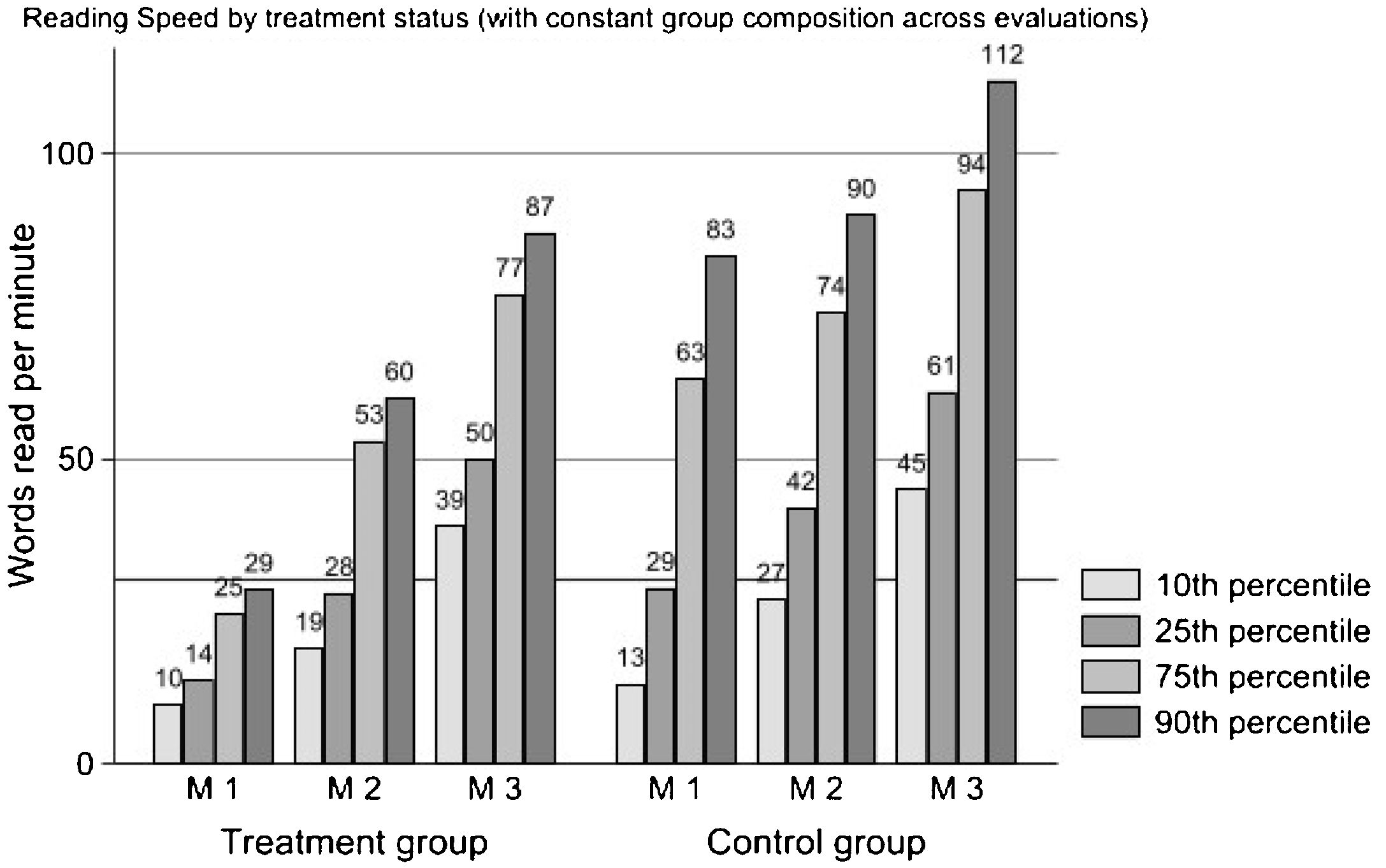
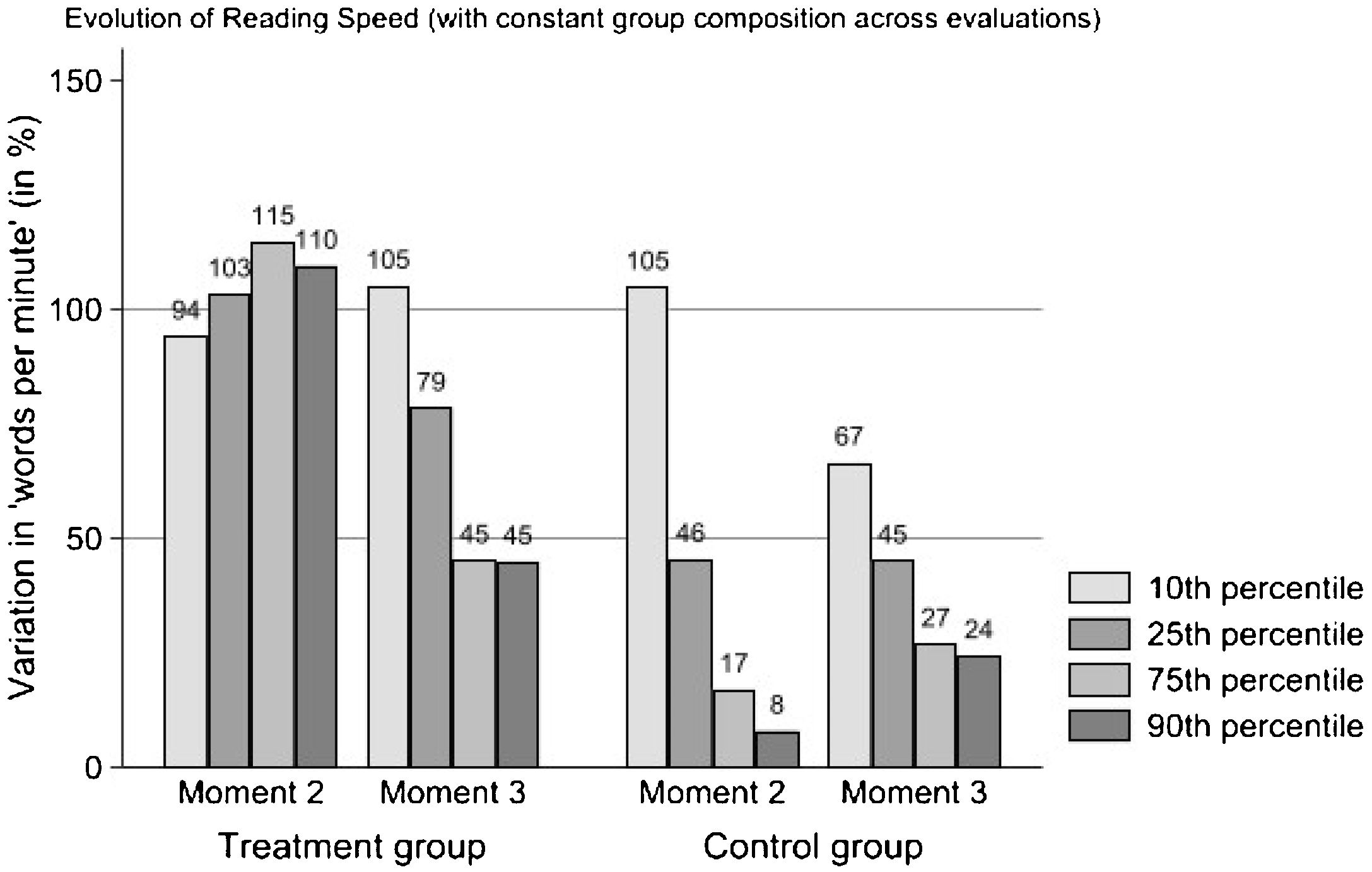
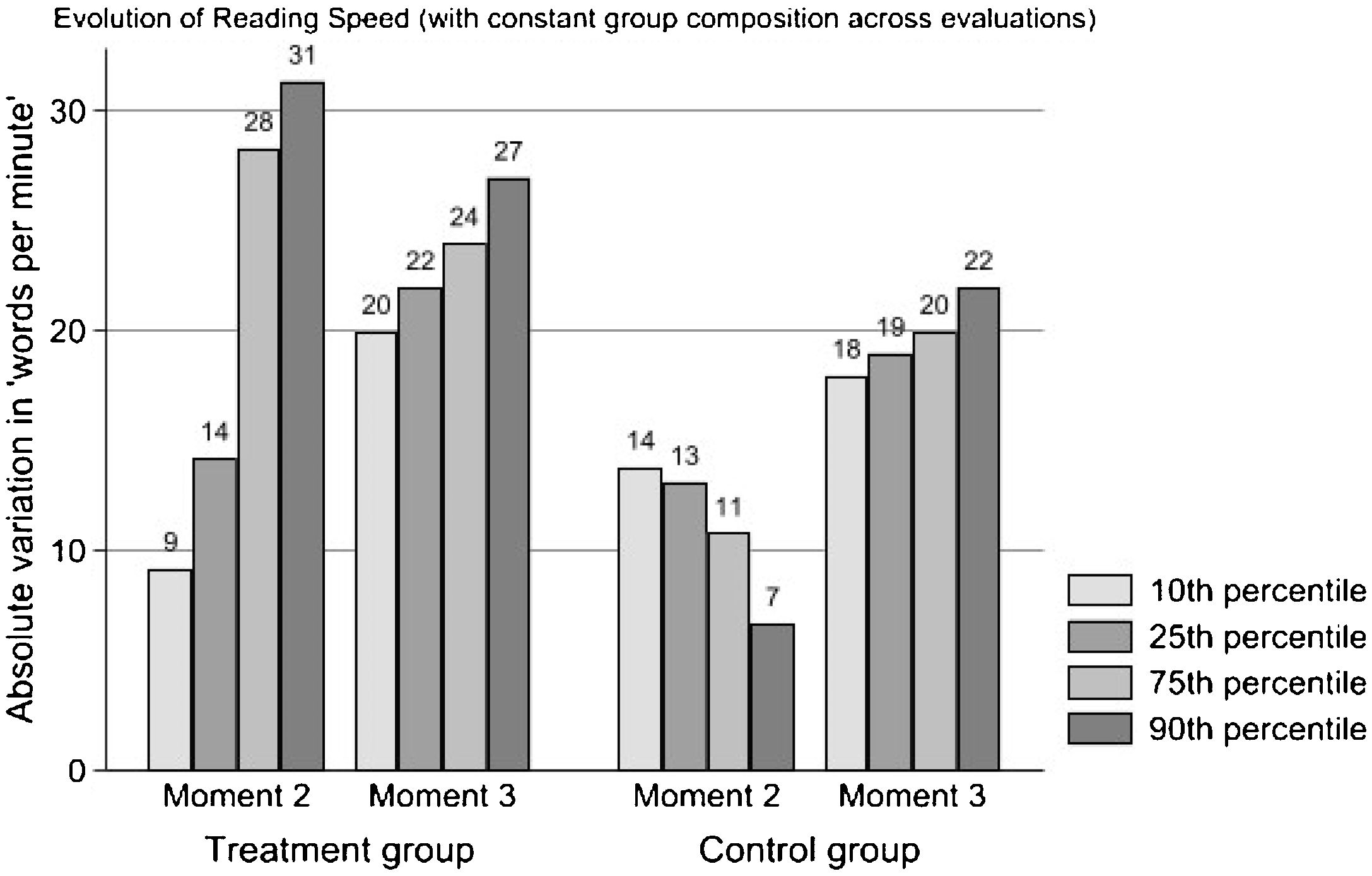
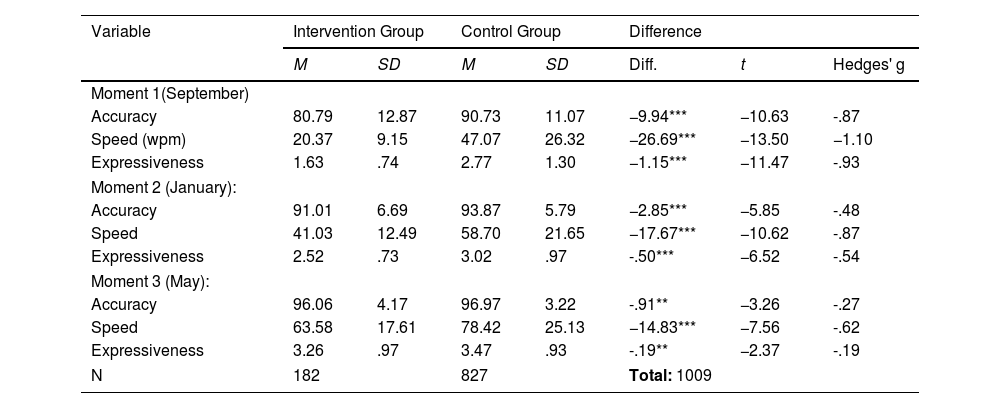
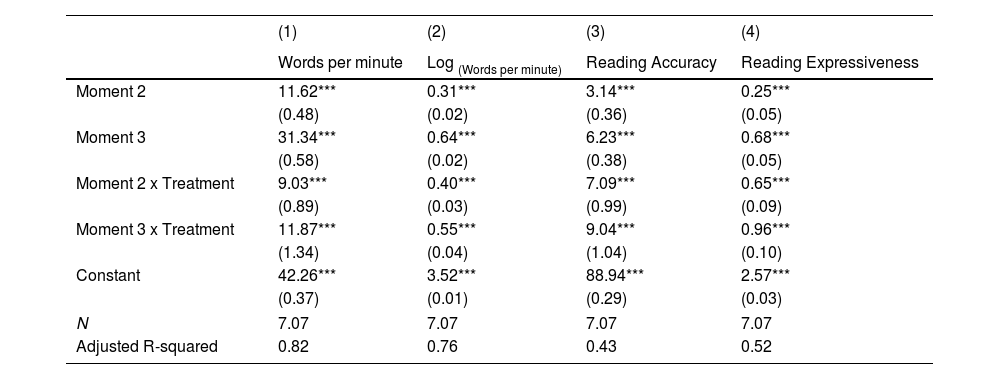
Many children in primary grades show difficulties with reading fluency, hardly reading text or doing it effortfully and fruitlessly, making intervention programs for struggling readers a priority for researchers and schools. This paper analyzes the results of a reading intervention program for 182 second-grade struggling readers (boys=aged 7-8 46.7%) from public schools. Students received a multi-component program, including repeated readings, word recognition, morphological analysis, text interpretation, and writing skills. Participants