A study of the susceptibility to antimicrobials of the extended spectrum beta-lactamase phenotypes (ESBL) in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. was performed to discover the evolution of this type of resistance from urinary tract infections.
Material and methodA retrospective study was carried out between 2012 and 2016. Susceptibility to ciprofloxacin, tobramycin, cefoxitin, fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin, co-trimoxazole, and carbapenems was analysed using MicroScan® system.
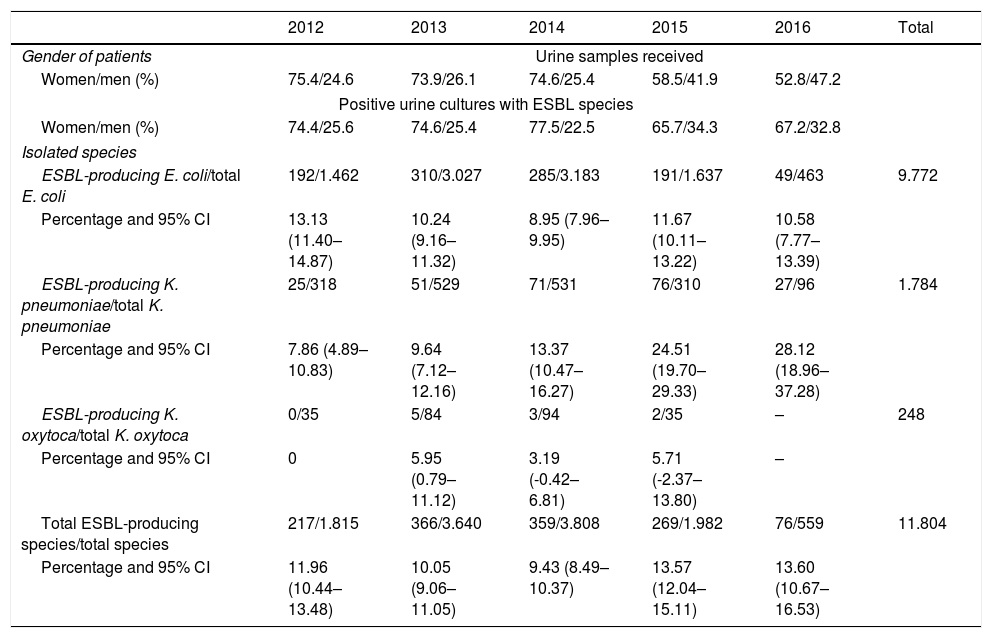
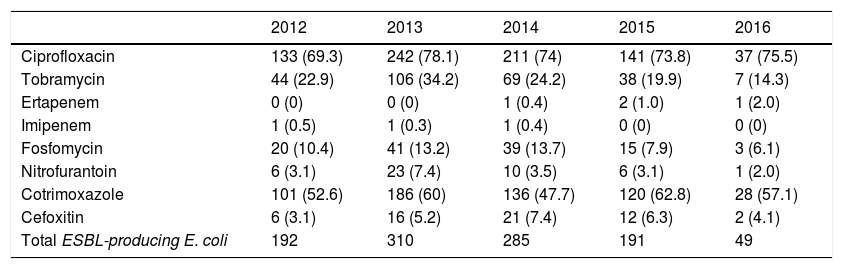
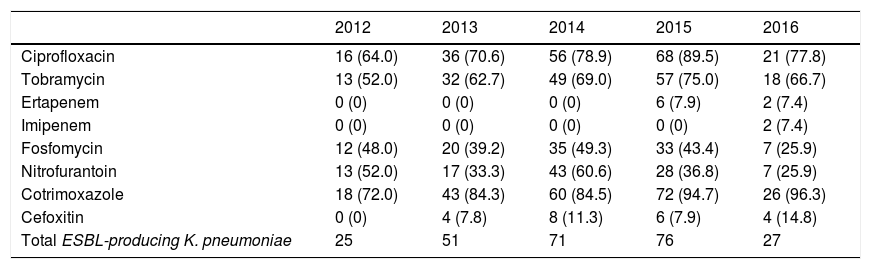
ResultsA total of 95,399 samples were processed and 9772 E. coli, 1784 Klebsiella pneumoniae and 248 Klebsiella oxytoca were isolated. ESBL strains were more frequent in women, although they decreased during 2015 and 2016 (65.7–67.2%). The prevalence of K. pneumoniae ESBL increased annually (28.1% in 2016). The average prevalence of E. coli ESBL was 10.5% with few oscillations. Higher resistance occurred to ciprofloxacin and cotrimoxazole, 89.5 and 94.7% in 2015, respectively, and there was lesser resistance to imipenem. Fosfomycin and nitrofurantoin were very active on E. coli ESBL.
ConclusionsESBL producing E. coli and K. pneumoniae were prevalent, especially the latter, with a significant resistance to ciprofloxacin and cotrimoxazole. Susceptibility to imipenem was high.
Se analiza la presencia, a lo largo de los años en infecciones urinarias, de aislados de Escherichia coli y Klebsiella spp. productores de betalactamasa de espectro extendido (BLEE), y su sensibilidad a antibióticos.
Material y métodoSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo entre 2012 y 2016. La sensibilidad a ciprofloxacino, tobramicina, cefoxitina, fosfomicina, nitrofurantoína, cotrimoxazol y carbapenémicos se analizó mediante el sistema MicroScan®.
ResultadosSe procesaron 95.399 muestras y se aislaron 9.772 E. coli, 1.784 Klebsiella pneumoniae y 248 Klebsiella oxytoca. Las cepas con BLEE fueron más frecuentes en mujeres, aunque disminuyó durante 2015 y 2016 (65,7–67,2%). La prevalencia de K. pneumoniae BLEE aumentó todos los años (28,1% en el 2016). La prevalencia media de E. coli BLEE fue del 10,5%, con escasas oscilaciones. Las mayores resistencias ocurrieron a ciprofloxacino y cotrimoxazol, 89,5 y 94,7% en 2015, respectivamente, y las menores a imipenem. Fosfomicina y nitrofurantoína fueron muy activos sobre E. coli BLEE.
ConclusionesE. coli y K. pneumoniae con BLEE fueron prevalentes y, sobre todo esta última, con una importante resistencia a ciprofloxacino y cotrimoxazol. La sensibilidad a imipenem fue elevada.