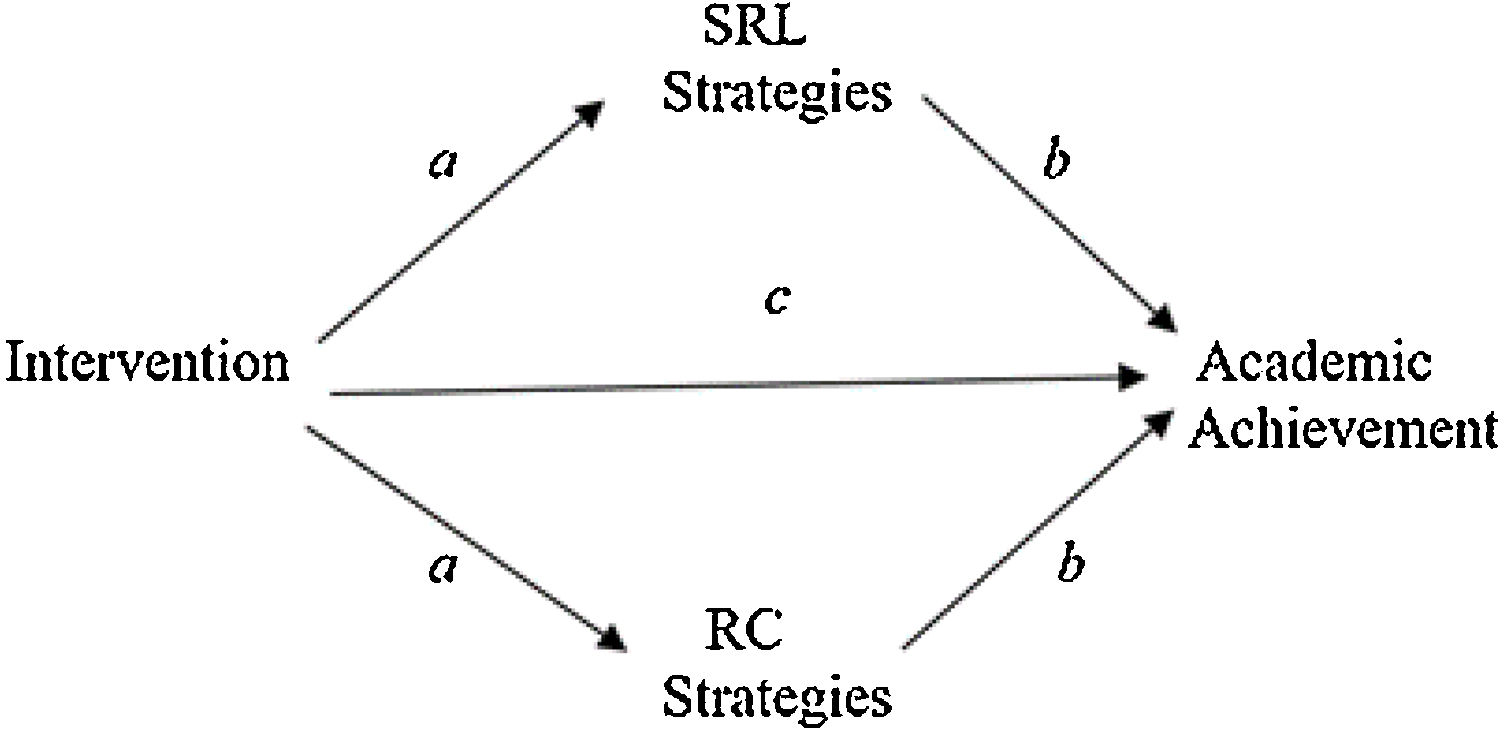
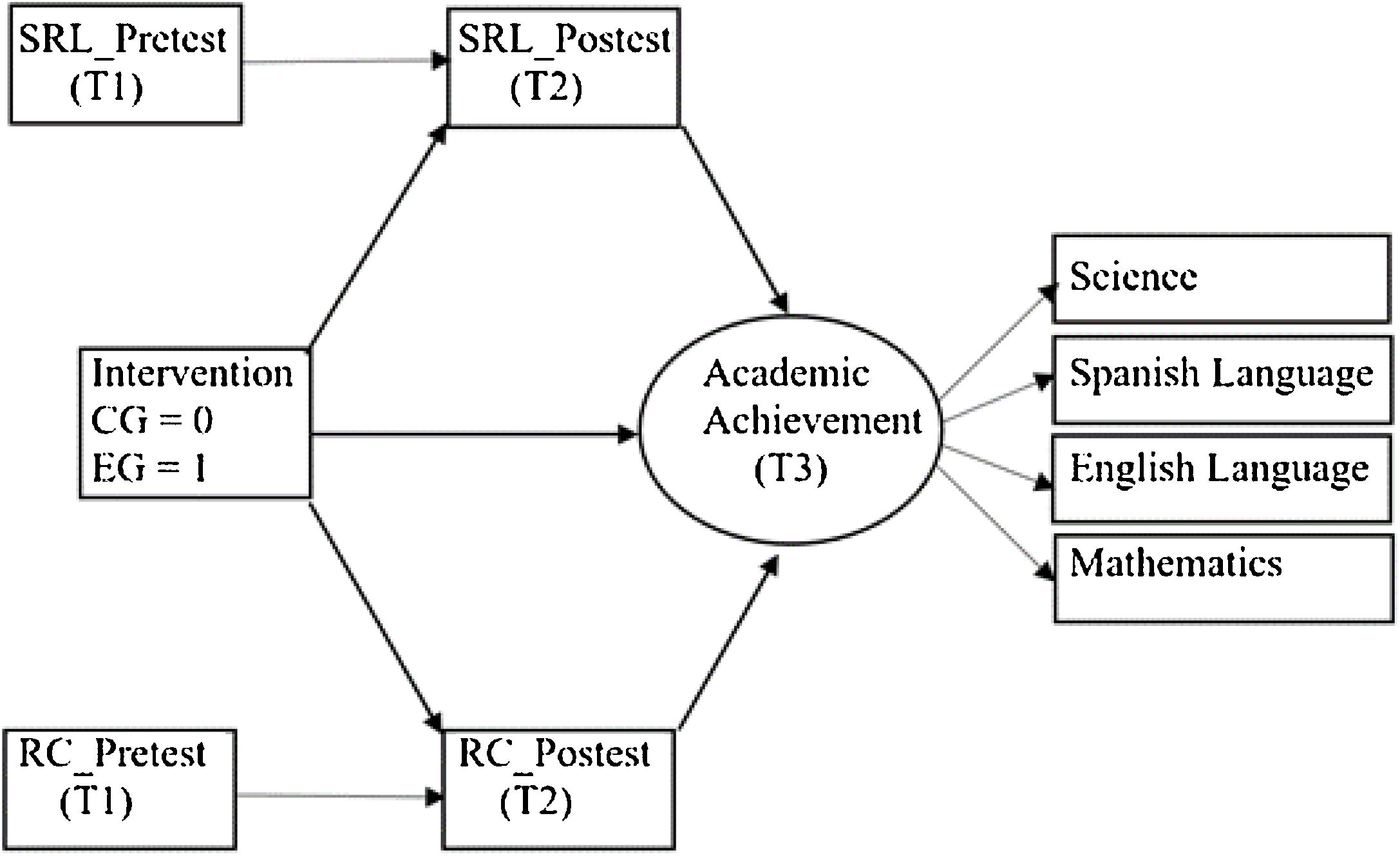
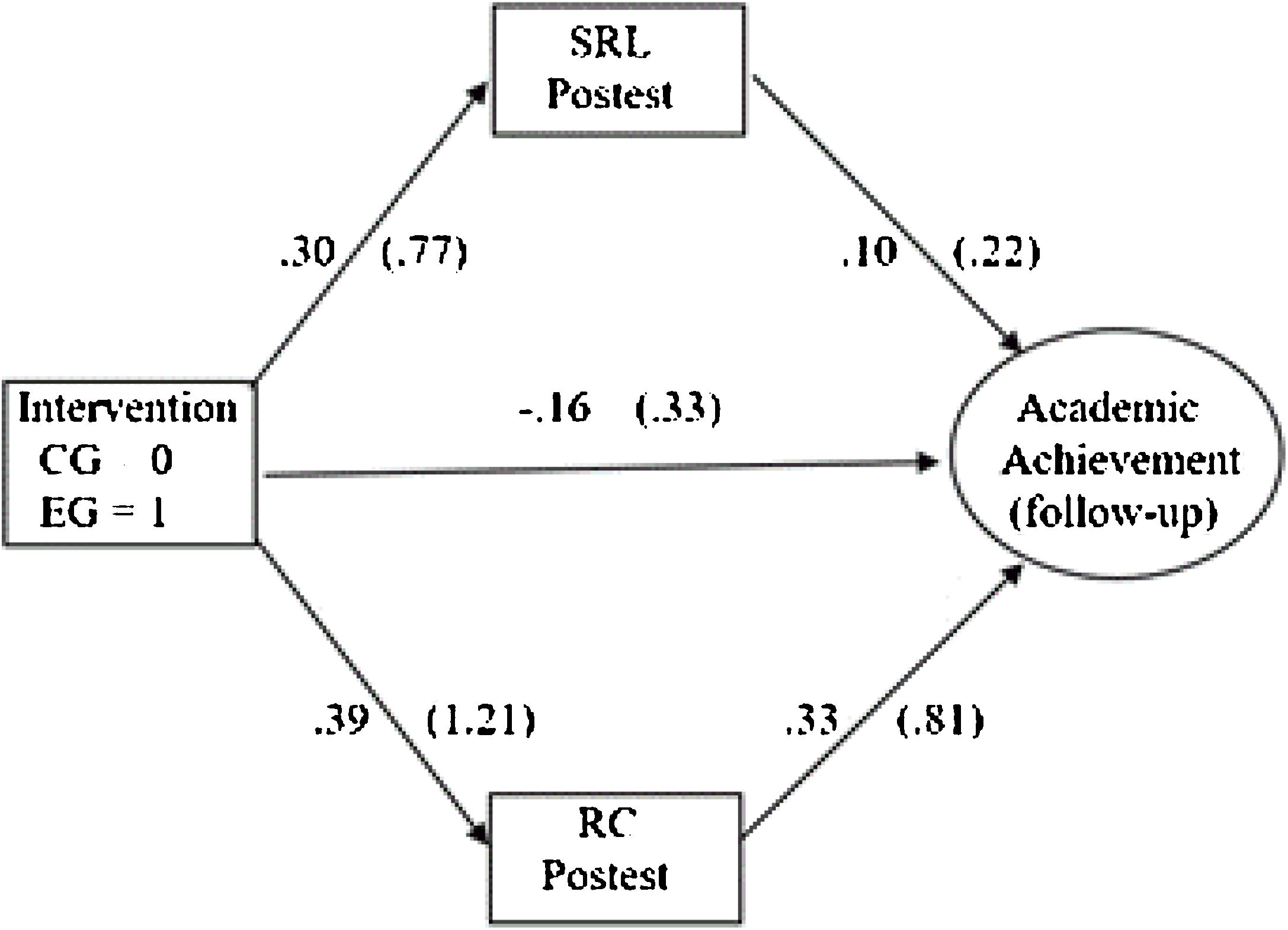
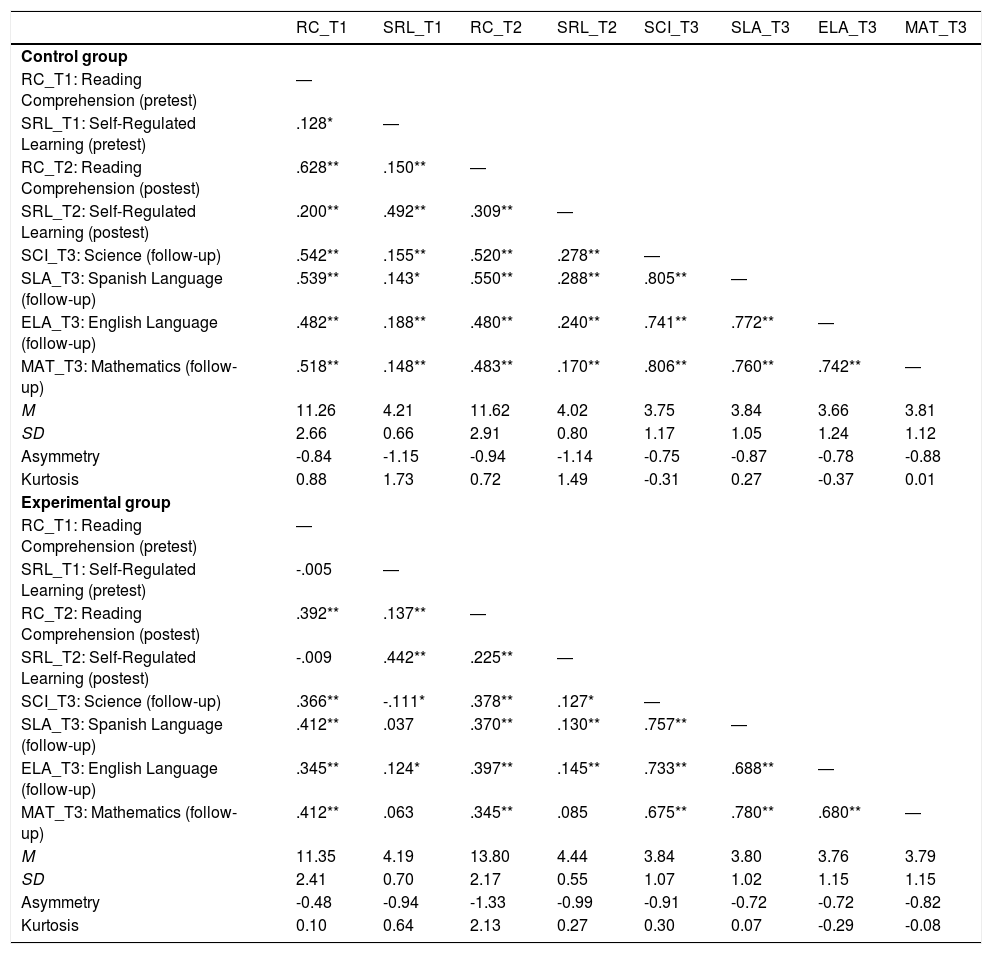
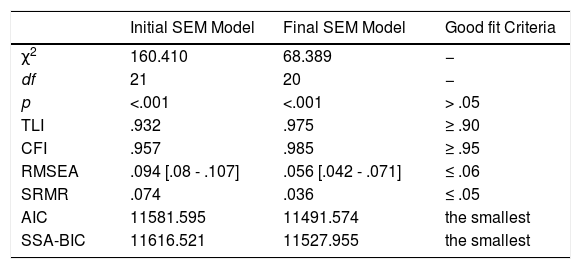
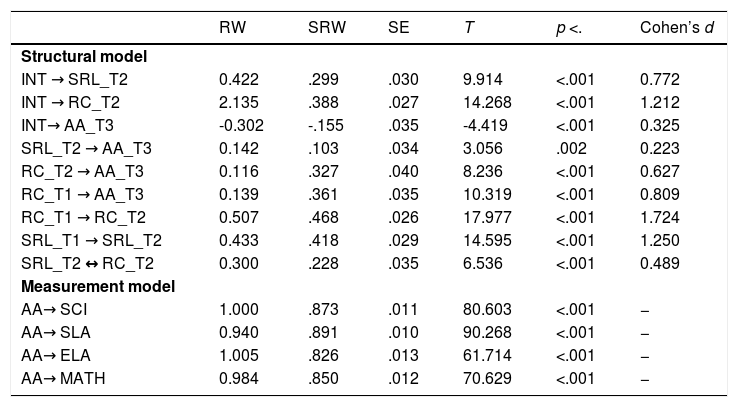
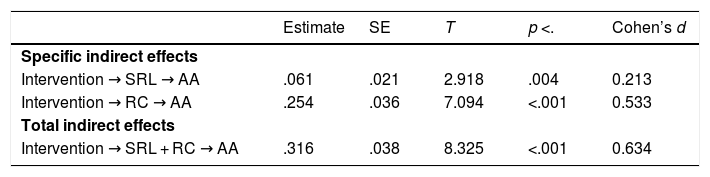
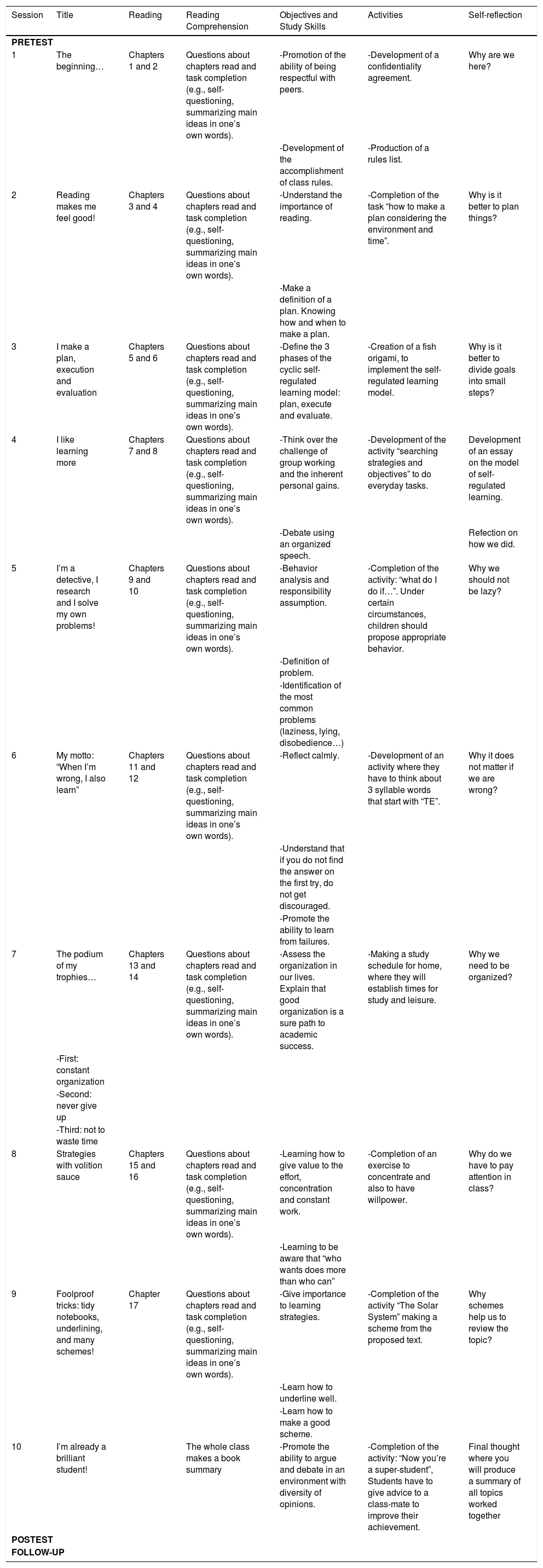
The aim of this study was twofold: (1) to analyse the extent to which a training program in Self-Regulated Learning (SRL) and Reading Comprehension (RC) strategies would lead to improvements in these competencies in elementary school students, and (2) the extent to which the improvements in these competencies would be associated with improvements in academic