The 3rd International Nursing & Health Sciences Students & Health Care Professionals Conference (INHSP) 2019
Más datosThe objectives of the systematic review are to evaluate the context and mechanism component of the stunting intervention.
MethodsThe selection process for systematic reviews, following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA). Searching in PubMed and Scinapse. The keywords “Stunting and Randomized Control Trials. Article on quality assessment by Grading of Recommendations on assessment Development and Evaluation.
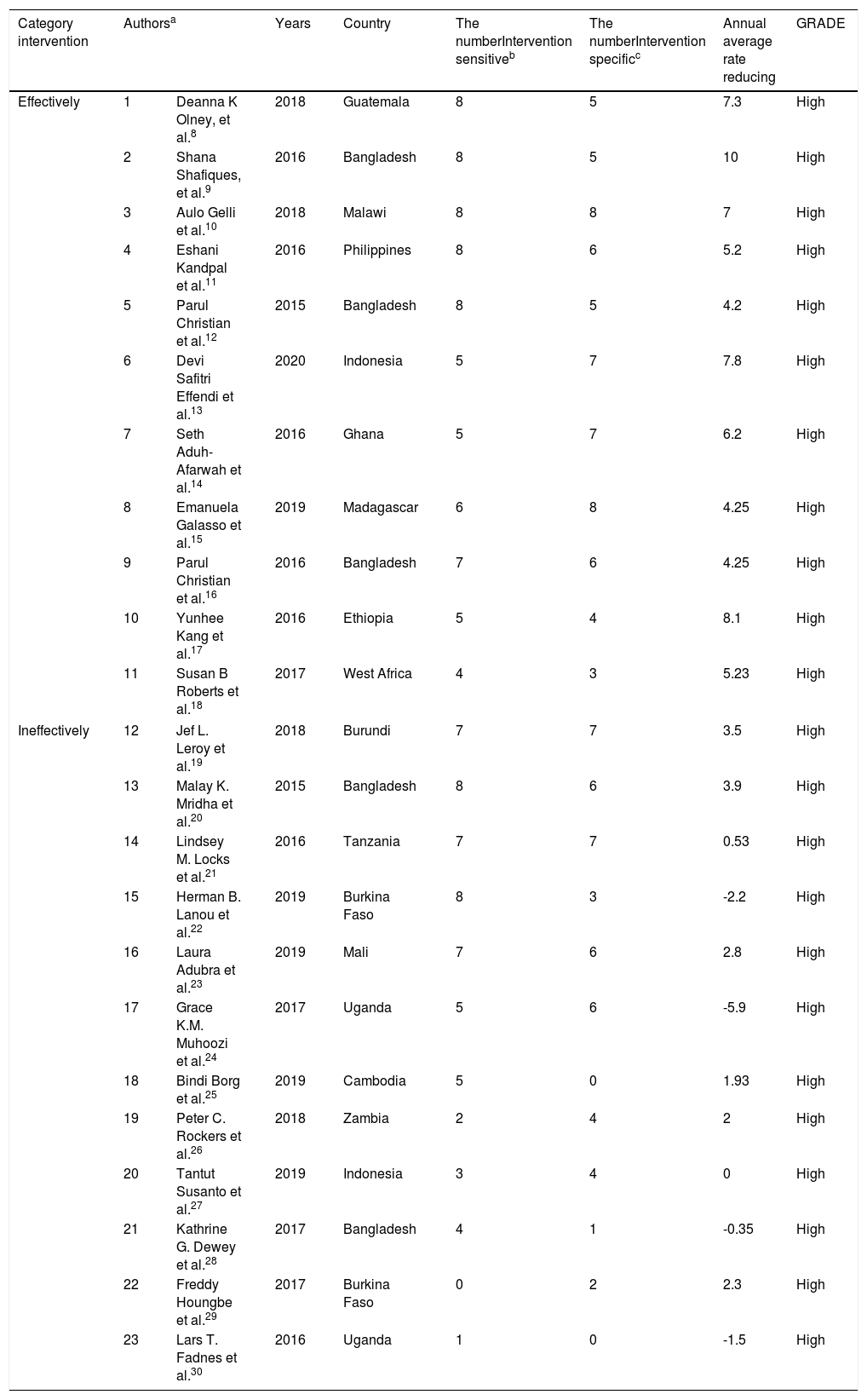
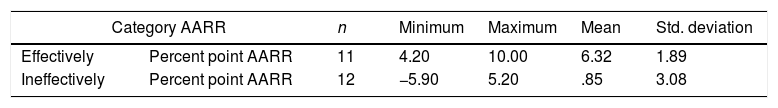
ResultsThe context of intervention should be in line with infant feeding (90.9%), Vitamin A supplementation and iron-folic acid (81.8%), infectious disease treatment (63.3%), promotion growth monitoring (100%), Management Integrated Infant Disease (54.5%) and food security (81.18%). The mechanism of intervention delivery by strong political commitment (100%) and multi-sector approach (90.9%). Steps the mechanism were assessment, diagnostic problem, intervention, monitoring and evaluation.
ConclusionEvaluation of stunting intervention could be carried out by local context. The mechanism of intervention should be delivered by political commitment.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora