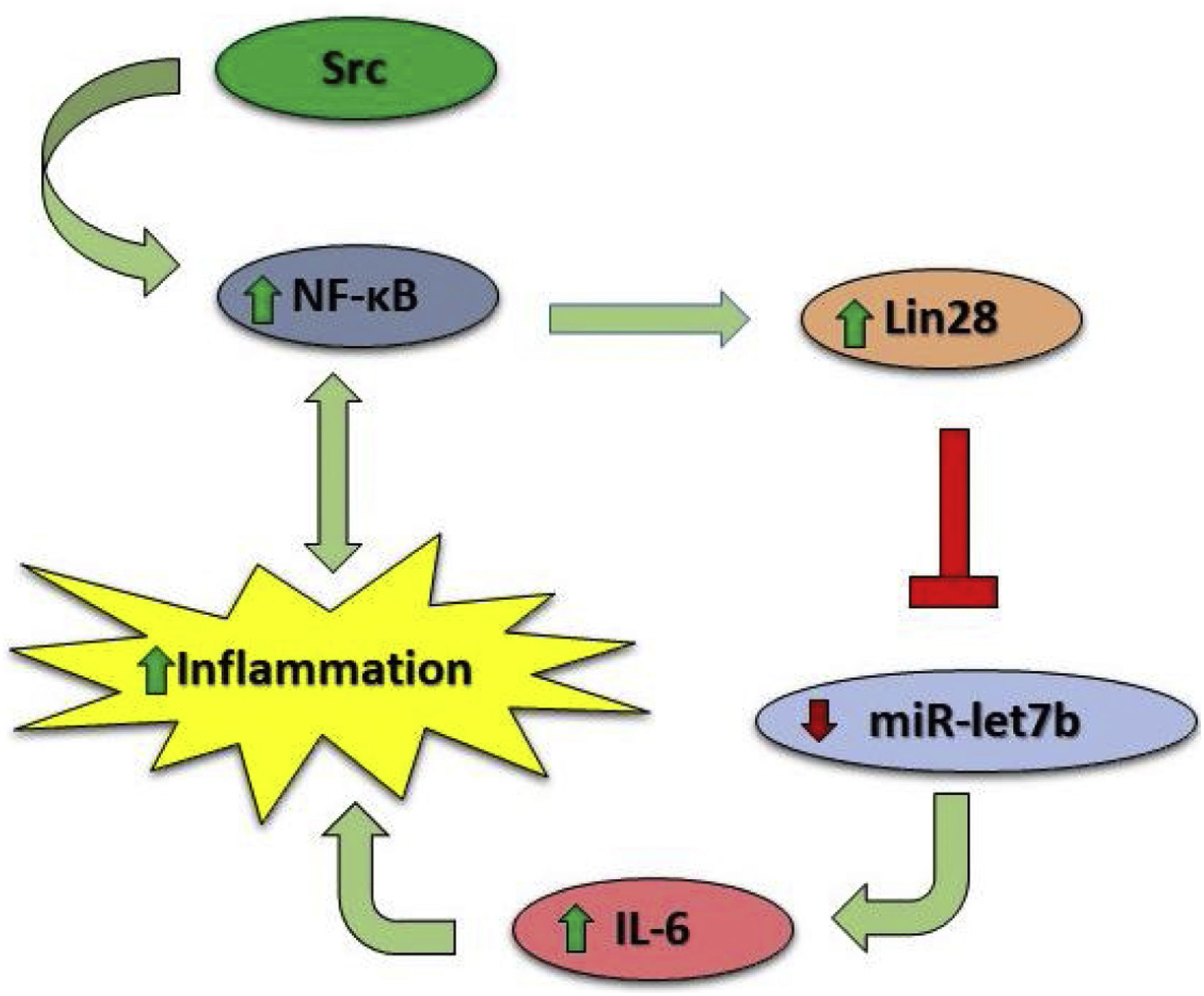
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a group of small non-coding RNAs that bind to the target mRNA and regulate gene expression. Recently circulating microRNAs were investigated as markers of diseases and therapeutic targets. Although various studies analyze the miRNA expression in liver disease, these studies on PFIC are few. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) is a rare liver disease with autosomal recessive inheritance. Most children with PFIC progress to cirrhosis and liver failure and consequently need to have a liver transplant. The aim of this study is the investigation of the miR-19b and miR-let7b expression levels in Iranian PFIC children.
