The aim is to evaluate tamsulosin efficacy and safety on the expulsion of distal ureteral stones compared to a standard therapy.
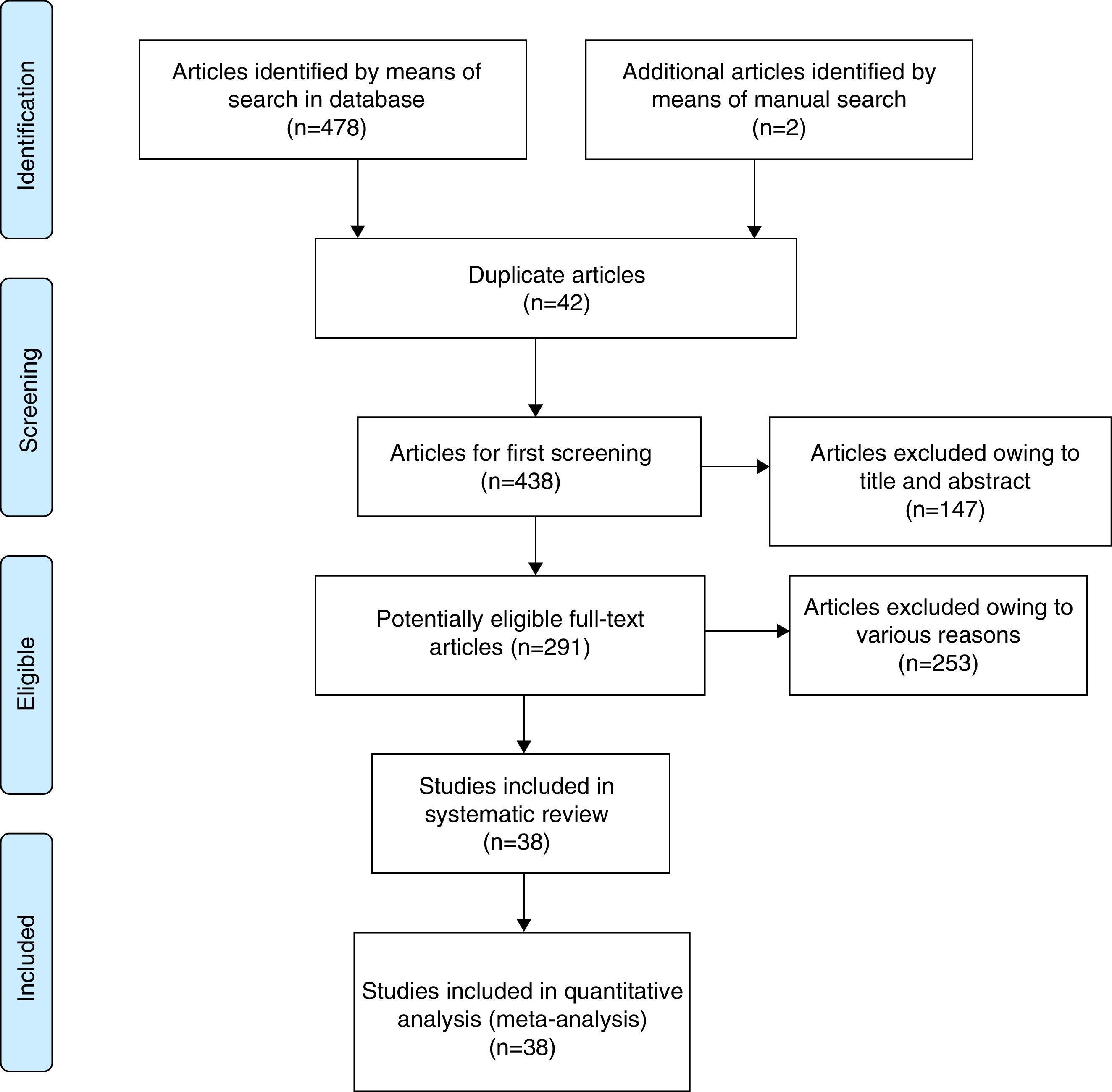
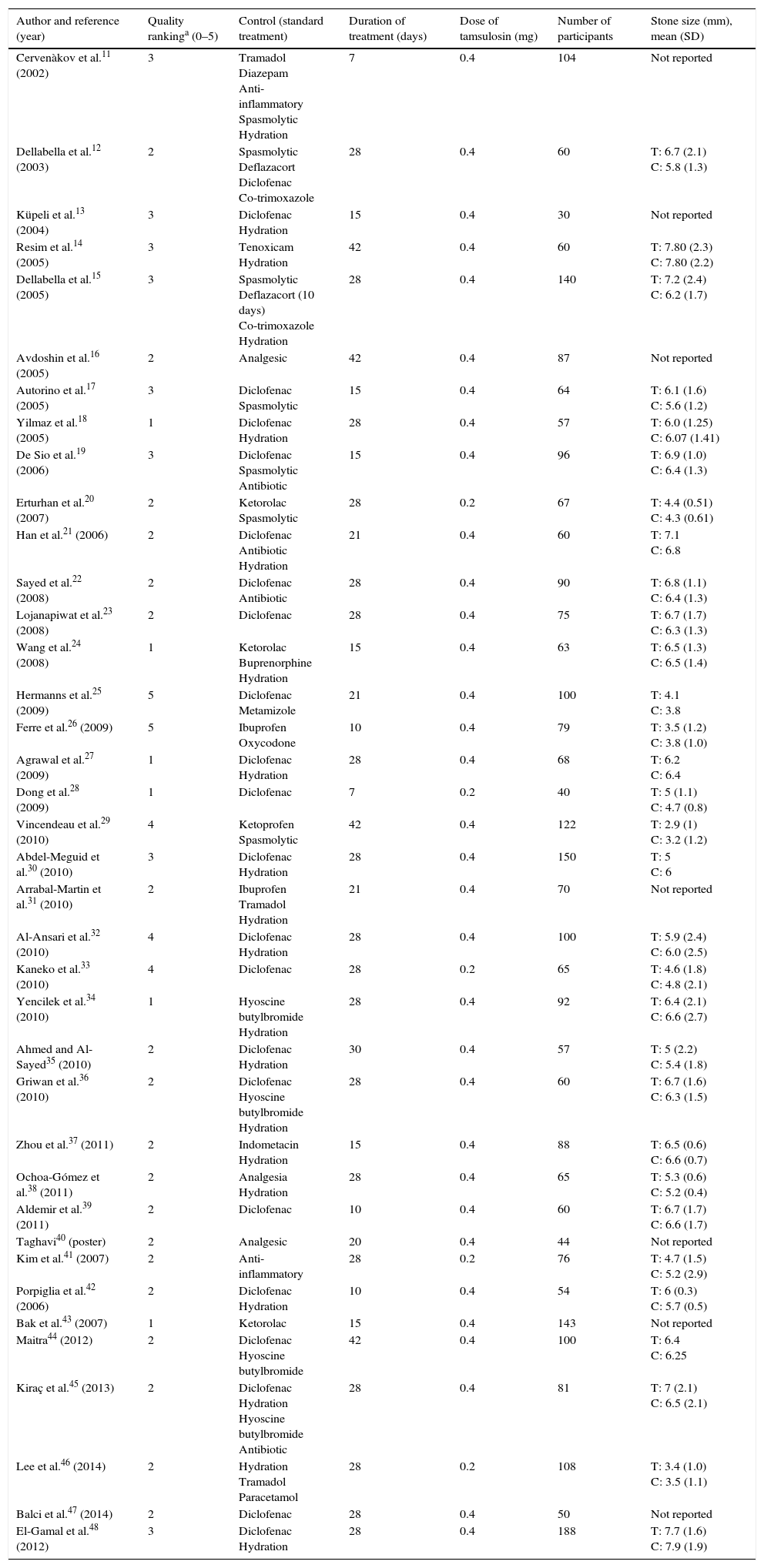
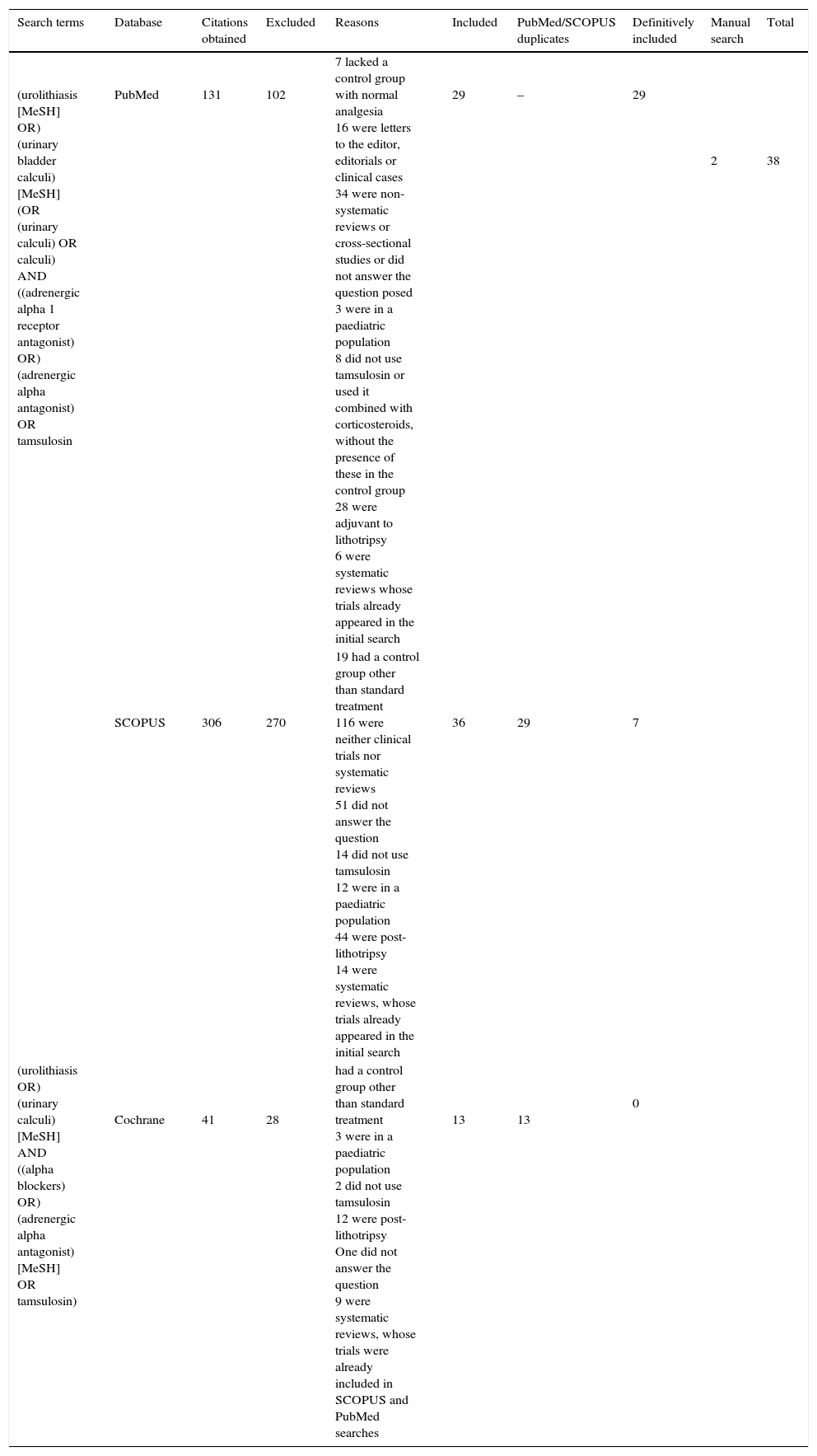
Materials and methodsSystematic searches were conducted on PubMed, SCOPUS and The Cochrane Library so as to identify randomized and controlled clinical trials in patients treated with tamsulosin with ureteral stone expulsion and adverse events published until 2014 December, without language restriction. Treatment effect was calculated along with the 95% confidence interval (95% CI), using the variance inverse method for random effects. Heterogeneity was determined by I2. Publication bias was assessed by Egger test.