achievement. An experimental study with an experimental group and a control group was conducted in an authentic environment with pre, post, and follow-up measures. A total of 758 elementary school students participated in the study, (403 in the experimental group and 355 in the control group). The results revealed that (1) the strategic activity mediated the effect of the intervention on academic achievement. In fact, (a) the intervention produced significant improvements in the reported use of SRL and on RC strategies and (b) the increase in such strategies was associated with higher academic achievement. In addition, (2) we found that, together with this indirect effect, the intervention influenced academic achievement through variables or conditions other than the strategic activity displayed. Likewise, (3) we were able to verify that the indirect effects through RC strategies were greater than those of SRL strategies. Finally, the analysis results showed that the total effect of the intervention explained 30% of the academic achievement variance. These results are discussed in relation to those reported by previous similar studies.
El objetivo de este estudio ha sido doble: (1) se ha analizado en qué medida un programa de capacitación en estrategias de aprendizaje autorregulado y comprensión lectora ha generado mejoras en estas competencias en estudiantes de primaria, y (2) en qué medida estas mejoras se han asociado con mejoras en el rendimiento académico. Se ha realizado un estudio experimental con un grupo experimental y un grupo de control en un entorno auténtico, con medidas pretest, postest y de seguimiento. En el estudio han participado un total de 758 estudiantes de primaria, (403 en el grupo experimental y 355 en el grupo control). Los resultados han mostrado que (1) la actividad estratégica ha mediado el efecto de la intervención sobre el rendimiento académico, ya que (a) la intervención ha producido mejoras significativas en el uso de las estrategias entrenadas (autorregulación del aprendizaje y comprensión lectora) y (b) el incremento en tales estrategias se ha asociado con un mayor rendimiento académico. Además, (2) se ha obtenido que, junto con este efecto indirecto, la intervención ha condicionado el rendimiento a través de otras variables o condiciones (distintas a la actividad estratégica entrenada). Asimismo, (3) se ha comprobado que los efectos indirectos a través de las estrategias de comprensión lectora han sido mayores que los de las estrategias de autorregulación. Finalmente, se ha observado que el efecto total de la intervención sobre el rendimiento académico no supera el 30% de la variabilidad del mismo. Estos resultados han sido discutidos en relación con los aportados por estudios previos semejantes.