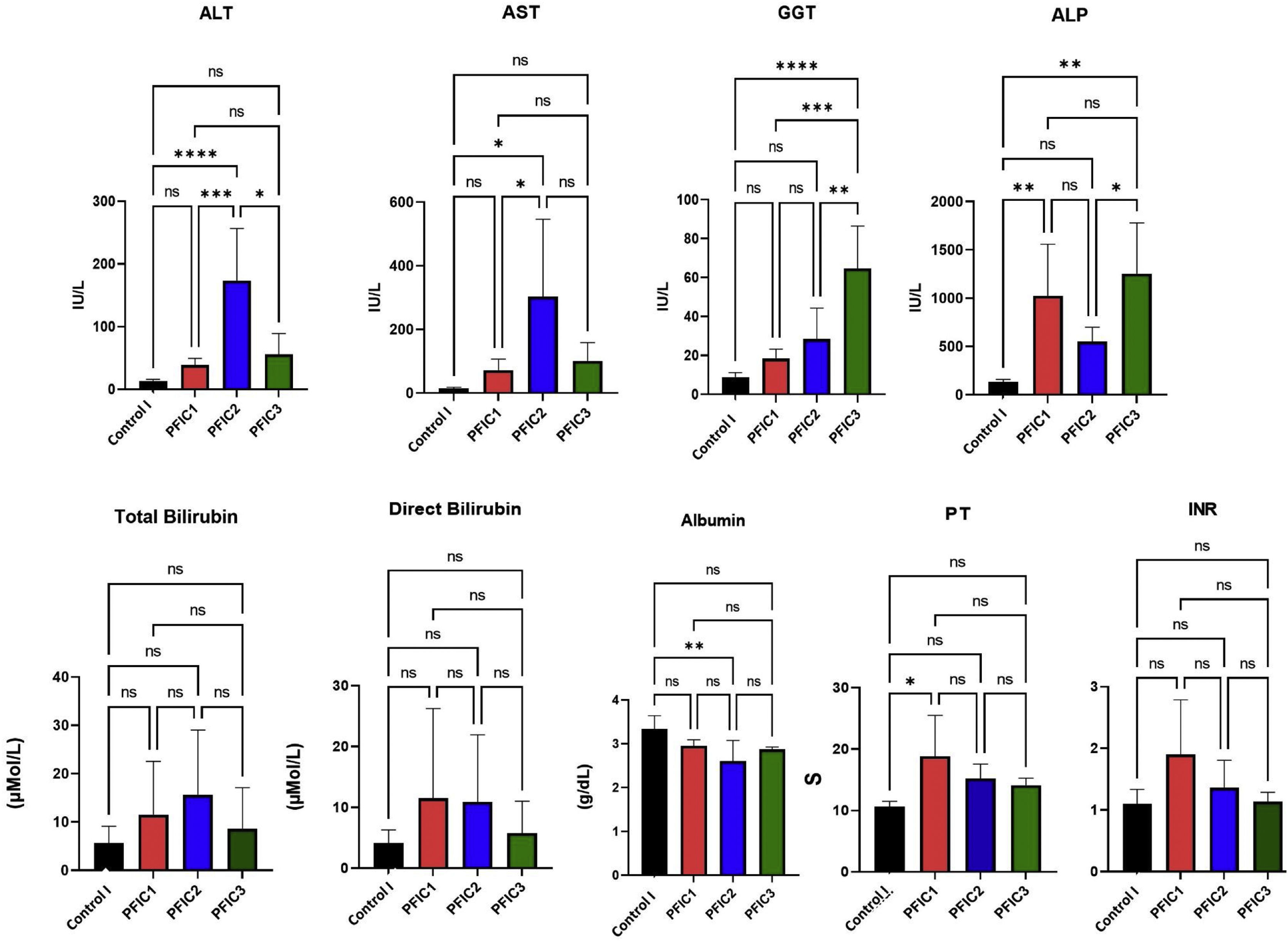
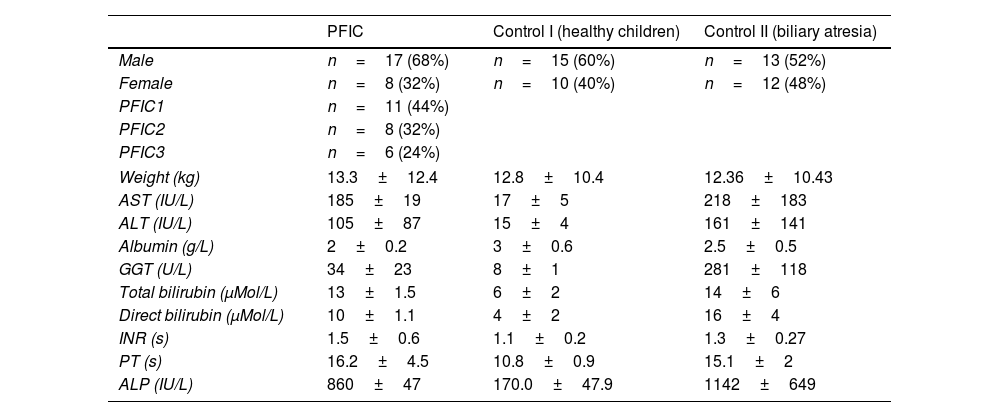
Methods25 PFIC patients, 25 healthy children and 25 Biliary Atresia patients were considered as case and two control groups respectively. Blood samples were obtained and Liver function tests (LFTs) were measured. After RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis, quantitative PCR was performed using specific primers for miR-19b and miR-let7b. The U6 gene is used as an internal control.
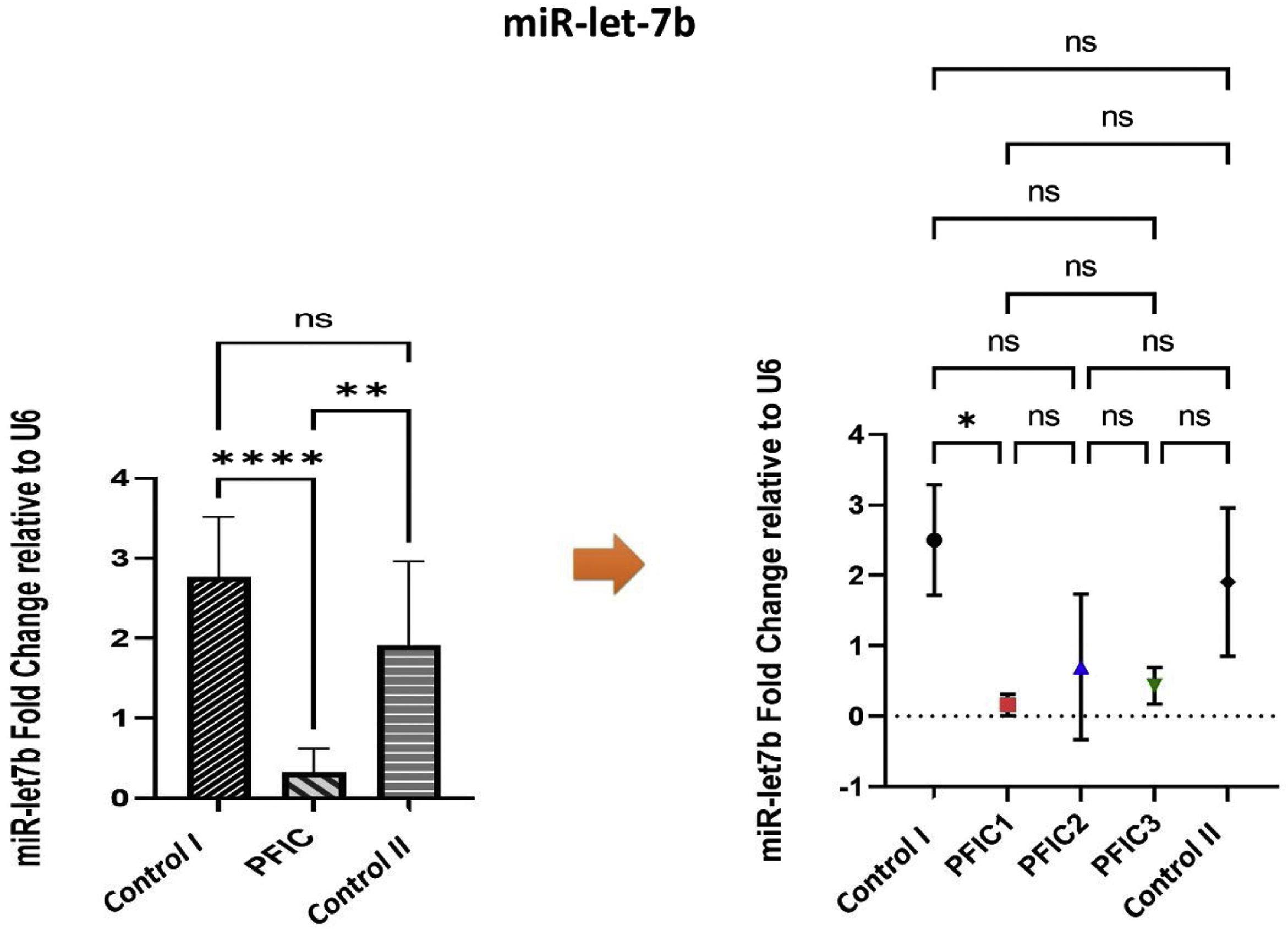
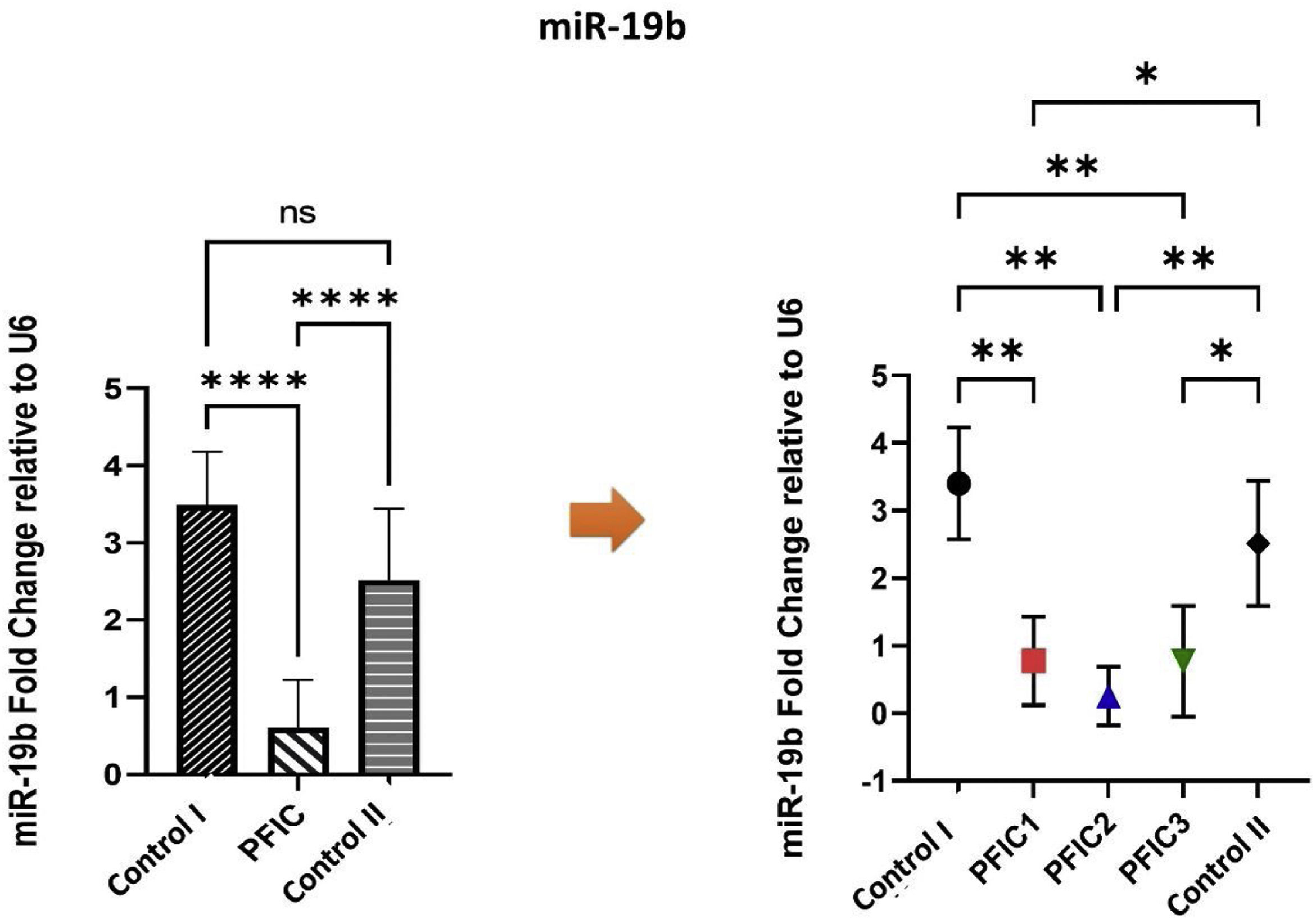
