To evaluate the feasibility of V/Q SPECT and analyze its contribution to planar V/Q lung scintigraphy in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism (PE).
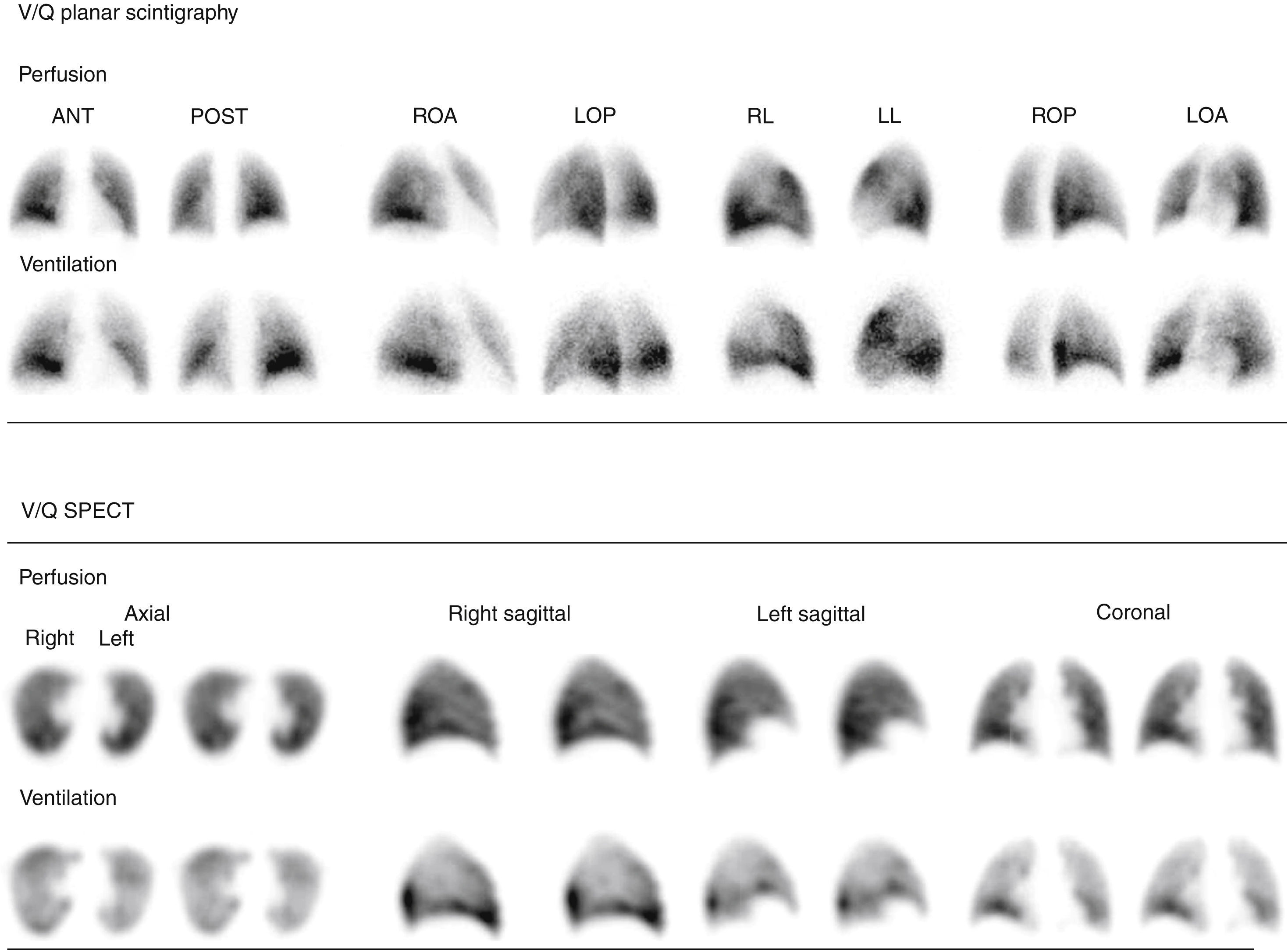
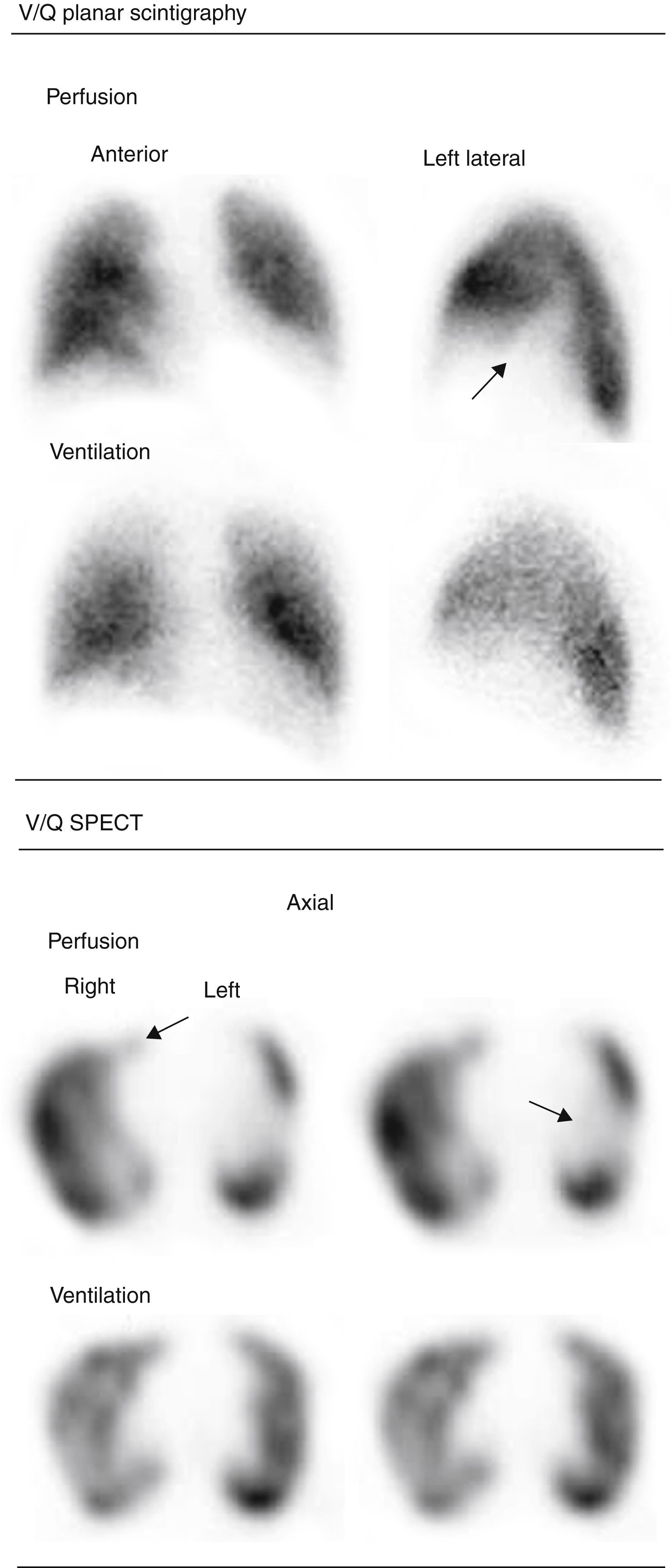
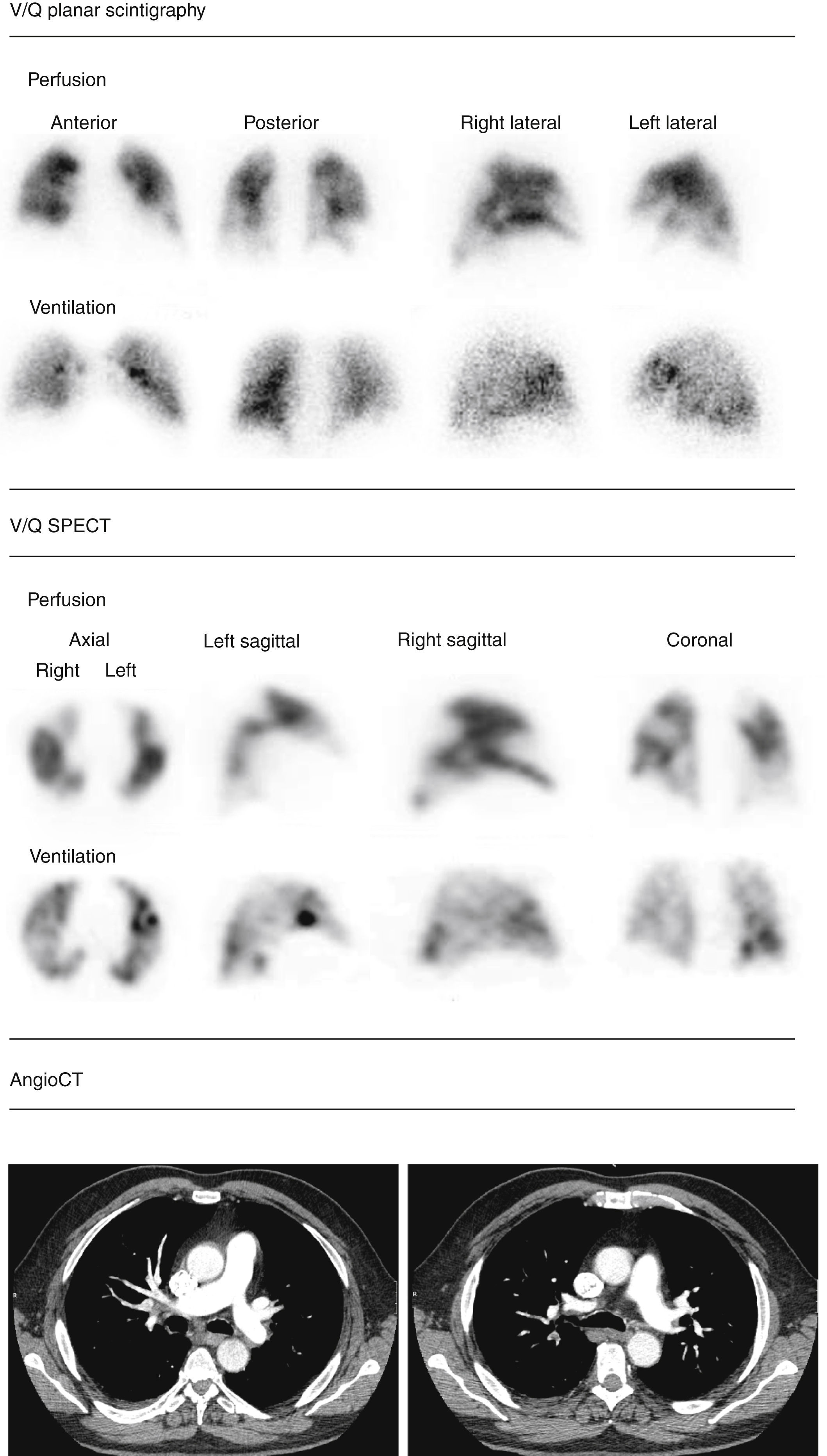
Material and methodsA total of 109 patients with suspected PE showing Wells score>2 and elevated D-dimer were studied. The V/Q could not be completed in 7 patients, so they were excluded. Ventilation and perfusion scans were done using Technegas and 99mTc-MAA. Planar study included 8 projections on a 256×256 matrix and 128 projections on a 128×128 matrix were acquired for the SPECT study, applying an iterative method. Planar images were interpreted according to modified PIOPED criteria, and SPECT by the guidelines of the EANMMI. The results with both techniques were compared.
