Persistent scrotal pain after varicocelectomy is stressful for both surgeon and patient. The number of researches focusing on which patient will benefit more from the operation is increasing in the literature. In this prospective study, we aimed to investigate whether the patient's physical activity levels and occupations affect the success of varicocelectomy in terms of pain relief.
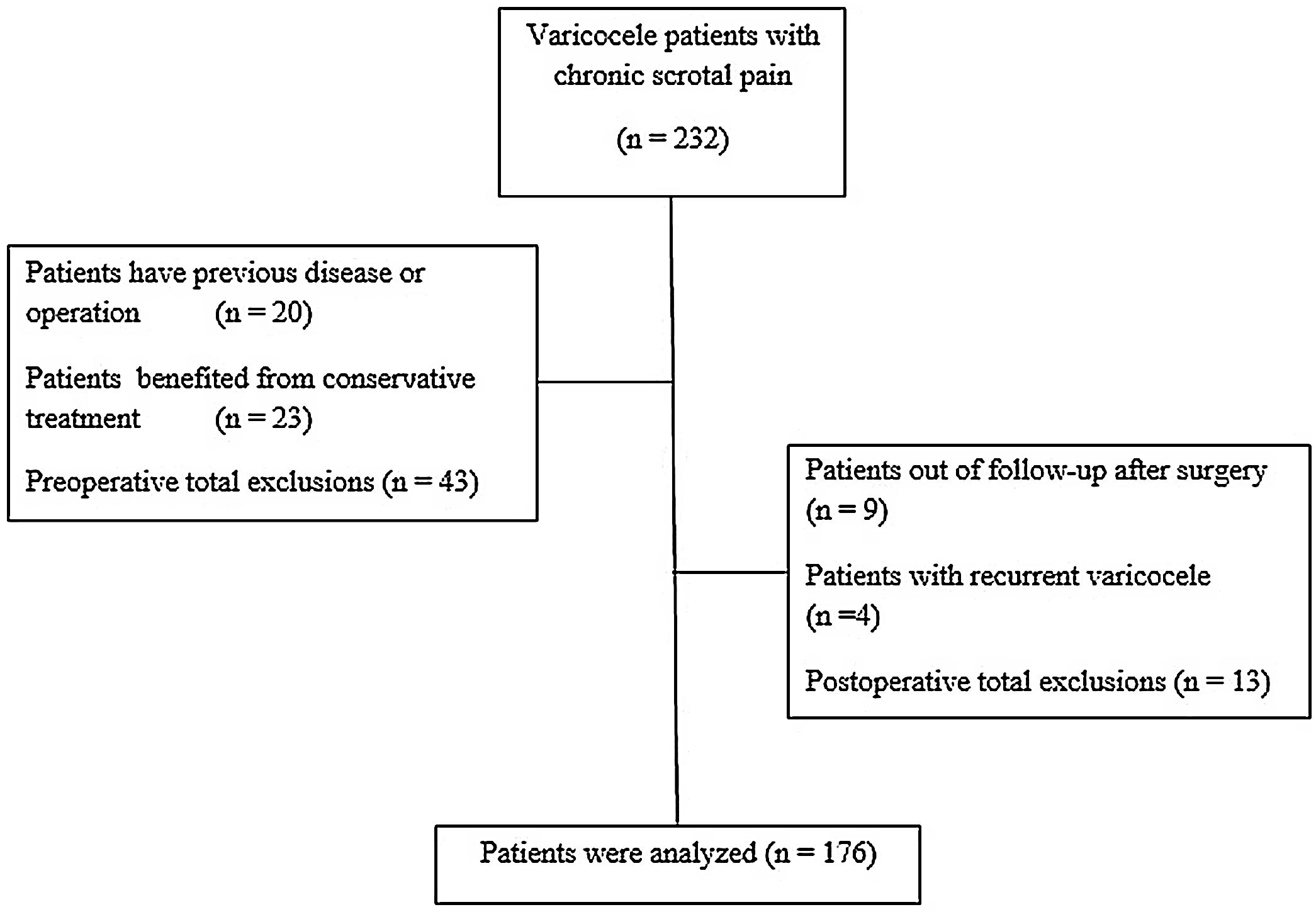
Materials and methodsThe data of 176 patients who underwent subinguinal microscopic varicocelectomy were analyzed according to BMI, age, varicocele grade, laterality, duration of pain, testicular volume difference, quality of pain, level of physical activity, and profession. The International Physical Activity Questionnaire was used to evaluate the level of physical activity. Patients were grouped as inactive, moderately active, and active according to this scale. Visual analog scale (VAS) scores of the patients were recorded before and after the procedure.
