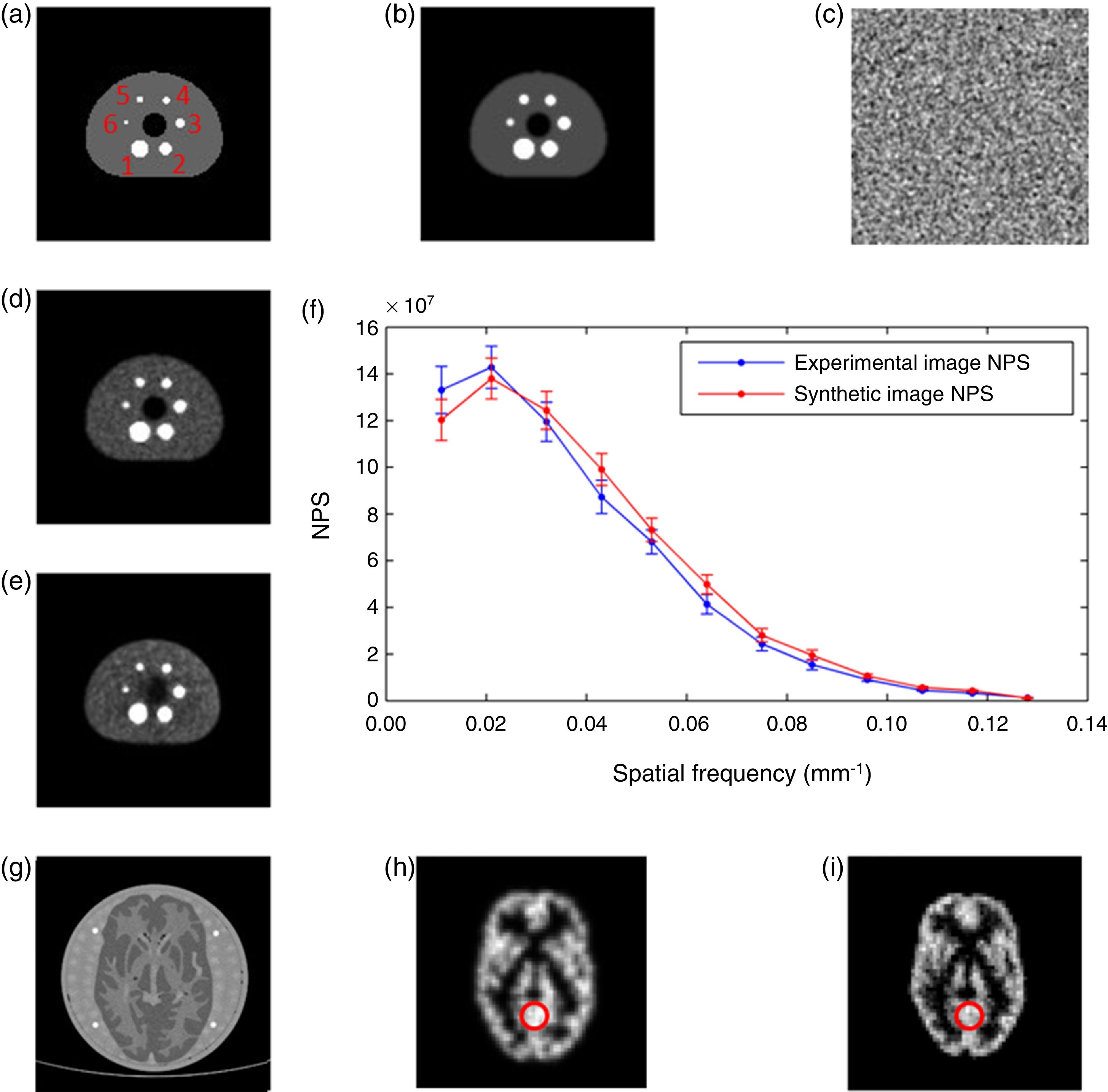
The goals of the study are to characterize imaging properties in 2D PET images reconstructed with the iterative algorithm Ordered-Subset Expectation Maximization (OSEM) and to propose a new method for the generation of synthetic images.