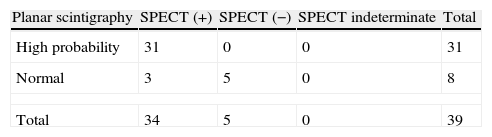
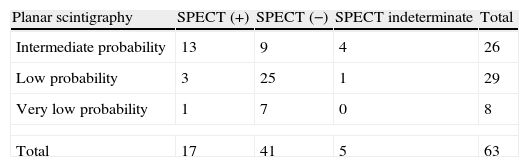
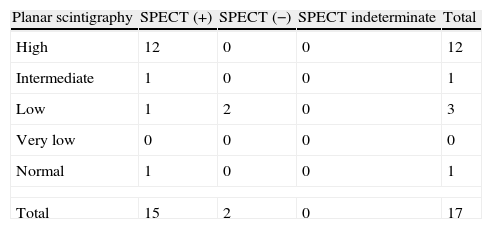
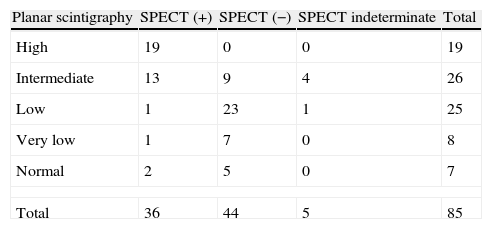
ResultsV/Q planar scintigraphy and SPECT could be performed in 102 patients. V/Q planar scintigraphy was considered “diagnostic” in 39 of the 102 patients, and “non-diagnostic” in 63. Of the 39 “diagnostic” studies, 31 were reported as high probability of PE and 8 as normal. Of the 63 “non-diagnostic”, 26 corresponded to intermediate, 29 to low, and 8 to very low probability. The SPECT study was “diagnostic” in 97 and indeterminate in only 5. All patients with a high probability planar scintigraphy had a positive SPECT. In the 8 patients with a normal planar scintigraphy SPECT was negative in 5 and positive in 3. In the 63 patients with a “non-diagnostic” planar scintigraphy SPECT was “diagnostic” in 58 of them, positive in 17 and negative in 41.
ConclusionV/Q SPECT is a feasible technique as it was performed in 102 of the 109 patients who were enrolled in the study (94%).
The addition of V/Q SPECT to planar V/Q decreases the number of “non-diagnostic” reports from 62% in planar scintigraphy to 4.9% in SPECT. Therefore, V/Q SPECT should be included in the diagnosis approach of PE due to its high diagnostic yield.
Evaluar la factibilidad de la SPECT V/Q y analizar su contribución a la gammagrafía planar en el diagnóstico del tromboembolismo pulmonar (TEP).
Material y métodosEstudio en 109 pacientes con sospecha de TEP, con escala de Wells>2 y dímero D elevado. Se excluyeron 7 pacientes porque no pudieron completar el estudio. Para la gammagrafía de ventilación se empleó Technegas y para el estudio de perfusión 99mTc-MAA. El estudio planar incluyó 8 proyecciones en matriz 256×256, en la SPECT se adquirieron 128 proyecciones en matriz 128×128, aplicándose una reconstrucción iterativa. Las imágenes planares fueron interpretadas según criterios PIOPED modificados y la SPECT según la guía de la EANMMI. Se compararon los resultados obtenidos entre ambas técnicas.
ResultadosFue posible realizar el estudio V/Q planar y la SPECT en 102. La gammagrafía planar V/Q fue considerada «diagnóstica» en 39 de los 102 pacientes, y «no diagnóstica» en 63. De las 39 gammagrafías «diagnósticas», 31 fueron de alta probabilidad para TEP y 8 fueron normales. De las 63 gammagrafías «no diagnósticas», 26 fueron probabilidad intermedia, 29 baja y 8 muy baja probabilidad. La SPECT fue diagnóstica en 97 e indeterminada solo en 5. En todos los pacientes con alta probabilidad en la gammagrafía planar la SPECT fue positiva. En los 8 pacientes con gammagrafía planar normal la SPECT fue negativa en 5 y positiva en 3. En 63 pacientes con gammagrafía planar «no diagnóstica», la SPECT fue «diagnóstica» en 58 de ellos, siendo positiva en 17 y negativa en 41.
ConclusiónLa SPECT V/Q es una técnica factible, ya que se realizó en 102 de los 109 pacientes incluidos en el estudio (94%).
La incorporación de la SPECT V/Q a la gammagrafía planar disminuyó el número de informes «no diagnóstico» de un 62% en la gammagrafía planar a un 4,9% con la SPECT. Por lo tanto la SPECT V/Q debe incluirse en el diagnóstico de TEP por su alto rendimiento diagnóstico.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)