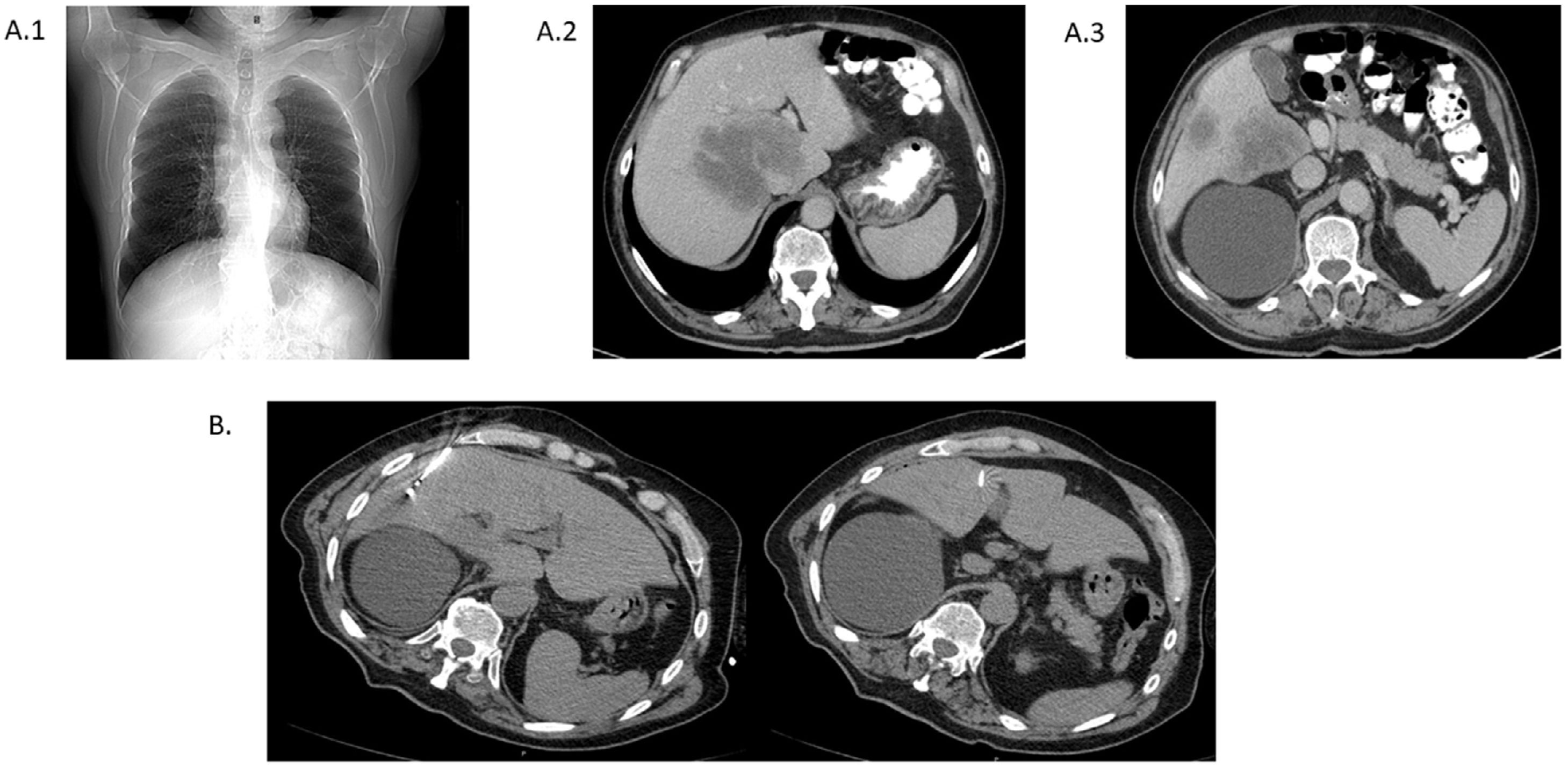
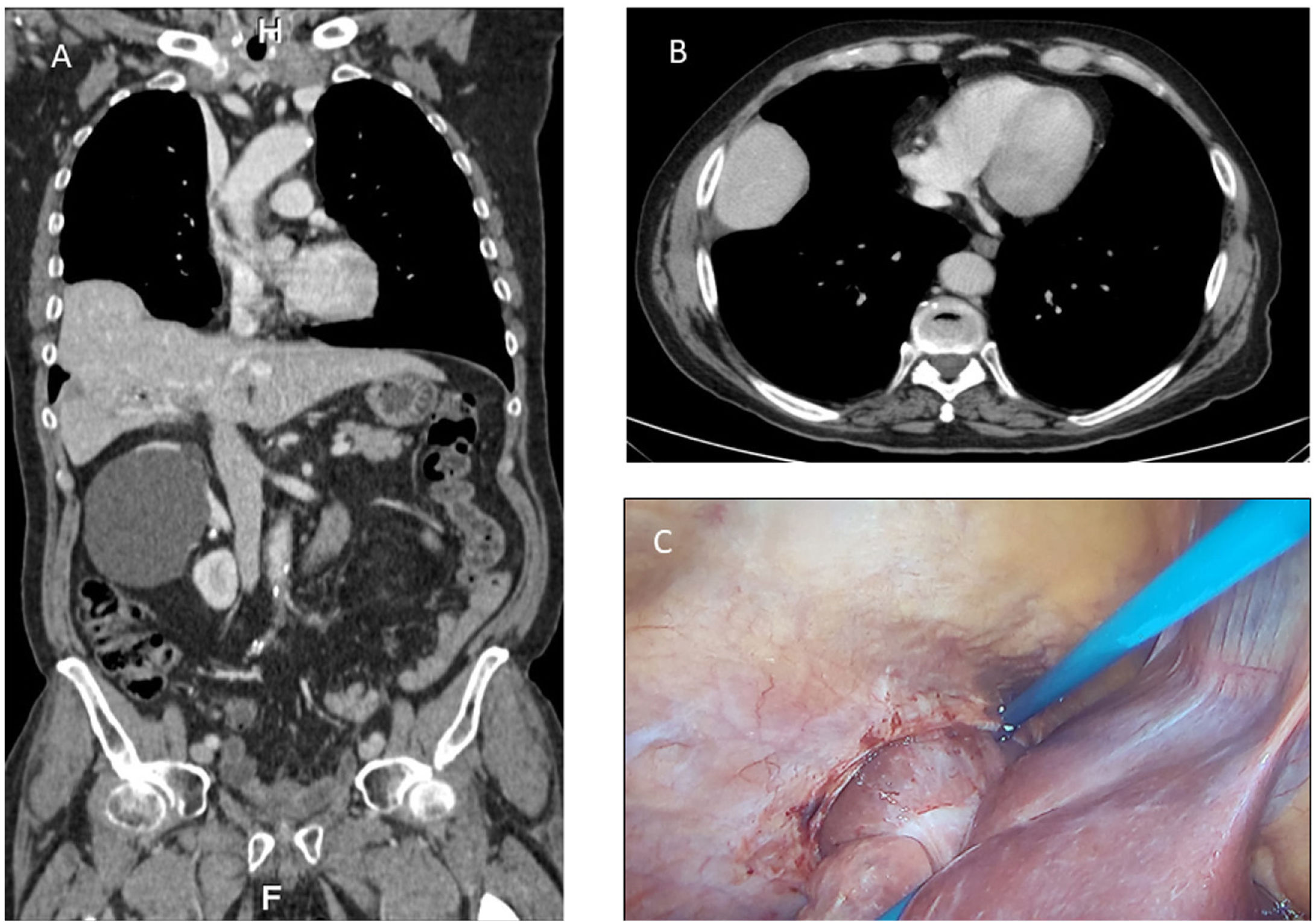
A diaphragmatic hernia is the protrusion of abdominal tissues into the thoracic cavity secondary to a defect in the diaphragm. Reviewing the literature, we found only 44 references to diaphragmatic hernia secondary to percutaneous radiofrequency treatment. The vast majority of these cases were secondary to the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in segments V and VIII. Nevertheless, to date, this is the first reported case of diaphragmatic hernia after radiofrequency ablation of a liver metastasis from colorectal cancer. Complications secondary to diaphragmatic hernias are very diverse. The principal risk factor for complications is the contents of the hernia; when small bowel or colon segments protrude in the thoracic cavity, they can become incarcerated. Asymptomatic cases have also been reported in which the diaphragmatic hernia was discovered during follow-up. The pathophysiological mechanism is not totally clear, but it is thought that these diaphragmatic hernias might be caused by locoregional thermal damage. Given that most communications correspond to asymptomatic and/or treated cases, it is likely that the incidence is underestimated. However, due to the advent of percutaneous treatments, this complication might be reported more often in the future. Most cases are treated with primary herniorrhaphy, done with a laparoscopic or open approach at the surgeon’s discretion; no evidence supports the use of one approach over the other. Nevertheless, it seems clear that surgery is the only definitive treatment, as well as the treatment of choice if complications develop. However, in asymptomatic patients in whom a diaphragmatic hernia is discovered in follow-up imaging studies, management should probably be guided by the patient’s overall condition, taking into account the potential risks of complications (contents, diameter of the opening into the thoracic cavity …).
La hernia diafragmática (HD) es la protrusión de los tejidos abdominales a la cavidad torácica secundaria a un defecto en el diafragma. Tras una revisión de la bibliografía, únicamente se han identificado 44 referencias al respecto, donde se describen 35 casos de HD secundarias a tratamientos percutáneos con RF. En su gran mayoría son secundarias a lesiones por carcinoma hepatocelular en los segmentos V y VIII. No obstante, hasta la fecha, este es el primer caso comunicado de HD tras RF para el tratamiento de una metástasis hepática por CCR. Las complicaciones secundarias a las HD este es muy diversas. El principal factor de riesgo para ello es su contenido; así se describen casos incarceración de colon e intestino delgado. Igualmente, se describen casos asintomáticos en los que la HD ha sido un hallazgo en el seguimiento de los pacientes. El mecanismo fisiopatológico no está del todo esclarecido, pero se especula con la posibilidad de un daño térmico locorregional. Dado que la mayoría de las comunicaciones corresponden a casos sintomáticos y/o tratados, probablemente, la incidencia esté infraestimada. No obstante, debido al advenimiento de los tratamientos percutáneos, esta complicación podría verse comunicada en mayor número en los próximos años. Respecto a los tratamientos descritos, en la mayoría de los casos se ha optado por una herniorrafia primaria, con una vía de abordaje abierta o laparoscópica a discreción del cirujano. No se dispone evidencia que soporte ninguna actitud al respecto. Si bien, parece claro que el tratamiento quirúrgico es el único definitivo y el de elección en caso complicación. Sin embargo, en pacientes asintomáticos en quienes la HD sea un hallazgo radiológico de control, la actitud de manejo, quizá deba guiarse por el estado general del paciente, así como los riesgos potenciales de complicación (contenido, diámetro del orificio herniario…).