To evaluate by in- vivo lymphoscintigraphy and SPECT-CT imaging, the lymphatic drainage patterns of para-nasal sinus(PNS) tumors. To confirm or refute the belief of the retropharyngeal lymph node (RPLN) being the significant draining lymph node for such tumors.
MethodsProspective cohort study conducted on previously untreated PNS tumors with no clinico-radiological evidence of lymph node metastasis. Lymphoscintigraphy undertaken by nasal endoscopic assisted peritumoral injection of 99mTc Sulfur colloid. Injections were classified as anterior or posterior as per a vertical line along the maxillary sinus ostium.
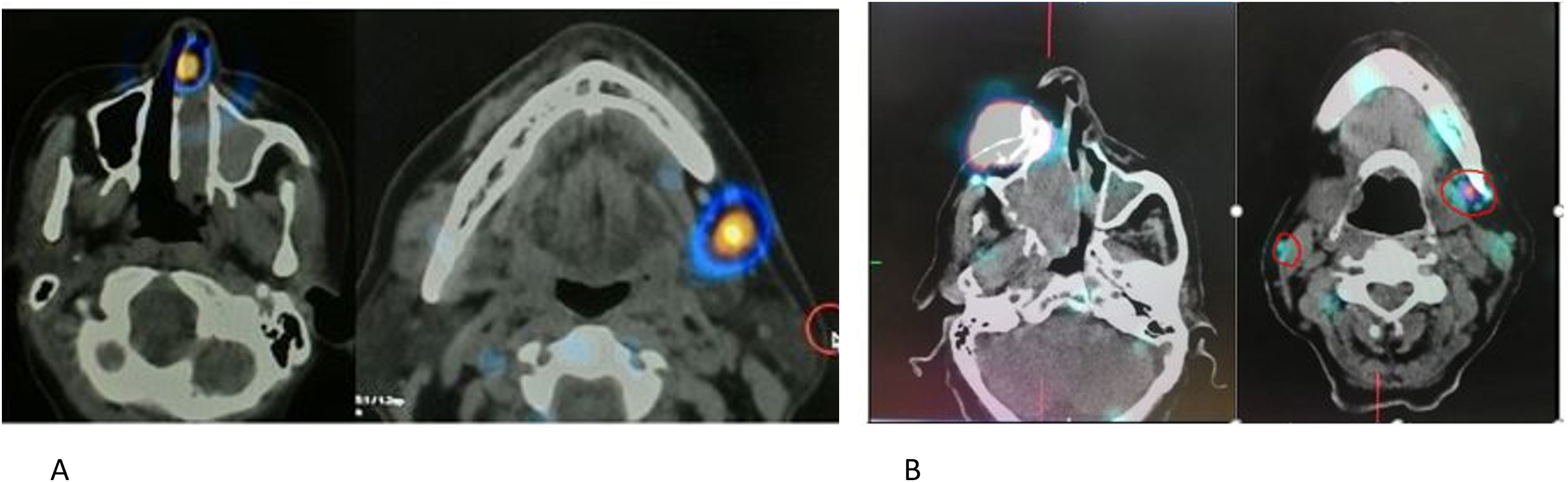
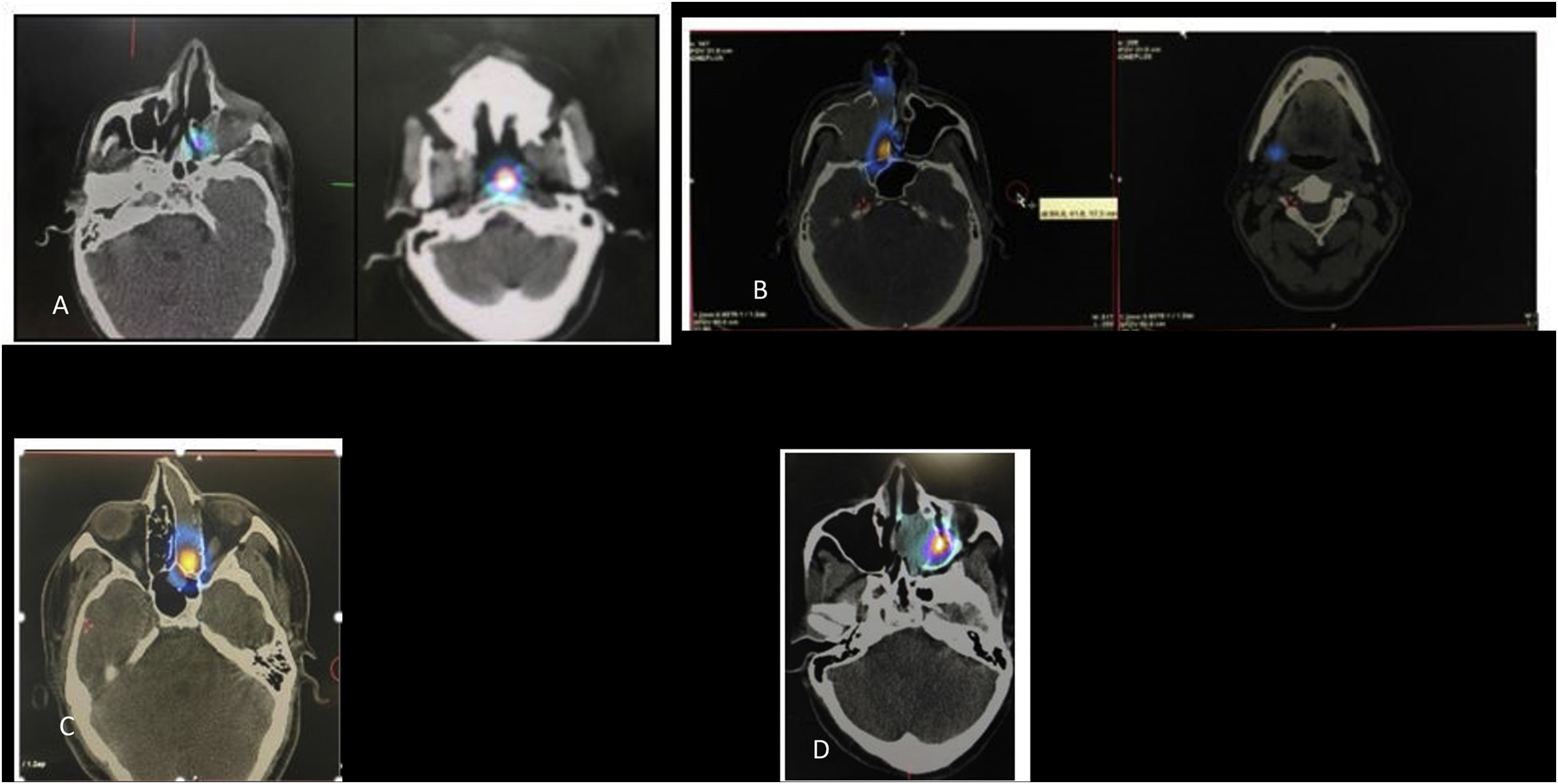
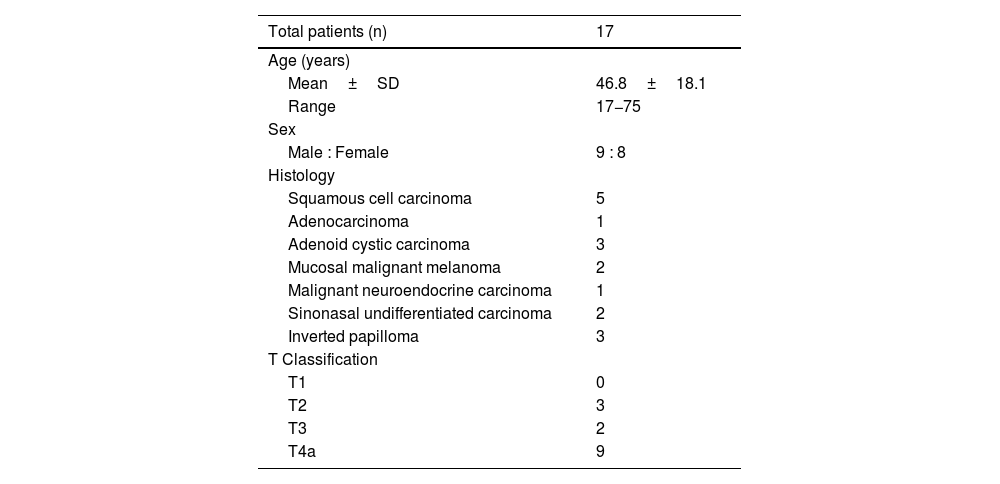
Results17 patients were included. Lymphoscintigraphy successfully identified 17 sentinel nodes in 15 patients and was unsuccessful (lymphoscintigraphy failure) in 2 patients. Predominant sites of sentinel lymphatic drainage were noted to be the RPLN (n = 8; 47%), and Level I (n = 7; 42%). Occasional drainage was identified at the peri-parotid node(n = 1) and at Level II (n = 1). Contralateral drainage was noted in 2 patients (level I-1 and RPLN-1).
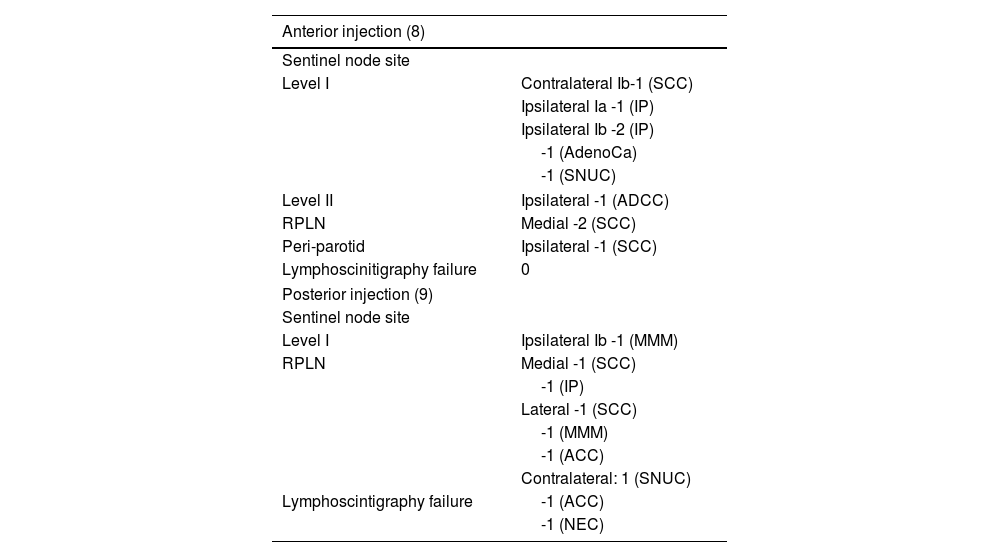
Anterior injections drained predominantly to Level I (6/8) and RPLN (2/8), while posterior injections drained predominantly to the RPLN ( 6/7). The relative risk of RPLN being identified as the sentinel node was significantly higher for posteriorly placed injections than for anteriorly placed injections (RR- 3.43; 95% CI-1.0-11.8, p = 0.05).
ConclusionThe RPLN is noted as a frequent draining node for sino-nasal tumours and merits routine attention in all sino-nasal tumors. The radio-colloid SPECT-CT technique described here offers an excellent in-vivo technique to further explore and validate the lymphatic drainage pathways of these tumours.
Evaluar mediante linfogammagrafía in vivo y SPECT-CT, el drenaje linfático patrones de tumores de los senos paranasales (SNP). Para confirmar o refutar la creencia de la linfa retrofaríngea (RPLN) siendo el ganglio linfático de drenaje significativo para tales tumores.
MétodosEstudio de cohorte prospectivo realizado en tumores del SNP no tratados previamente sin antecedentes clinicorradiológicos. evidencia de metástasis en los ganglios linfáticos. Linfogammagrafía realizada por vía endoscópica nasal inyección peritumoral asistida de 99mTc coloide de azufre. Las inyecciones se clasificaron como anteriores o posteriores. según una línea vertical a lo largo del ostium del seno maxilar.
Resultadosse incluyeron 17 pacientes. La linfogammagrafía identificó con éxito 17 ganglios centinela en 15 pacientes y no tuvo éxito (fracaso de la linfogammagrafía) en 2 pacientes. Sitios predominantes de Centinela se observó que el drenaje linfático era el RPLN (n=8; 47%) y el nivel I (n=7; 42%). Drenaje occasional se identificó en el ganglio periparotídeo (n=1) y en el nivel II (n=1). Se observó drenaje contralateral en 2 pacientes (nivel I-1 y RPLN-1). Las inyecciones anteriores drenaron predominantemente al nivel I (6/8) y RPLN (2/8), mientras que las inyecciones posteriors drenado predominantemente al RPLN (6/7). El riesgo relativo de que la RPLN sea identificada como el ganglio Centinela fue significativamente mayor para las inyecciones colocadas posteriormente que para las inyecciones colocadas anteriormente (RR 3,43; IC 95% 1,0-11,8, p=0,05).
ConclusiónEl RPLN se señala como un nódulo de drenaje frecuente para tumores sinonasales y amerita rutina. atención en todos los tumores sino-nasales. La técnica SPECT-CT con radiocoloides aquí descrita ofrece una excelente técnica in vivo para explorar más a fondo y validar las vías de drenaje linfático de estos tumores.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)