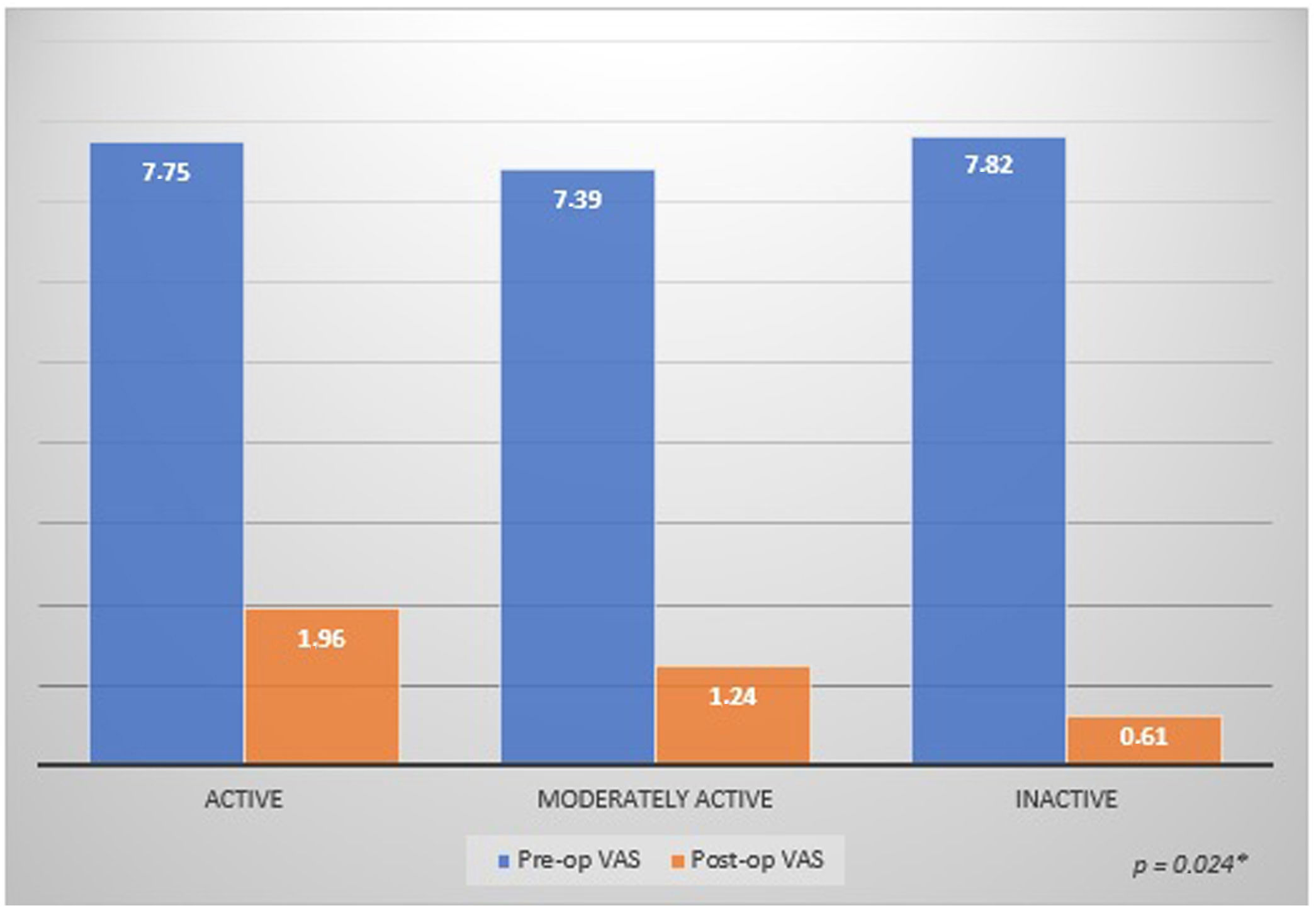
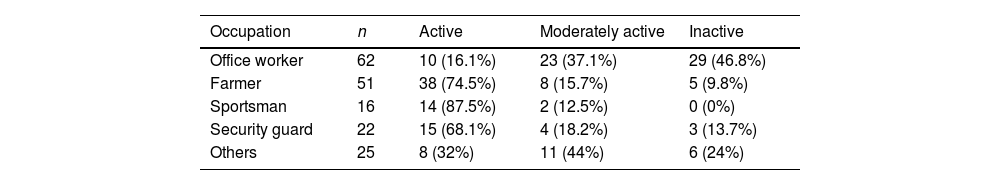
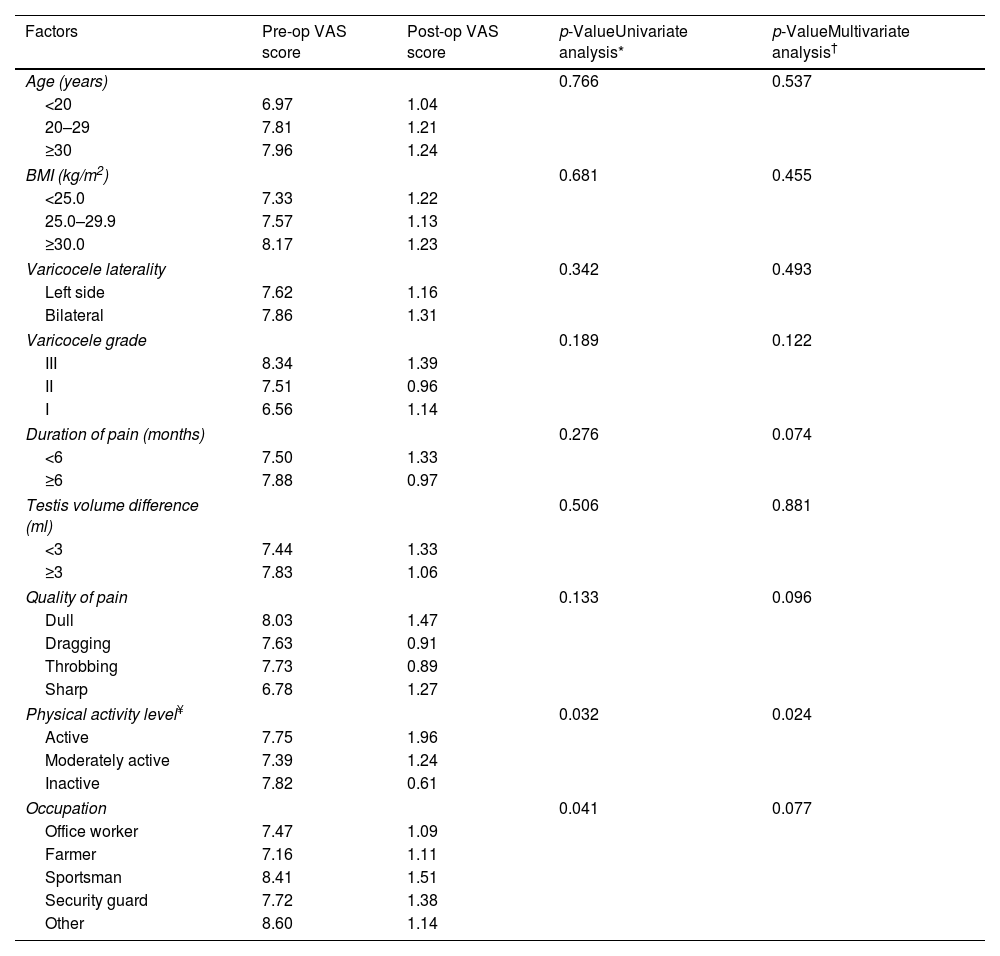
Results135 patients (76.7%) reported complete resolution of their pain. Partial resolution of pain was observed in 34 patients (19.3%). Seven patients (4%) complained of the same pain level. Univariate analysis showed that patient occupations and physical activity levels significantly affected the pain level (p=0.041, p=0.032, respectively). In the multivariate analysis, only physical activity levels of the patients were statistically significant in predicting the resolution of pain (p=0.024).
ConclusionsPatients with low physical activity levels who underwent microscopic varicocelectomy surgery are less likely to have postoperative pain.
El dolor escrotal persistente después de la varicocelectomía es una situación estresante tanto para el cirujano como para el paciente. En este estudio prospectivo, nuestro objetivo fue investigar si los niveles de actividad física y las ocupaciones del paciente afectan el éxito de la varicocelectomía en términos de alivio del dolor.