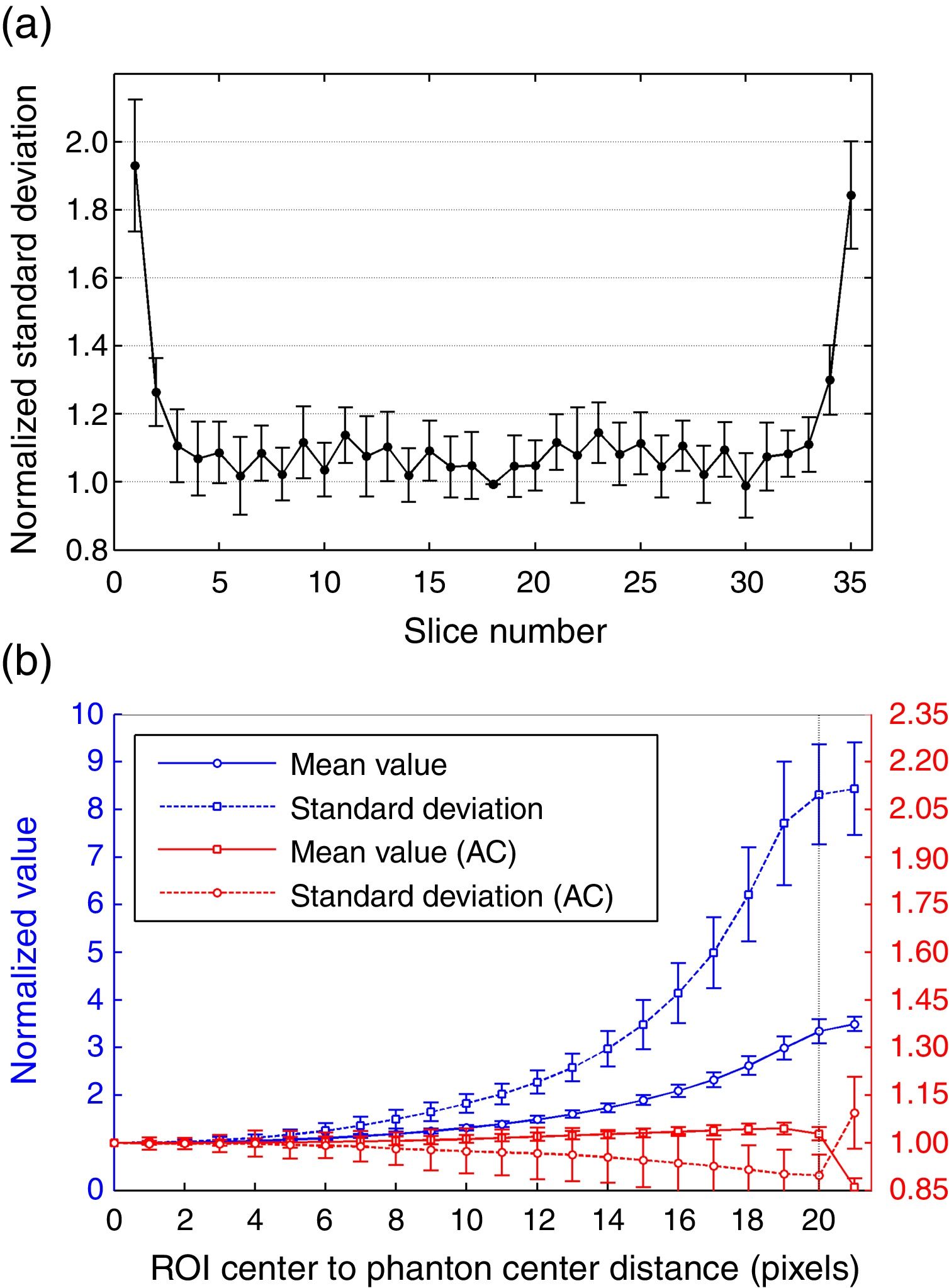
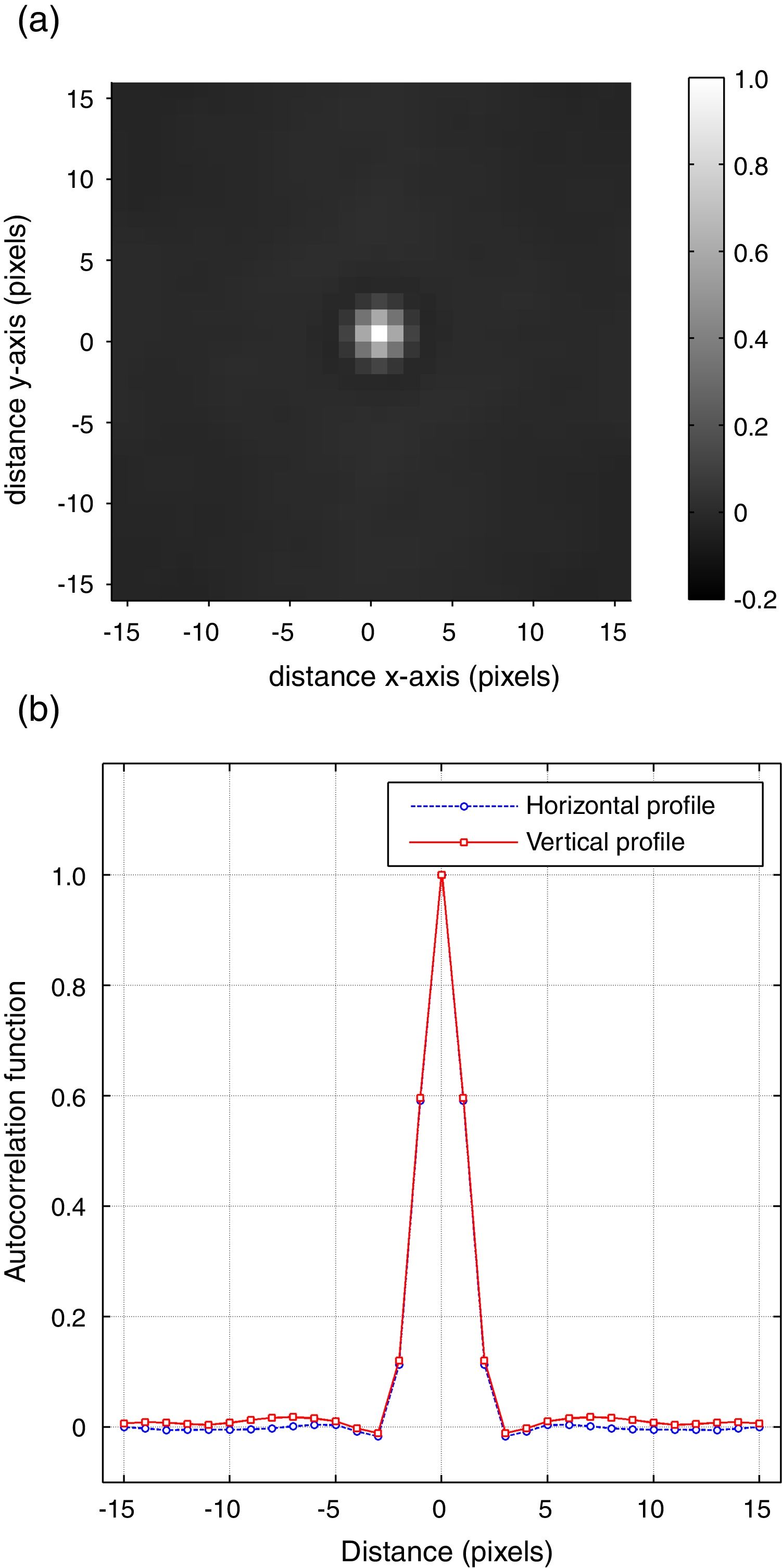
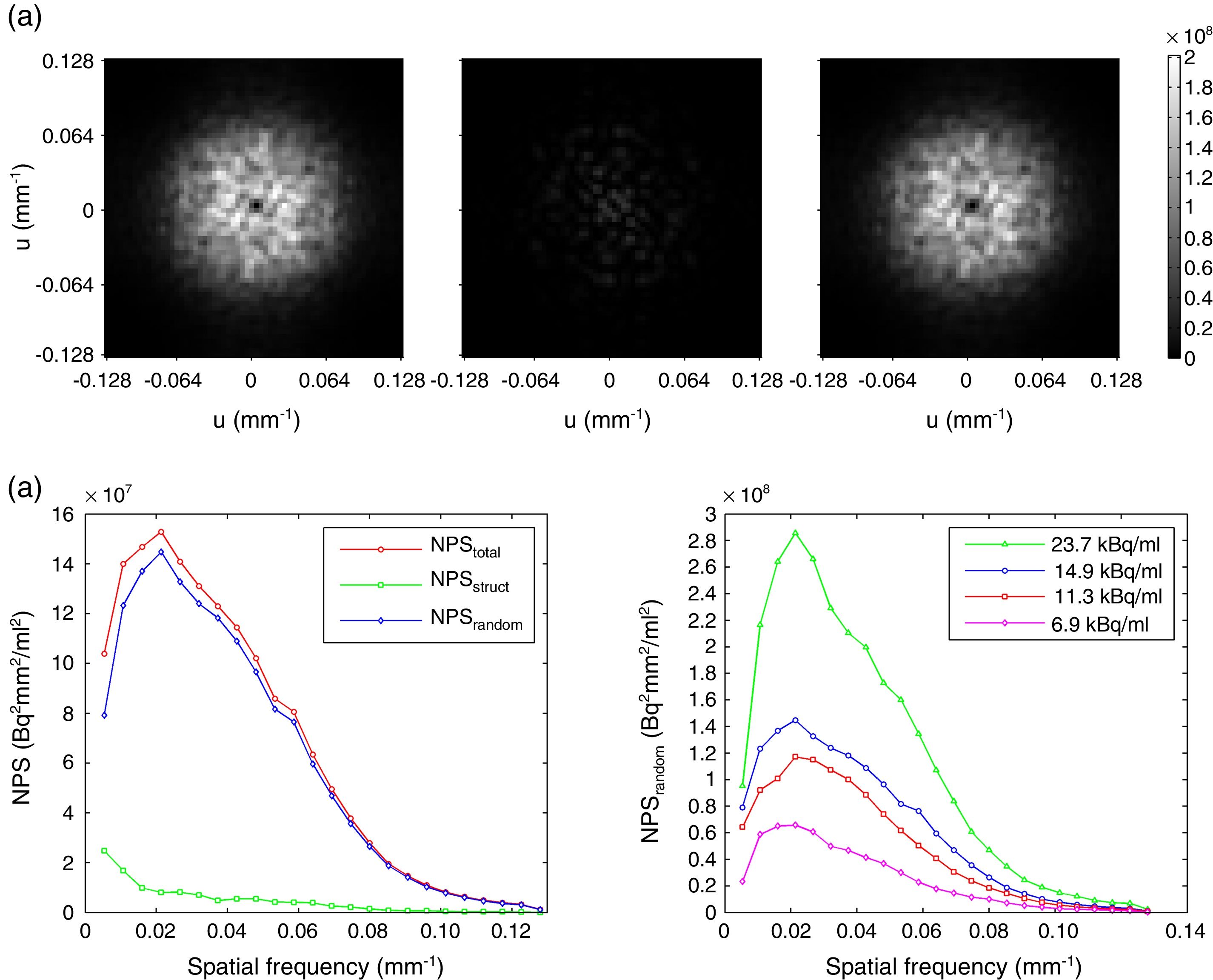
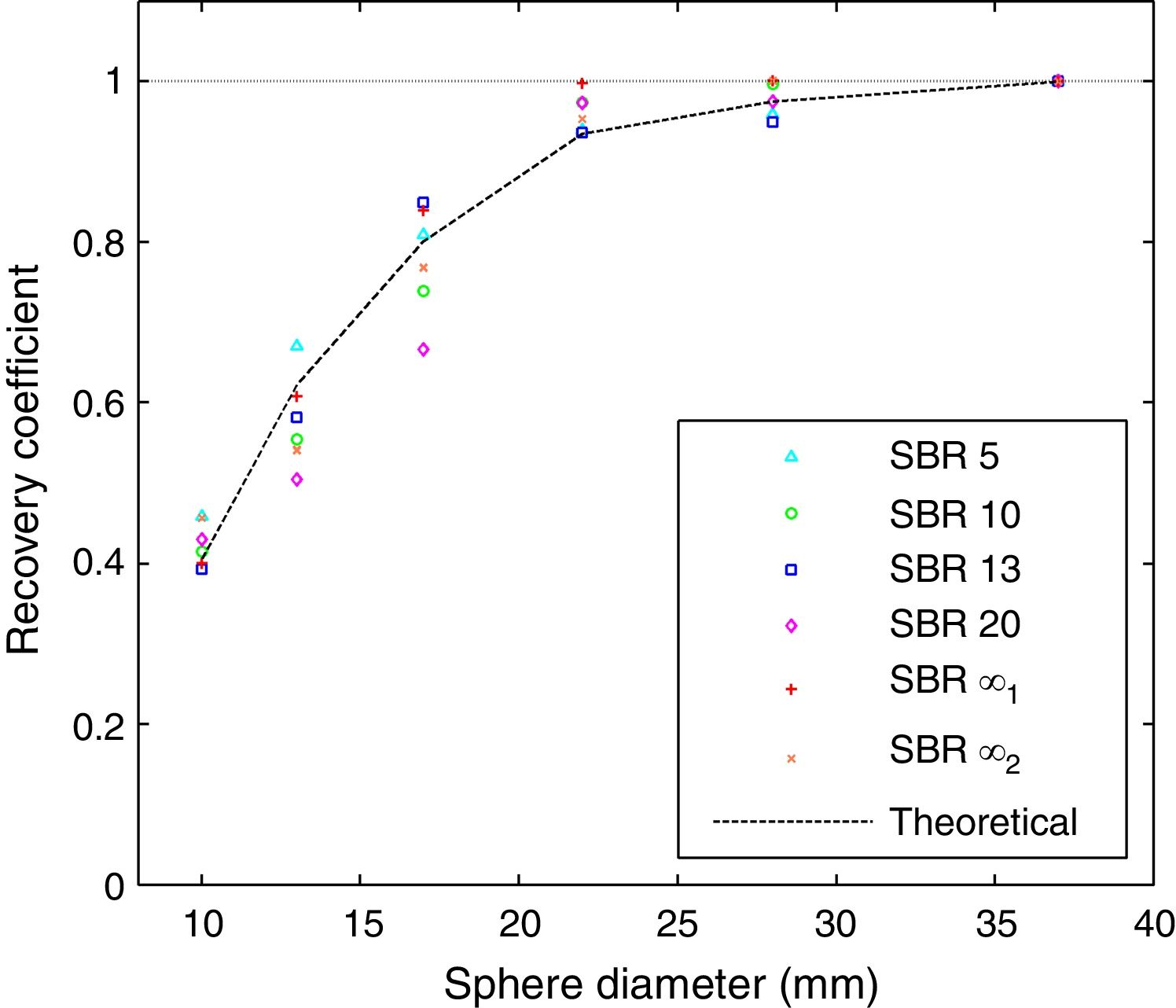
Material and methodsThe noise is analyzed in terms of its magnitude, spatial correlation, and spectral distribution through standard deviation, Autocorrelation Function, and Noise Power Spectrum (NPS), respectively. Their variations with position and activity level are also analyzed. This noise analysis is based on phantom images acquired from 18F uniform distributions. Experimental Recovery Coefficients of hot spheres in different backgrounds are employed to study the spatial resolution of the system through Point Spread Function (PSF). The NPS and PSF functions provide the baseline for the proposed simulation method: convolution with PSF as kernel and noise addition from NPS.
