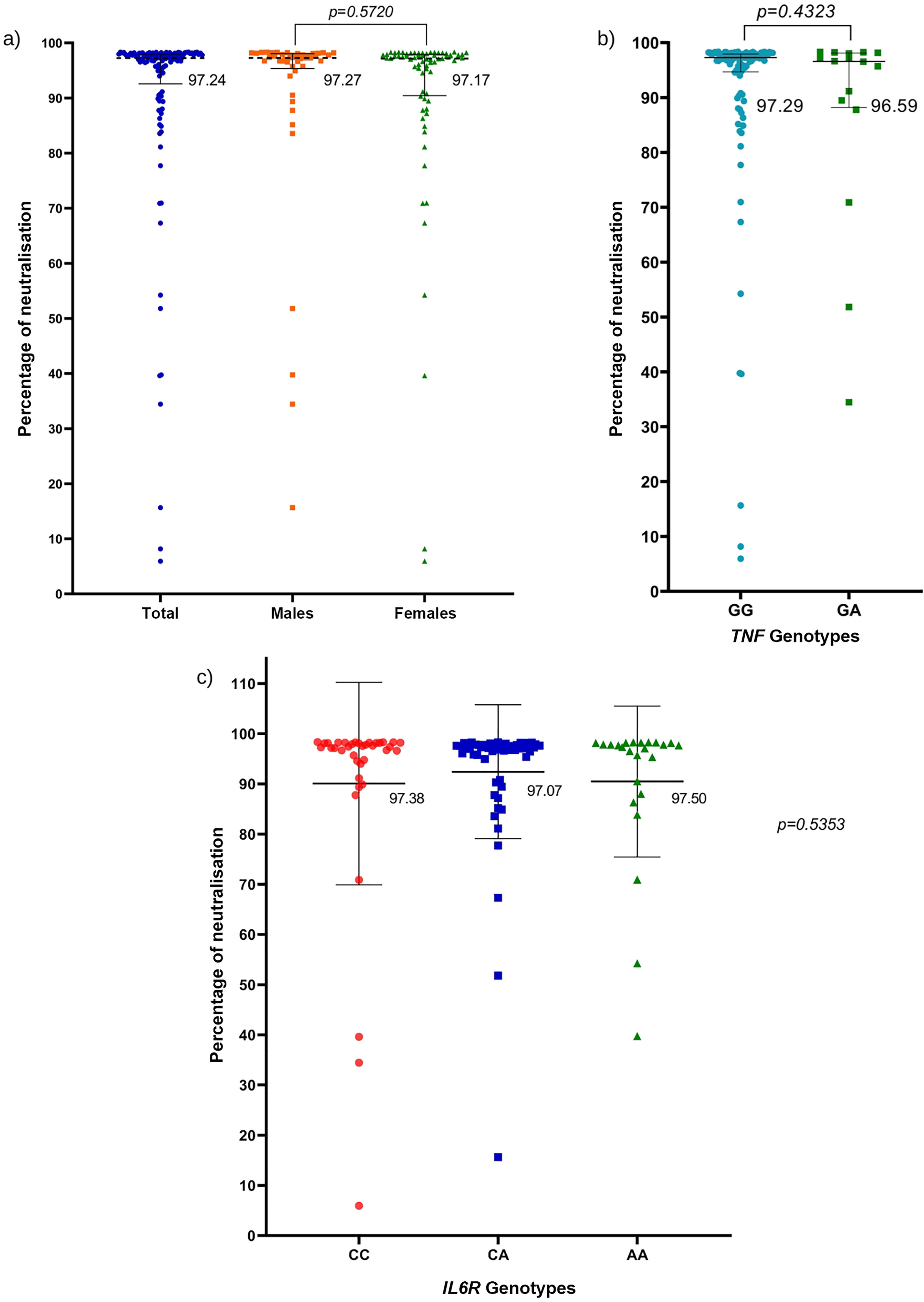
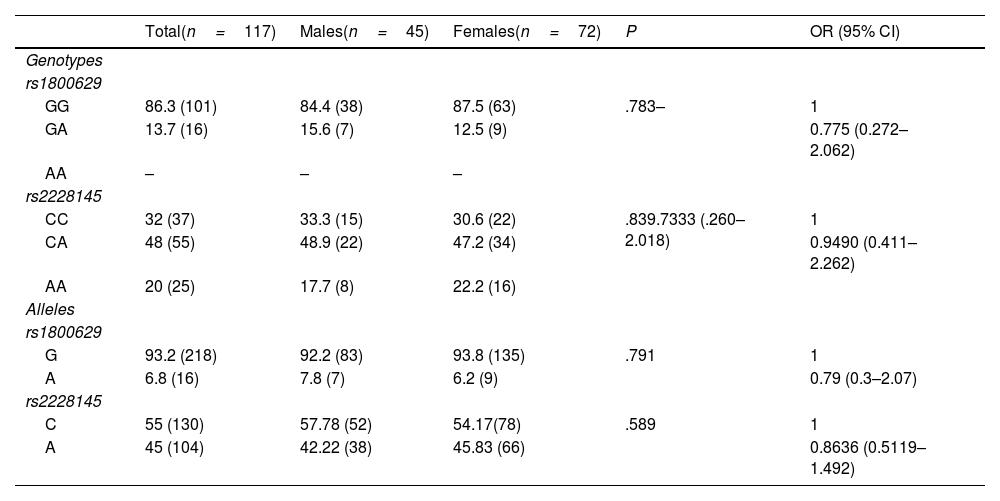
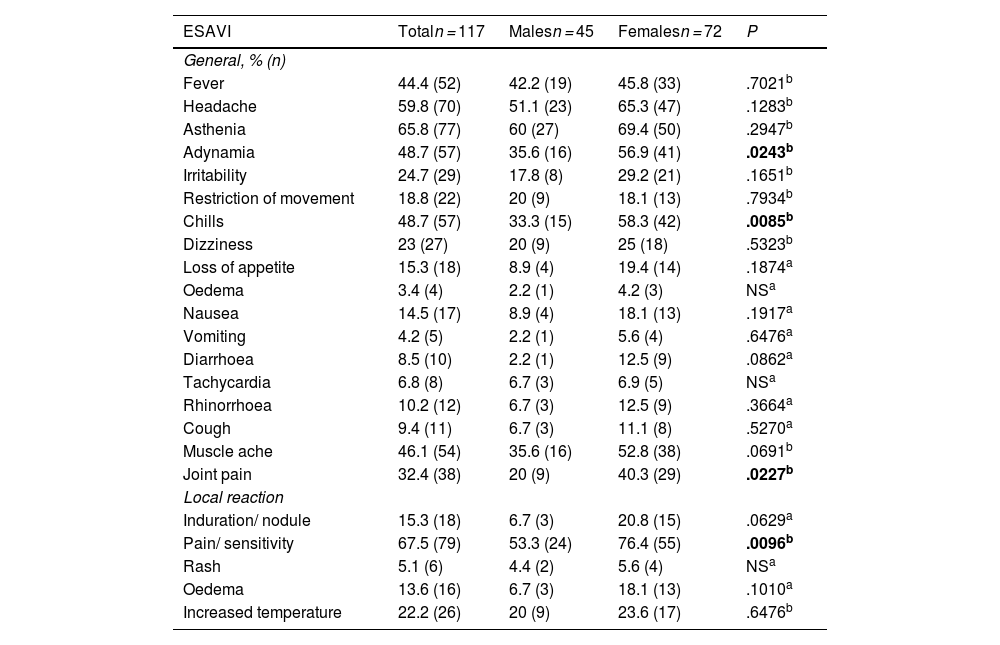
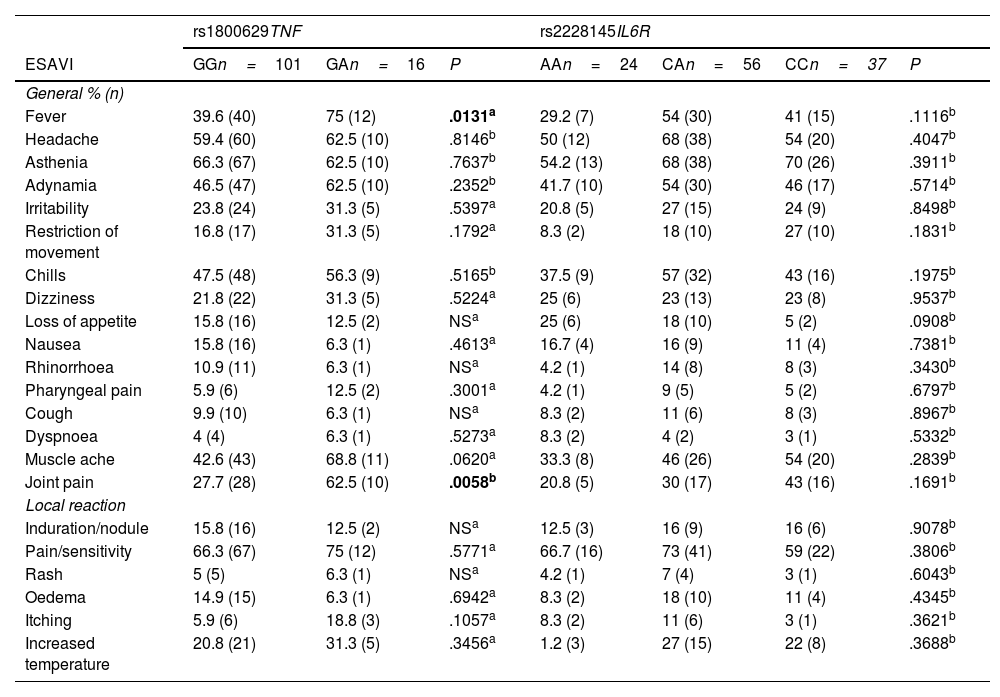
ResultsThe genotype frequencies of rs1800629 variant were: GG (86%) and GA (14%), and for rs2228145 variant were: AA (20%), CA (48%), and CC (32%). The percentage of post-vaccination antibodies was similar between men and women (median, 97.24%). An association was found between the frequency of AEFIs with the sex; being adynamia (P=.0243), chills (P=.0085), arthralgia (P=.0227), and pain in application area (P=.0096) more frequent in women. The GA genotype of rs1800629 variant showed an association with fever (P=.0131) and arthralgia (P=.0058) post-vaccination, but no relationship was found with the production of neutralising antibodies after AZD1222 vaccination. The rs2228145 variant was not associated with the production of antibodies nor with the AEFIs reported.