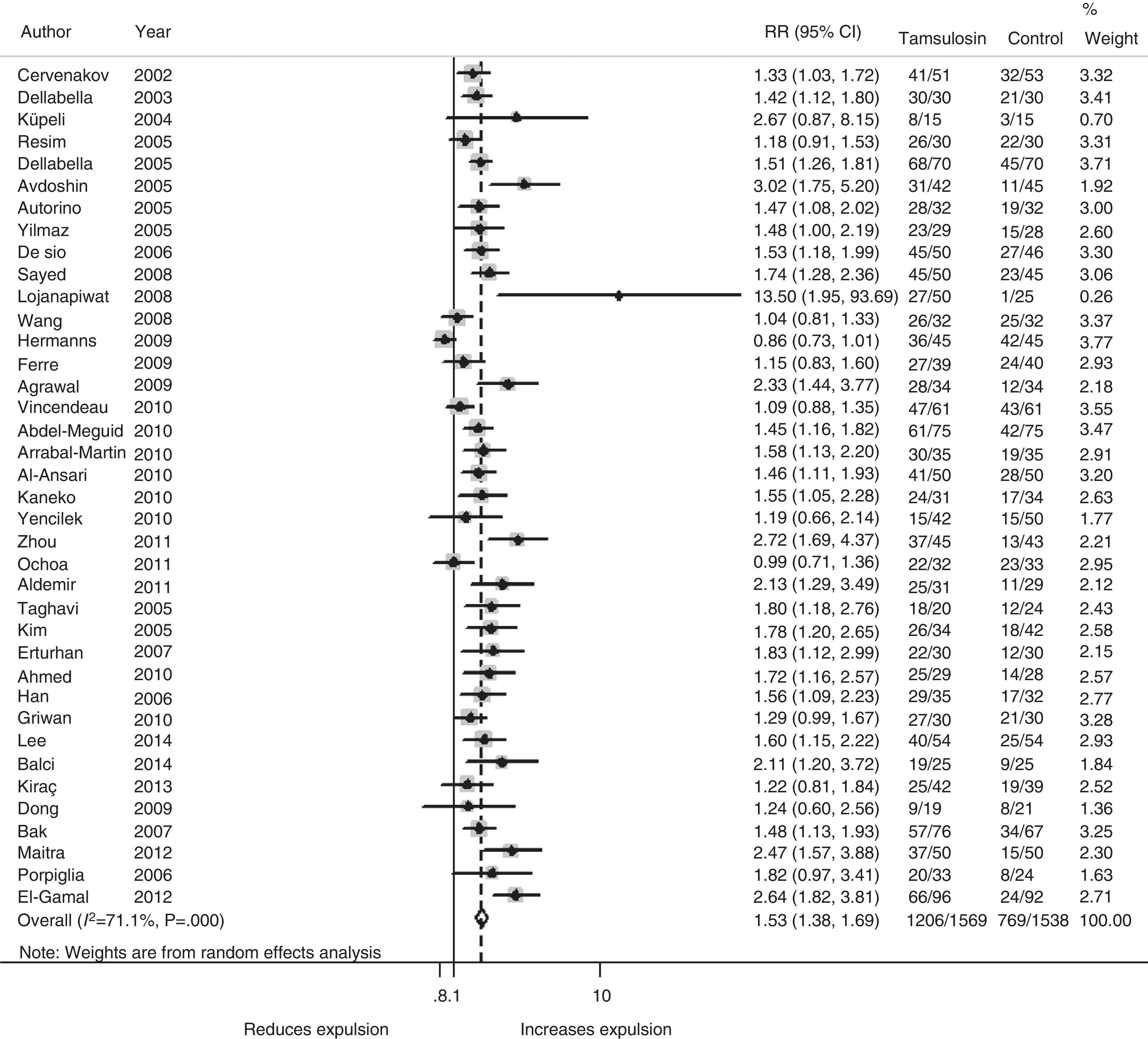
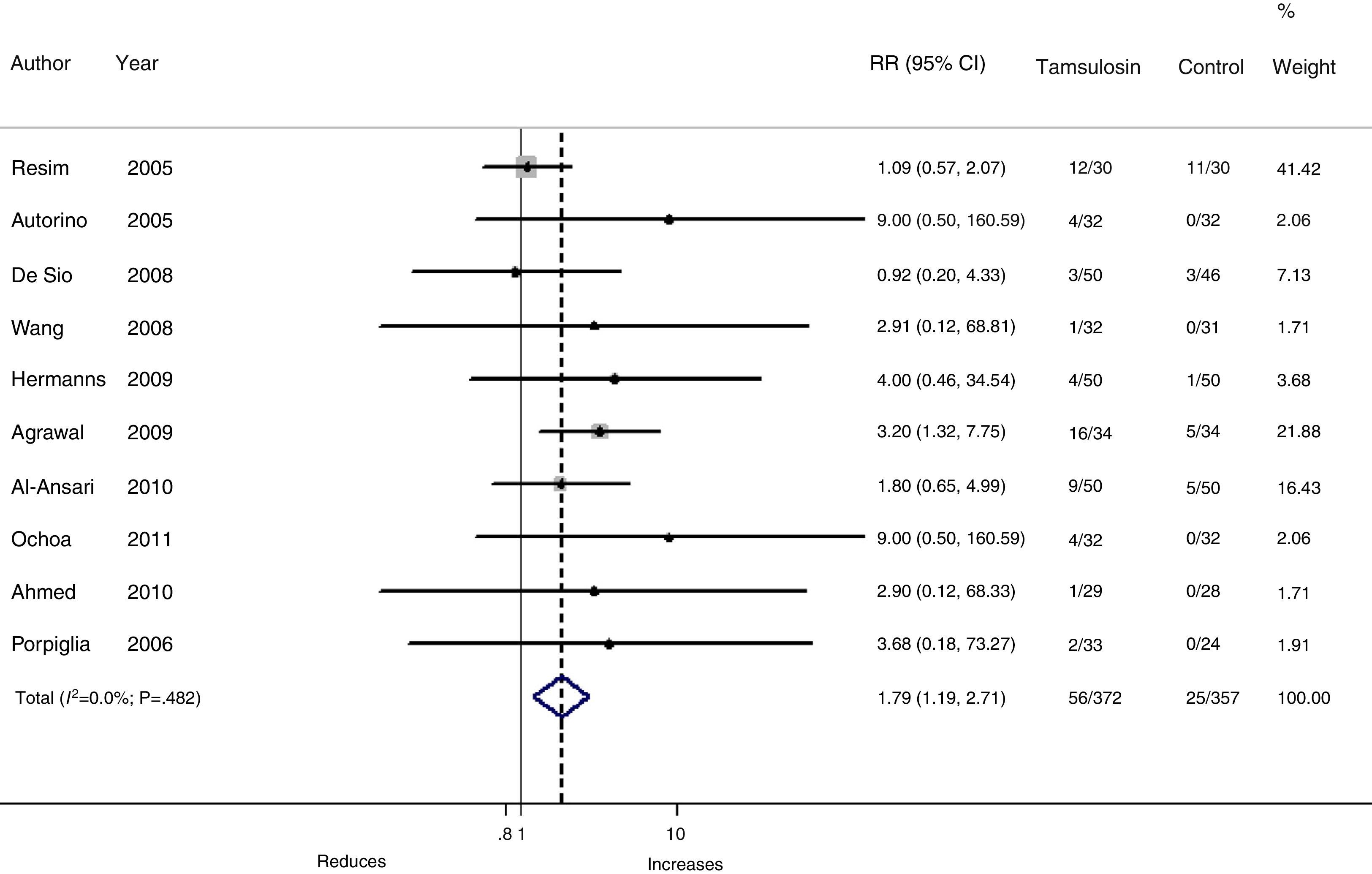
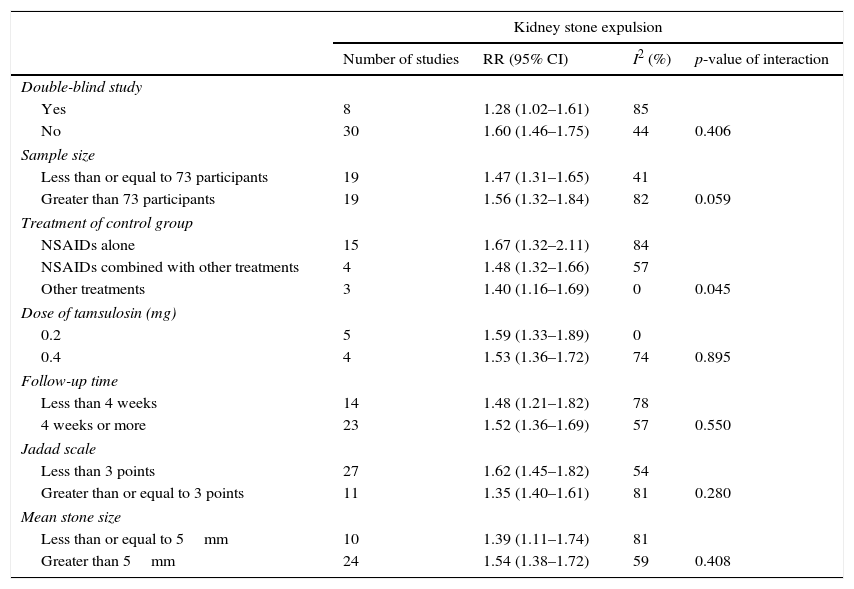
ResultsThe search identified 480 articles. Thirty-eight met the selection criteria, a total of 3107 patients. The relative risk (RR) of expulsion was 1.53 (95% CI 1.38–1.69; I2=71%.), while the RR of adverse effects was 1.79 (95% CI 1.19–2.71; I2=0).
ConclusionsTamsulosin treatment seems to bring on the expulsion of distal ureteral stones, although at the expense of an appreciable risk of side effects.
El objetivo fue evaluar la eficacia y seguridad de tamsulosina, comparada con otro tratamiento estándar o con placebo, en la expulsión de las litiasis ureterales distales.
Material y métodosSe realizaron búsquedas sistemáticas en PubMed, SCOPUS y The Cochrane Library para identificar los ensayos clínicos aleatorizados y controlados en pacientes tratados con tamsulosina con resultados de expulsión de litiasis ureteral y de episodios adversos, publicados hasta diciembre de 2014, sin limitaciones de idioma. Se calculó el efecto de los tratamientos junto con el intervalo de confianza del 95% (IC 95%) utilizando el método de la inversa de la variancia para efectos aleatorios. La heterogeneidad se determinó mediante el estadístico I2. El sesgo de publicación se evaluó mediante la prueba de Egger.
ResultadosLa búsqueda identificó 480 artículos. Treinta y ocho cumplían los criterios de selección, con un total de 3.107 participantes. El riesgo relativo (RR) de expulsión de litiasis de los pacientes tratados con tamsulosina comparado con el tratamiento control fue de 1,53 (IC 95% 1,38-1,69; I2=71%). El RR de cualquier episodio adverso de tamsulosina fue de 1,79 (IC 95% 1,19-2,71; I2=0%).
ConclusionesEl tratamiento con tamsulosina parece favorecer la expulsión de litiasis renales, aunque con un riesgo no desdeñable de efectos secundarios.