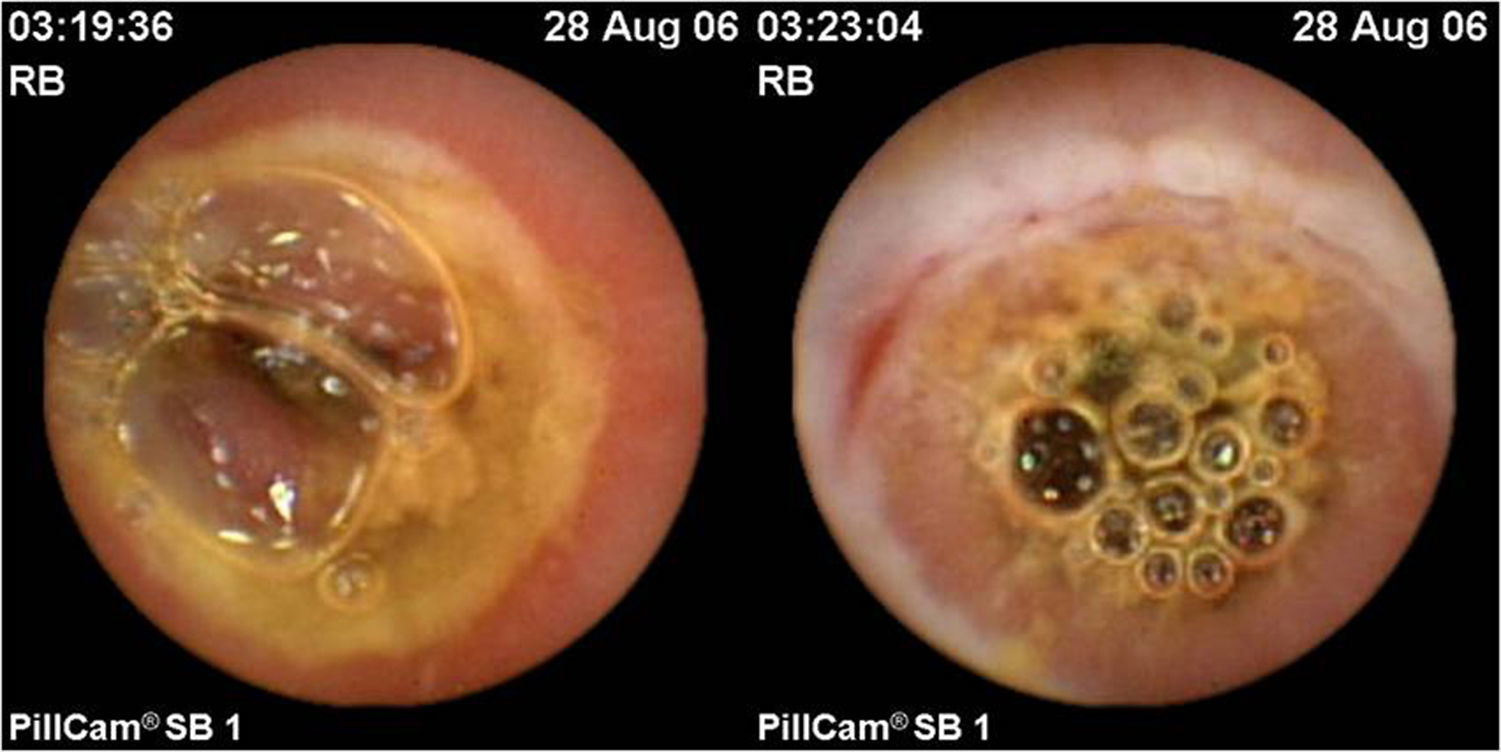
Enteropathy of the small intestine due to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is an increasingly relevant disease that is being diagnosed more and more frequently in patients with obscure gastrointestinal bleeding (OGIB). Endoscopic lesions are common in patients who are chronic consumers of NSAIDs, and can occur in up to 71% of such cases.1 Their course is usually subacute or chronic and are usually occult, presenting in the form of anaemia, which improves once the drug is discontinued. They can be present with non-specific lesions, such as multiple petechiae or denudation, canker sores, erosions or ulcers (often multiple),2 but also with more typical findings such as diaphragm-like rings, and even stenosis3 (Fig. 1). Their distribution could vary depending on the concomitant use of antiplatelet agents4 and, although the small intestine is the most commonly affected area, there may also be lesions in other areas, such as the colon.5 Capsule endoscopy and balloon-assisted enteroscopy play a significant role in the diagnosis and treatment of this disease because they are able to assess the severity and extent of mucosal damage. CT and MRI enterography could also play a diagnostic role in this disease, especially in more severe cases, although the differential diagnosis between Crohn's disease and actinic enteritis may be difficult.6 We present a series of retrospective cases for the purpose of analysing the OGIB risk factors in patients who are chronic consumers of NSAIDs, through a case–control study.