ConclusionThe genetic variants rs1800629 in TNF and rs222815 in IL6R are not associated with the production of neutralising antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 after receiving AZD1222 scheme in population from western of Mexico; however, the results suggest that rs1800629 variant increases the frequency of post-vaccination events, particularly fever and arthralgia.
En esta investigación se evaluó la asociación de las variantes genéticas rs1800629 en TNF y rs2228145 en IL6R con la producción de anticuerpos neutralizantes contra SARS-CoV-2 y la frecuencia de eventos supuestatemente atribuibles a la vacunación o inmunización (ESAVIs) en población adulta del occidente de México con esquema de vacunación AZD1222.
MétodosSe evaluaron 117 adultos [33 años (23–40), 65% mujeres]. Se registró la frecuencia autoreportada de ESAVIs y se cuantificó el porcentaje de anticuerpos neutralizantes post-vacunación. La identificación de las variantes genéticas rs1800629 y rs2228145 se realizó mediante qPCR.
ResultadosLa frecuencia de los genotipos de la variante rs1800629 en TNF fue: GG (86%) y GA (14%) y de la variante rs2228145 en IL6R: AA (20%), CA (48%) y CC (32%). El porcentaje de anticuerpos post-vacunación fue similar entre hombres y mujeres (mediana 97.24%). La frecuencia de los ESAVIs adinamia (p = 0.0243), escalofríos (p = 0.0085), artralgia (p = 0.0227) y dolor en zona de aplicación (p = 0.0096) fueron más frecuentes en mujeres. El genotipo GA de rs1800629 se asoció con fiebre (p = 0.0131) y artralgia (p = 0.0058) post-vacunación, pero no con la producción de anticuerpos neutralizantes. La variante rs2228145 no se asoció con la producción de anticuerpos ni con la frecuencia de ESAVIs.
ConclusiónLas variantes rs1800629 en TNF y rs222815 en IL6R no se asocian con la producción de anticuerpos neutralizantes contra SARS-CoV-2 después de recibir el esquema AZD1222 en población del occidente de México, sin embargo, los resultados sugieren que la variante rs1800629 incrementa la frecuencia de los ESAVIs fiebre y artralgia.