received about fifty 45-minute intervention sessions over the school year. Using a difference-in-differences, quasi-experimental between- (intervention and control group) and within-group longitudinal design (three-point measurements), we found that the intervention group progressed significantly faster than a classmate control group (n=827, boys=aged 7-8, 52.4%) in all reading outcomes (speed, accuracy, and expressiveness). By the end of the school year, differences between the intervention and control groups in accuracy and expressiveness become small but are still large in reading speed. Implications for research and practice are presented at the end of the paper.
Muchos niños de Educación Primaria muestran dificultades con la fluidez de la lectura, leyendo textos con muchas dificultades o leyendo con esfuerzo y sin éxito, lo que hace que los programas de intervención para lectores con dificultades sean una prioridad para los investigadores y las escuelas. Este artículo analiza los resultados de un programa de intervención en lectura para 182 estudiantes de segundo grado (edades 7-8, 46.7% de sexo masculino), con dificultades de lectura. Los participantes han recibido un programa de componentes múltiples, que ha incluido lecturas repetidas, reconocimiento de palabras, análisis morfológico, interpretación de textos y habilidades de escritura. A lo largo del año escolar, los estudiantes han participado en aproximadamente cincuenta sesiones de intervención de 45 minutos. Utilizando un diseño longitudinal cuasiexperimental, de diferencia-en-diferencias, entre grupos (grupo de intervención y grupo de control) y dentro del grupo (tres mediciones), se ha encontrado que el grupo de intervention progresa significativamente más rápido en todos los resultados (velocidad de lectura, precisión y expresividad) que un grupo de control de compañeros de clase (n=827, edades 7-8, 52.4% de sexo masculino). Al final del año escolar, las diferencias entre los grupos de intervention y control en precisión y expresividad se han vuelto pequeñas, pero se mantienen grandes en la velocidad de lectura. Se presentan al final del artículo las implicaciones de estos resultados para la investigación y la práctica.