Materiales y métodosSe analizaron los datos de 176 pacientes que se sometieron a varicocelectomía microscópica subinguinal según IMC, edad, grado de varicocele, lateralidad, duración del dolor, diferencia de volumen testicular, calidad del dolor, nivel de actividad física y profesión. Se utilizó el Cuestionario Internacional de Actividad Física para evaluar el nivel de actividad física. Los pacientes se agruparon en inactivos, moderadamente activos y activos según esta escala. Las puntuaciones de la escala visual analógica visual de los pacientes se registraron antes y después del procedimiento.
ResultadosCiento treinta y cinco pacientes (76,7%) informaron resolución completa de su dolor. Se observó resolución parcial del dolor en 34 pacientes (19,3%). Siete pacientes (4%) todavía se quejaban del mismo nivel de dolor. El análisis univariado mostró que las ocupaciones de los pacientes y los niveles de actividad física afectaron significativamente el nivel de dolor (p=0,041; p=0,032, respectivamente). En el análisis multivariado, solo los niveles de actividad física de los pacientes fueron estadísticamente significativos para predecir la resolución del dolor (p=0,024).
ConclusionesLos pacientes con bajo nivel de actividad física que serán operados de varicocelectomía microscópica tienen menor probabilidad de presentar dolor postoperatorio.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora