To investigate the role of whole-body fluorine-18-2-deoxy-2-fluoro-d-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) in the identification of peritoneal carcinomatosis in patients with ovarian cancer (OC).
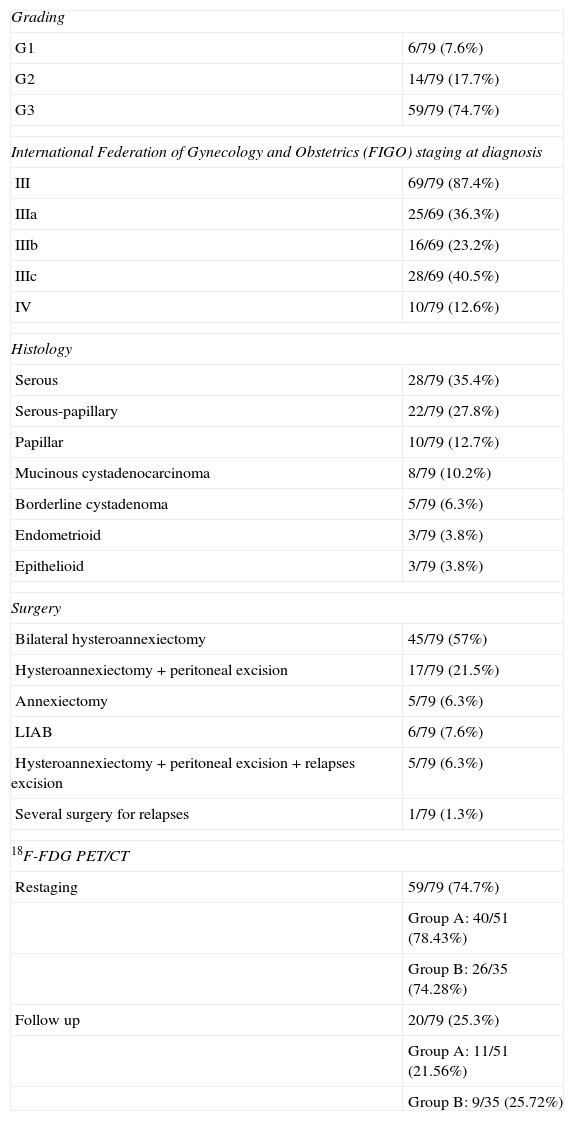
Material and methodsSeventy-nine patients with histologically proven stages III–IV OC who underwent 18F-FDG PET/CT were studied retrospectively. We considered group A as 51 patients who also underwent computed-tomography with contrast-enhancement (CECT), and group B as 35 patients who had also been tested for biomarker Ca-125. Sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive values (PPV) and negative predictive values (NPV) of 18F-FDG PET/CT as compared to CECT and to Ca-125 were evaluated.
Results18F-FDG PET/CT’ sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, PPV and NPV for all 79 patients were: 85%, 92.31%, 88.61%, 91.89% and 85.71%, respectively. 18F-FDG PET/CT sensitivity in group A was 78.6%, while it was 53.6% for CECT. 18F-FDG PET/CT specificity, calculated in the same group, was 91.3%, while that of CECT was 60.9% (statistically significant difference, McNemar 4, P=0.039). Accuracy was 84.3% and 56.9%, respectively. 18F-FDG PET/CT’ sensitivity in group B was 86.4%, while that of Ca-125 was 81.8% (no statistical difference, McNemar 0, P=1). 18F-FDG PET/CT specificity in group B was 84.6% while that of Ca-125 was 38.5% (clear but not statistically significant difference, McNemar 3.12, P=0.070). Accuracy calculated in the same group was 85.7% for 18F-FDG PET/CT and 65.7% for Ca-125.
Conclusion18F-FDG PET/CT is a useful diagnostic tool when peritoneal biopsy cannot be performed and it can better select those who are candidates for adjuvant chemotherapy.
Investigar el papel de flúor-18-2-desoxi-2-fluoro-D-glucosa tomografía por emisión de positrones/tomografía computarizada (18F-FDG PET/CT) en la identificación de la carcinomatosis peritoneal en pacientes con cáncer de ovario (CO).
Material y métodosSetenta y nueva pacientes con CO en estadio III-IV que se sometieron a 18F-FDG PET/CT fueron estudiadas retrospectivamente. Consideramos el grupo A de 51 pacientes que también realizaron la tomografía computarizada con contraste (CECT) y el grupo B de 35 pacientes que tenían cuantificación del Ca-125. Se evaluó sensibilidad, especificidad, exactitud, valor predictivo positivo (VPP) y valores predictivos negativos (VPN) de 18F-FDG PET/CT en comparación con CECT y Ca-125.
ResultadosLa sensibilidad, especificidad, exactitud, VPP y VPN de 18F-FDG PET/CT en los 79 pacientes fueron: 85, 92,31, 88,61, 91,89 y 85,71% respectivamente. La sensibilidad de 18F-FDG PET/CT en el grupo A fue de 78,6% y de 53,6% por CECT. La especificidad de 18F-FDG PET/CT en el mismo grupo fue de 91,3%, mientras la de CECT del 60,9% (diferencia estadísticamente significativa, McNemar=4, P=0,039); la exactitud fue respectivamente de 84,3 y 56,9%. La sensibilidad de la 18F-FDG PET/CT en el grupo B fue de 86,4%, mientras que la del Ca-125 fue de 81,8% (sin diferencia estadística, McNemar=0, P=1). La especificidad 18F-FDG PET/CT en el grupo B fue de 84,6%, mientras que la del Ca-125 fue de 38,5% (diferencia evidente, no estadísticamente significativa, McNemar=3,12, P=0,070). La exactitud en el mismo grupo fue 85,7% para el 18F-FDG PET/CT y 65,7% para Ca-125.
ConclusiónLa 18F-FDG PET/CT es un instrumento de diagnóstico útil cuando la biopsia peritoneal no se puede realizar y puede seleccionar de manera mejor las candidatas a quimioterapia adyuvante.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)