Between 2008 and 2015, 37 patients with NSAID-induced OGIB and enteropathy, detected by capsule endoscopy, were seen at our hospital. These patients presented with arthrosis (n=27; 72.9%), rheumatoid arthritis (n=5; 13.5%) and other conditions (n=5; 13.5%). Two controls were randomly selected per case from among consecutive patients with the same underlying diseases, who were also chronic consumers of NSAIDs and who visited the rheumatology department between January and March 2015. Three controls were excluded due to a history of OGIB. A multivariate analysis was conducted using a binomial logistic regression to establish the factors associated with the risk of bleeding. A total of 108 patients (37 cases with OGIB and 71 controls without OGIB) were included. Both groups were similar in terms of the number of women included (67.6 vs 61.4%; p=0.57) and the consumption of proton-pump inhibitors (71.9 vs 55.5%; p=0.121). In the multivariate analysis, diabetes [OR: 3.25, (95%CI: 1.05–10.08); p=0.041], coronary artery disease [OR: 6.23, (95%CI: 1.46–26.5); p=0.013] and the consumption of aspirin [OR: 17.02, (95%CI: 4.28–67.63); p<0.001] were shown to be independent risk factors for OGIB. Blood pressure (p=0.87), as well as the consumption of clopidogrel (p=0.7), oral anticoagulants (p=0.29) and proton-pump inhibitors (p=0.85) were not linked to a greater risk of bleeding. In a similar study, Cho et al.7 concluded that coronary artery disease and the use of thienopyridine derivatives (clopidogrel) were independent risk factors for OGIB in patients who take NSAIDs. Furthermore, the use of aspirin and proton-pump inhibitors has been described as a risk factor for mucosal lesions in the small intestine.8 In our study, these patients had a greater risk of developing OGIB if they suffered from diabetes or coronary artery disease, or if they consumed acetylsalicylic acid, but not clopidogrel. It should be noted that 71.43% of the diabetic patients had coronary artery disease, which could affect the significance of diabetes as a risk factor. The type of NSAID, particularly those derived from oxicam, has also been reported as a possible risk factor in gastrointestinal bleeding.9 Various pharmacological treatments have been proposed to reduce or cure intestinal mucosal damage caused by NSAIDs, such as irsogladine10 and rebamipide11; however, there is currently no conclusive evidence of their benefit.
Therefore, NSAID-induced enteropathy is an underdiagnosed OGIB aetiology due to its often asymptomatic and benign long-term course.2 This disease should be taken into account and suspected in patients with chronic NSAID consumption. These drugs should be indicated with caution in patients with specific risk factors and comorbidities, especially coronary artery disease, in order to prevent the risk of bleeding.
Please cite this article as: Pérez-Cuadrado-Robles E, Quesada-Vázquez N, Martínez-Andrés B, Sánchez-Melgarejo JF, Rubio-Mateos JM, López-Higueras A, et al. La enteropatía de intestino delgado por antiinflamatorios no esteroideos y la hemorragia digestiva de origen oscuro. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;41:39–40.