ResultsqPCR on PFIC patients’ samples demonstrated that the miR-19b and the miR-let7b expression were significantly decreased in patients compared to the control groups, with a p-value<0.0001 and p-value=0.0006 receptively.
ConclusionIn conclusion, circulating micro-RNA like miR-19b and miR-let7b have a potential opportunity to be a non-invasive diagnostic marker or therapeutic target for PFIC in the future.
Los microRNA (miRNA) son un grupo de pequeños RNA no codificantes que se unen al ARNm diana y regulan la expresión génica. Recientemente se han investigado los microRNA circulantes como marcadores de enfermedades y dianas terapéuticas. Aunque varios estudios analizan la expresión de miRNA en enfermedades hepáticas, estos estudios sobre PFIC son escasos. La colestasis intrahepática familiar progresiva (PFIC) es una enfermedad hepática rara con herencia autosómica recesiva. La mayoría de los niños con PFIC progresan a cirrosis e insuficiencia hepática y, en consecuencia, requieren de un trasplante de hígado. El objetivo de este trabajo es la investigación de los niveles de expresión de miR-19b y miR-17b en niños iraníes con PFIC.
MétodosSe consideraron 25 pacientes con PFIC, 25 niños sanos y 25 pacientes con atresia biliar como grupos de casos y controles. Se obtuvieron muestras de sangre y se midieron las pruebas de función hepática (LFT). Después de la extracción de RNA y la síntesis de cDNA, se realizó PCR cuantitativa usando cebadores específicos para miR-19b y miR-17b. El gen U6 se utiliza como control interno.
ResultadosLa qPCR en muestras de pacientes con PFIC demostró que la expresión de miR-19b y miR-17b disminuyó significativamente en los pacientes en comparación con dos grupos de control, con un valor de p<0,0001 y un valor de p=0,0006, receptivamente.
ConclusiónEn conclusión, los micro-RNA circulantes, como miR-19b y miR-let7b, tienen una oportunidad potencial de ser un marcador de diagnóstico no invasivo o un objetivo terapéutico para PFIC en el futuro.