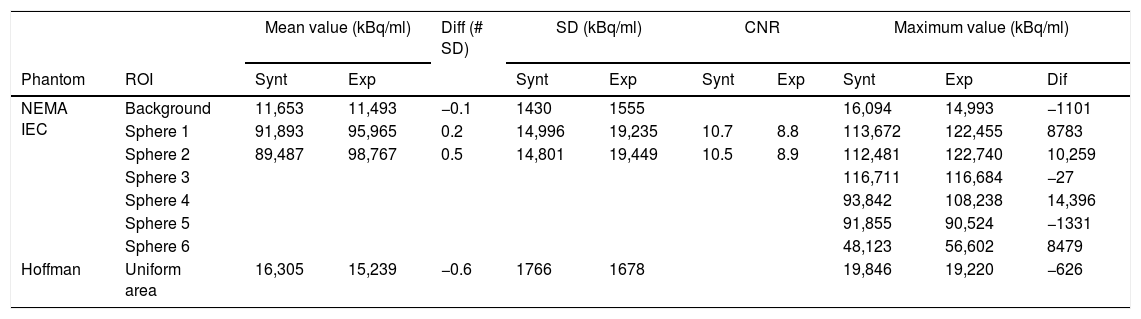
ResultsThe noise spectral analysis shows that the main contribution is of random nature. It is also proven that attenuation correction does not alter noise texture but it modifies its magnitude. Finally, synthetic images of two phantoms, one of them an anatomical brain, are quantitatively compared with experimental images showing a good agreement in terms of pixel values and pixel correlations. Thus, the Contrast to Noise Ratio for the biggest sphere in the NEMA IEC phantom is 10.7 for the synthetic image and 8.8 for the experimental image.
ConclusionsThe properties of the analyzed OSEM-PET images can be described by NPS and PSF functions. Synthetic images, even anatomical ones, are successfully generated by the proposed method based on the NPS and PSF.
Los objetivos del trabajo son caracterizar las propiedades de la imagen 2D PET reconstruida mediante el algoritmo Ordered-Subset Expectation Maximization (OSEM) y proponer un nuevo método de generación de imágenes sintéticas.
Material y métodosEl ruido se analiza en términos de magnitud, correlación espacial y distribución espectral a través de la desviación estándar, la función de autocorrelación y el espectro de potencias de ruido (Noise Power Spectrum, NPS), respectivamente. También se estudian sus variaciones con la posición y la cantidad de actividad. Este análisis del ruido se realiza sobre imágenes de maniquí a partir de distribuciones de actividad de 18F homogéneas. Para estudiar la resolución espacial del sistema a través de Point Spread Function (PSF) se emplean los coeficientes de recuperación medidos en esferas calientes en diferentes entornos radiactivos. Las funciones PSF y NPS proporcionan la base del método de simulación propuesto: convolución con la PSF como núcleo y adición de ruido a partir del NPS.
ResultadosEl análisis del ruido espectral muestra que la principal contribución es de naturaleza aleatoria. También se observa que la corrección de atenuación no altera la textura del ruido pero sí modifica su magnitud. Finalmente, las imágenes sintéticas de dos maniquíes, uno de ellos un cerebro anatómico, son comparadas cuantitativamente con las imágenes experimentales, encontrando un buen acuerdo en términos de valores de píxel y correlaciones entre píxeles. Así, la razón contraste-ruido para la esfera más grande del maniquí NEMA IEC es 10,7 en la imagen sintética y 8,8 en la imagen experimental.
Conclusioneslas propiedades de las imágenes PET-OSEM pueden ser descritas por las funciones NPS y PSF. Las imágenes simuladas, incluyendo regiones anatómicas, son generadas satisfactoriamente mediante el método propuesto basado en las funciones NPS y PSF.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)