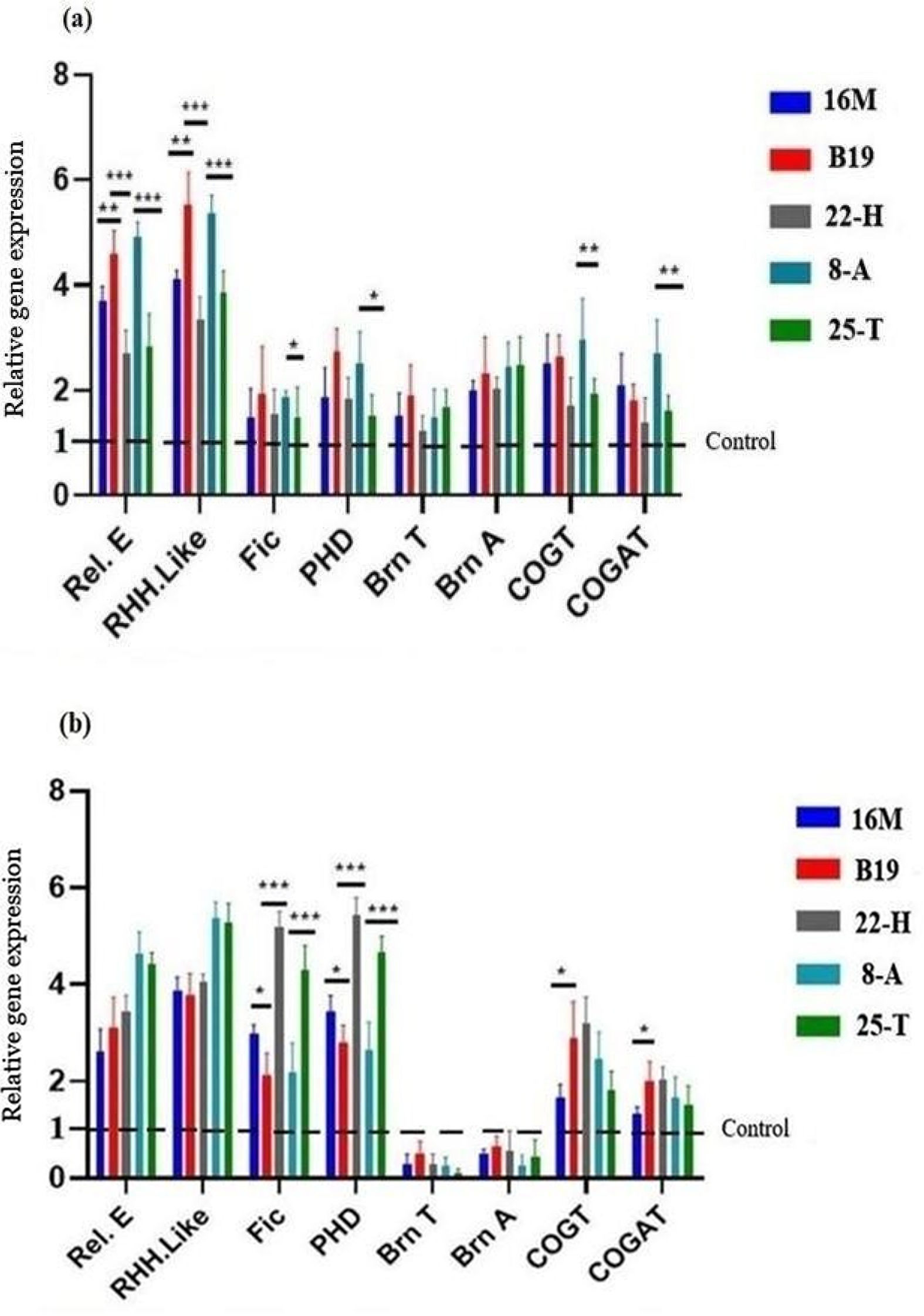
Bacteria can react to stress conditions using the Toxin-Antitoxin (TA) system. This study investigated the expression of TA system genes under heat and antibiotic stresses in Brucella spp.
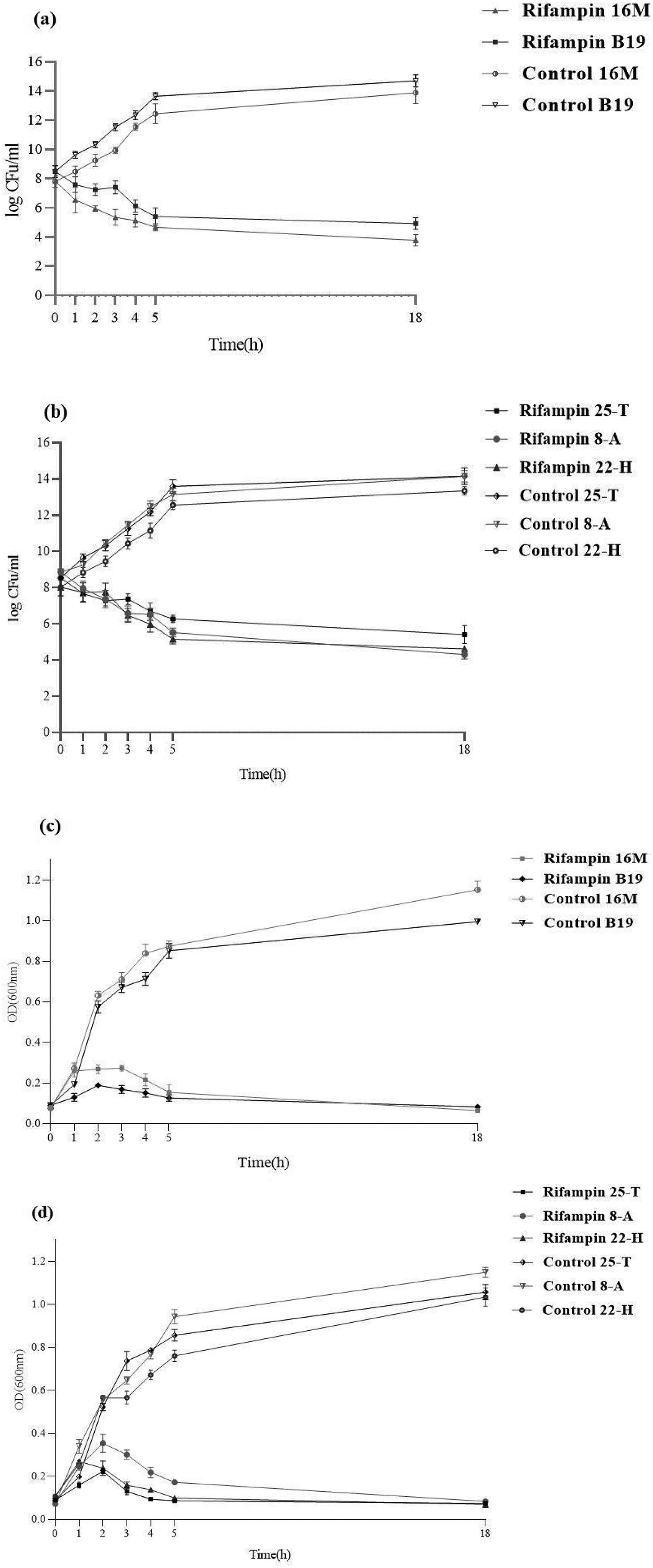
MethodsTo determine the effects of sub-inhibitory concentration (sub-MIC) of rifampin on bacterial survival and growth, a colony-forming unit was quantitated, and turbidity was assessed following the treatment of Brucella isolates, with ½ minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antibiotic at different time intervals. Also, Brucella isolates were exposed to heat stress (42 °C) compared to the control (37 °C). Finally, the expression of TA system genes in Brucella isolates was evaluated one hour after treatment using the quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) method.
ResultsOur results showed that the growth of the Brucella isolates reduced in the presence of the sub-MIC of antibiotics compared to the control. The results of the qPCR assay showed that, in the presence of rifampicin the expression of the TA system genes increased and, under the heat stress conditions, the expression of the TA system genes increased compared to controls expect brnT / brnA system.
ConclusionAlthough the exact role of the TA system in response to various stresses is not yet fully understood, our study provided information on the effectiveness of the type II TA system under heat and antibiotic stress conditions by examining the gene expression of type II systems in Brucella isolates.
Las bacterias pueden reaccionar a condiciones de estrés utilizando el sistema Toxina-Antitoxina (TA). Este estudio investigó la expresión de los genes del sistema TA bajo estrés por calor y antibióticos en Brucella spp.
MétodosPara determinar los efectos de la concentración subinhibitoria (sub-MIC) de rifampicina sobre la supervivencia y el crecimiento bacteriano, se cuantificó una unidad formadora de colonias y se evaluó la turbidez después del tratamiento de aislados de Brucella, con la mitad de la concentración inhibitoria mínima (MIC) de antibiótico a diferentes intervalos de tiempo. Además, los aislados de Brucella estuvieron expuestos a estrés por calor (42 °C) en comparación con el control (37 °C). Finalmente, la expresión de genes del sistema TA en aislados de Brucella se evaluó una hora después del tratamiento utilizando el método de PCR de transcripción inversa cuantitativa (qRT-PCR).
ResultadosNuestros resultados mostraron que el crecimiento de los aislados de Brucella se redujo en presencia de sub-MIC de antibióticos en comparación con el control. Los resultados del ensayo qPCR mostraron que, en presencia de rifampicina, la expresión de los genes del sistema TA aumentó y, en condiciones de estrés por calor, la expresión de los genes del sistema TA aumentó en comparación con los controles que esperan el sistema brnT / brnA.
ConclusiónAunque aún se desconoce el papel exacto del sistema TA en la respuesta al estrés, nuestro estudio proporcionó información sobre la eficacia del sistema TA Tipo II en condiciones de estrés por calor y antibióticos.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora