Ernest syndrome involves the stylomandibular ligament. It is characterised by pain in the preauricular area and mandibular angle, radiating to the neck, shoulder, and eye on the same side, and associated with pain during palpation of that ligament. The purpose of this study is to describe the clinical characteristics, treatment, and course of the disease in a series of patients with Ernest syndrome.
MethodsRetrospective observational study covering the period from 1998 to 2008. We recorded patients’ age, sex, duration of the disorder, and pain characteristics. All patients were injected with 40mg triamcinolone acetonide at the mandibular insertion of the stylomandibular ligament.
ResultsThe study included a total of 6 patients. Mean age was 40.3 years (range, 35–51). All the subjects were women. Four patients had undergone lengthy dental treatments in the month prior to onset of the pain. The mean time between pain onset and first consultation was 23 months. The syndrome resolved completely in all cases after treatment, with a minimum follow-up period of 12 months.
ConclusionsWe analysed the clinical characteristics, treatment, and course of disease in 6 patients with Ernest syndrome. Correct diagnosis is the key to being able to provide proper treatment. This disorder is sometimes confused with other types of orofacial pain, and may therefore be more prevalent than the literature would indicate.
El síndrome de Ernest se define como una alteración del ligamento estilomandibular, caracterizado por la presencia de dolor en la región preauricular y en el ángulo mandibular, irradiado al cuello, el hombro y el ojo del mismo lado, asociado a dolor durante la palpación del ligamento estilomandibular. El objetivo es presentar las características clínicas, el tratamiento y la evolución de una serie de pacientes con el síndrome de Ernest.
MétodosSe realizó un estudio clínico, observacional, retrospectivo, entre los años 1998 y 2008. Se recogieron todos los datos con respecto a la edad, el sexo, el tiempo de evolución y las características del dolor. A todos los pacientes se les infiltró 40mg de acetónido de triamcinolona en la inserción mandibular del ligamento estilomandibular.
ResultadosSe incluyó a 6 pacientes. La edad media fue de 40,3 años (rango 35-51). El 100% eran mujeres. Cuatro de las 6 pacientes recibieron tratamientos odontológicos prolongados el mes previo a la aparición del dolor. El tiempo de evolución medio antes de la primera visita fue de 23 meses. Tras el tratamiento realizado, se obtuvo una resolución completa de todos los pacientes, con un periodo de seguimiento mínimo de 12 meses.
ConclusionesSe han analizado las características clínicas del dolor, el tratamiento recibido y la evolución de 6 pacientes con el síndrome de Ernest. Es importante realizar un correcto diagnóstico para poder establecer el tratamiento correcto. Creemos que esta enfermedad es más prevalente de lo encontrado en la literatura, pudiéndose confundir con otros dolores orofaciales.
Ernest syndrome was described by Dr Ernest in 1981 and a published article appeared one year later1; Shankland et al.2 were the first to publish a case series in the PubMed database. Ernest syndrome affects the stylomandibular ligament. It is characterised by the presence of pain in the preauricular region and angle of the mandible radiating to the neck, shoulder, and eye on the same side, and it is associated with pain upon palpation of that ligament. Since 1987 when Shankland et al.2 described 68 patients with Ernest syndrome, no new case series have been published in the medical literature.
A good medical history, manual examination of the insertion of the stylomandibular ligament in the gonial angle, and immediate relief of symptoms after administration of local anaesthesia to this region will confirm this diagnosis.2,3
The current article presents 6 additional cases with masticatory orofacial pain that were diagnosed with the Ernest syndrome and discusses the symptoms, treatment, and course of the disease.
Patients and methodsThis retrospective observational study conducted between 1998 and 2008 examined patients who visited the oral surgery unit of the dental clinic pertaining to the University of Valencia's School of Medicine and Dentistry due to orofacial pain. The following inclusion criteria were used to identify cases of Ernest syndrome: (a) presence of pain in the preauricular region and angle of the mandible; (b) pain upon palpation of the mandibular insertion of the stylomandibular ligament; (c) pain relief after injection of mepivacaine 3% (Normon Laboratory, Madrid, Spain) in the mandibular insertion of the painful stylomandibular ligament, and (d) no significant changes in the extraoral panoramic radiography.
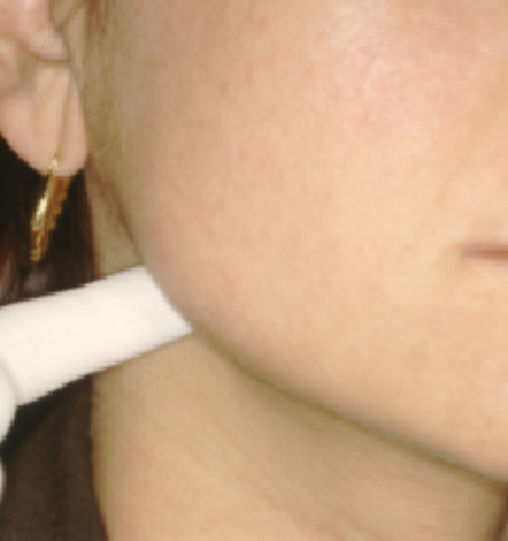
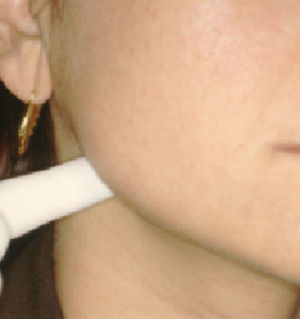
We recorded data for age, sex, progression timeline, and pain characteristics. We also searched for any traumatic episodes or prolonged use of a dental treatment that may have proceeded onset of pain. Patients were considered to have a positive history when they had undergone treatment in the month prior to the onset of pain. We examined each patient's oral cavity, muscles of mastication, stylomandibular ligament (Fig. 1), and temporomandibular joint. We also took extraoral panoramic radiographs. Pain was scored on following scale: 0: no pain; 1: mild pain (pain is present, but it does not cause discomfort); 2 moderate (pain causes discomfort, but is tolerable), and 3: intense (pain causes significant discomfort and it is difficult to tolerate).
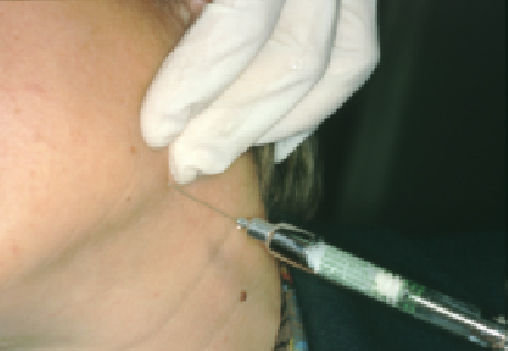
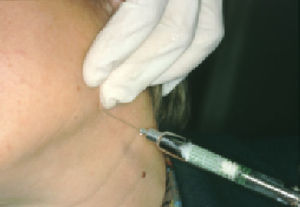
Once a diagnosis of Ernest syndrome had been established, all patients were injected with 40mg of triamcinolone acetonide (Trigon depot®, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Madrid, Spain) in the mandibular insertion of the stylomandibular ligament (Fig. 2). Patients whose symptoms persisted received an additional injection 15 days after the first one. In all cases, occlusion was corrected with a prosthesis. Patients were told to avoid forcing the jaw open and prescribed a soft diet for the 15 days following treatment. The minimum follow-up period was 1 year. All patients gave their written informed consent before treatment so as to be included in the study, which respects the principles stated in the Declaration of Helsinki.
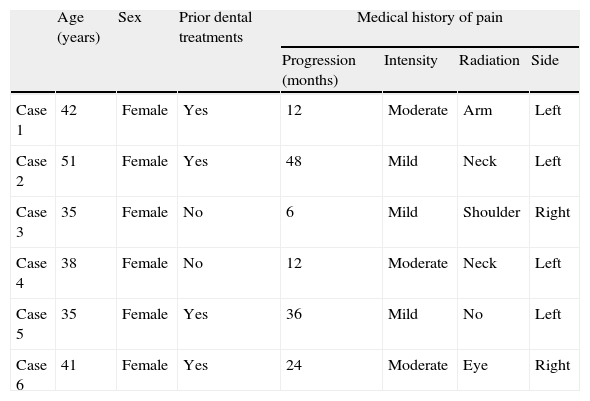
ResultsThe patients’ clinical characteristics are listed in Table 1. The series included 6 female patients aged between 35 and 51 years, with a mean age of 40.3. None of the patients reported prior history of traumatic episodes; however, 4 of the 6 women experienced pain following dental treatment (in 2 patients after endodontic procedures and in the other 2 patients after complex extractions) and they reported prolonged mouth opening during the procedures.
Patient characteristics: age, sex, prior dental treatments, and type of pain.
| Age (years) | Sex | Prior dental treatments | Medical history of pain | ||||
| Progression (months) | Intensity | Radiation | Side | ||||
| Case 1 | 42 | Female | Yes | 12 | Moderate | Arm | Left |
| Case 2 | 51 | Female | Yes | 48 | Mild | Neck | Left |
| Case 3 | 35 | Female | No | 6 | Mild | Shoulder | Right |
| Case 4 | 38 | Female | No | 12 | Moderate | Neck | Left |
| Case 5 | 35 | Female | Yes | 36 | Mild | No | Left |
| Case 6 | 41 | Female | Yes | 24 | Moderate | Eye | Right |
The pain timeline prior to the patient's first visit ranged from 6 months to 4 years, with a mean of 23 months. Pain was mild in 3 patients and moderate in the other 3; all subjects reported that pain appeared slowly with no clear trigger event and that it was dull, continuous, and poorly defined. All patients presented symptoms unilaterally, with the left side being dominant (66.6%).
Intraoral examination revealed missing teeth in 5 patients. During palpation of the muscles of mastication, 2 patients experienced pain in the ipsilateral masseter muscles and 2 in the ipsilateral internal masseter and pterygoid muscles. Palpation of the temporomandibular joint was painless in all cases.
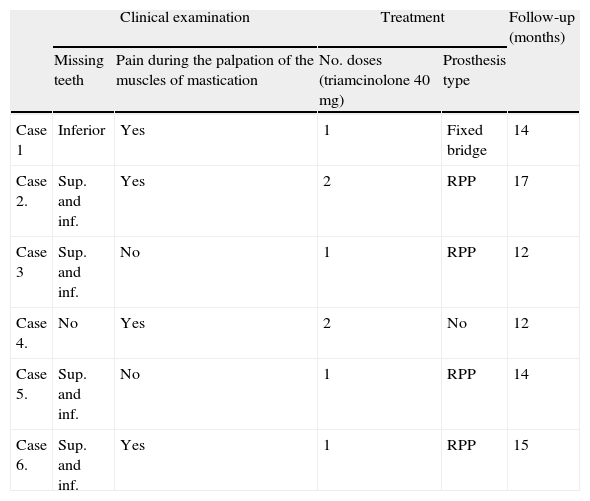
Four patients achieved complete symptom remission with treatment (Table 2). The 2 remaining patients needed additional injections 15 days after the first one since residual pain persisted. Occlusion was corrected in all 5 patients with missing teeth by means of removable partial dental prostheses in 4 patients (cases 2 to 5) and a fixed dental prosthesis in the other case (case 1) (Table 2). All patients recovered completely after treatment and remained stable at least during those months in which they were monitored (minimum follow-up period of 12 months).
Data referring to clinical examination, treatment, and follow-up time.
| Clinical examination | Treatment | Follow-up (months) | |||
| Missing teeth | Pain during the palpation of the muscles of mastication | No. doses (triamcinolone 40mg) | Prosthesis type | ||
| Case 1 | Inferior | Yes | 1 | Fixed bridge | 14 |
| Case 2. | Sup. and inf. | Yes | 2 | RPP | 17 |
| Case 3 | Sup. and inf. | No | 1 | RPP | 12 |
| Case 4. | No | Yes | 2 | No | 12 |
| Case 5. | Sup. and inf. | No | 1 | RPP | 14 |
| Case 6. | Sup. and inf. | Yes | 1 | RPP | 15 |
Fixed P. fixed prosthesis; RPP: removable partial prosthesis; Sup. and inf.: superior and inferior.
The present study presents 6 clinical cases of orofacial pain that were diagnosed as Ernest syndrome. Other similar entities do exist, such as Eagle syndrome, which presents as a painful alteration of the stylohyoid process in patients who have undergone a tonsillectomy. This syndrome was described by Dr Eagle in 1937.4 The aetiology and pathogenesis of Eagle syndrome are both controversial.5 Symptoms include mineralisation, lengthening, or even calcification of the stylohyoid ligament. Unlike Ernest syndrome, which only affects the stylomandibular ligament, especially at the mandibular insertion, Eagle syndrome is usually bilateral.2 The clinical, radiological, and therapeutic characteristics of both syndromes are listed in Table 3.
Diagnosis, symptoms, aetiology, and treatment of both syndromes.
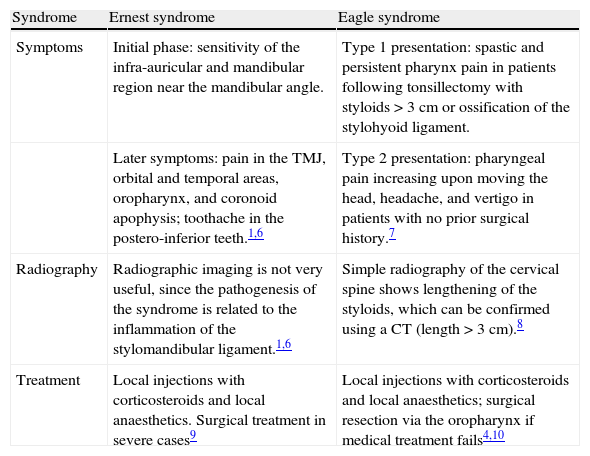
| Syndrome | Ernest syndrome | Eagle syndrome |
| Symptoms | Initial phase: sensitivity of the infra-auricular and mandibular region near the mandibular angle. | Type 1 presentation: spastic and persistent pharynx pain in patients following tonsillectomy with styloids>3cm or ossification of the stylohyoid ligament. |
| Later symptoms: pain in the TMJ, orbital and temporal areas, oropharynx, and coronoid apophysis; toothache in the postero-inferior teeth.1,6 | Type 2 presentation: pharyngeal pain increasing upon moving the head, headache, and vertigo in patients with no prior surgical history.7 | |
| Radiography | Radiographic imaging is not very useful, since the pathogenesis of the syndrome is related to the inflammation of the stylomandibular ligament.1,6 | Simple radiography of the cervical spine shows lengthening of the styloids, which can be confirmed using a CT (length>3cm).8 |
| Treatment | Local injections with corticosteroids and local anaesthetics. Surgical treatment in severe cases9 | Local injections with corticosteroids and local anaesthetics; surgical resection via the oropharynx if medical treatment fails4,10 |
No new studies of Ernest syndrome have been published in the medical literature since 1987, the year in which the largest series in the literature appeared.2 This study2 analysed 68 patients with a mean age of 37.7 years; 82% of the patients in the sample were female. These results are similar to those from our study, in which the mean age was 40.3 and 100% of the subjects were women. A retrospective study11 of 850 patients with temporomandibular joint disorder showed that men were affected less than women by a ratio of 1:6.2. Several studies11 have tried to explain this discrepancy between the sexes by evaluating psychological, endocrine, physical, and behavioural factors, but researchers have been unable to draw any conclusions.
Performing a literature search of the PubMed database using the key words ‘Ernest Syndrome’ and ‘stylomandibular ligament’ yields 7 hits; as 2 are duplicated, only 5 hits are related to this syndrome. Of these articles, 4 are reviews9,12–14 and 1 is the case series by Shankland et al.2 The scarcity of literature may be due to the fact that Ernest syndrome is a little-known syndrome that may be underdiagnosed. This would not have to be the case, however, if the syndrome were included in the International Classification of Headache Disorders.15
The stylomandibular ligament is a thickened band of cervical fascia that extends from the styloid process to the posterior border of the ramus of the mandible, medially to the angle of the mandible. The stylomandibular ligament is responsible for limiting the opening and protrusion movements of the jaw. The aetiopathogenesis of Ernest syndrome is not completely clear; it could be related to macrotrauma caused by blows to the jaw, cranial trauma, or whiplash caused by traffic accidents.16,17 All of these processes produce the same clinical symptoms: distension of the ligament connecting the styloid process to the mandibular gonial angle.9,18 Researchers have indicated that when this ligament stretches more than 25 to 30mm, it may cause cervical and pharyngeal pain as well as pain when swallowing, speaking, and opening the mouth, perception of a foreign body in the oropharynx, and pain radiating to the ear.5,19 Some have suggested that prolonged dental procedures may lengthen and strain the stylomandibular ligament, thereby causing painful symptoms.2 This hypothesis is supported by the fact that 4 of our patients experienced pain during the month following lengthy dental procedures.
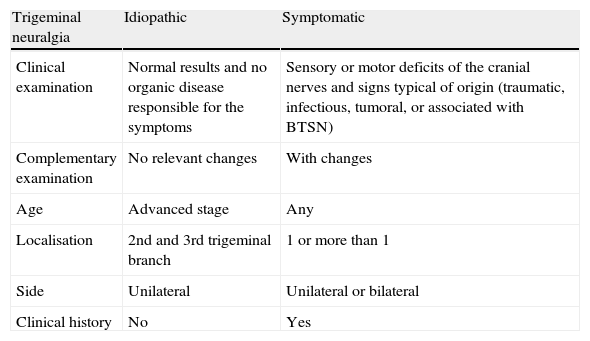
The pain due to Ernest syndrome can be confused with that resulting from masticatory muscle disorders, especially in cases of myofascial pain, and other entities such as Eagle syndrome, neuralgia of the third branch of the trigeminal nerve, glossopharyngeal neuralgia, persistent idiopathic facial pain, temporomandibular joint dysfunction syndrome, pain associated with pericoronitis, parotid pain, and cervical pain. Trigeminal neuralgia is a disorder related to the peripheral or central fibres of the trigeminal nerve. As such, it causes pain limited to one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve. This neuralgia may be idiopathic or present as a result of the syndrome's underlying aetiology (secondary or symptomatic). Table 4 presents the differential diagnosis for idiopathic and symptomatic trigeminal neuralgia.20
Differential diagnosis for idiopathic and symptomatic trigeminal neuralgia.
| Trigeminal neuralgia | Idiopathic | Symptomatic |
| Clinical examination | Normal results and no organic disease responsible for the symptoms | Sensory or motor deficits of the cranial nerves and signs typical of origin (traumatic, infectious, tumoral, or associated with BTSN) |
| Complementary examination | No relevant changes | With changes |
| Age | Advanced stage | Any |
| Localisation | 2nd and 3rd trigeminal branch | 1 or more than 1 |
| Side | Unilateral | Unilateral or bilateral |
| Clinical history | No | Yes |
BTSN: benign trigeminal sensory neuropathy.
The study by Shankland et al.2 described 68 patients with Ernest syndrome; of this number, 77.9% were successfully treated non-surgically with injection of an anaesthetic in the insertion of the ligament, localised corticosteroid injections, and soft diet. Our patients underwent the same treatment.
While the sample size is small, 4 patients recovered completely after treatment. The other 2 patients required an additional injection 15 days after the first treatment due to residual pain. Based on these results, we believe that this treatment, which is easily provided, may alleviate pain and improve quality of life in patients. Here, we analyse the clinical characteristics, treatment, and progression of 6 patients with Ernest syndrome. We believe that the prevalence of this syndrome is higher than the literature may lead us to think, and that Ernest syndrome may be mistaken for other causes of orofacial pain.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Please cite this article as: Peñarrocha-Oltra D, et al. Tratamiento del dolor orofacial en pacientes con síndrome del ligamento estilomandibular (síndrome de Ernest). Neurología. 2013;28:294–8.